Blog
Top Stories
Customs duty waiver on raw cotton offers relief to textile sector

Mumbai: India’s textile industry is set to benefit from a temporary exemption of customs duties on raw cotton imports, effective from 19 August to 30 September 2025. The move, announced by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs, removes the 5% Basic Customs Duty, the 5% Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess, and the 10% Social Welfare Surcharge previously levied on cotton imports. In total, the waiver eliminates an 11% import duty, offering immediate cost relief to manufacturers across the textile value chain.
The exemption is expected to ease pressure on domestic cotton prices, which have remained elevated due to supply constraints and seasonal volatility. By allowing duty-free imports, the government aims to improve raw cotton availability, reduce input costs, and stabilise prices for downstream products such as yarn, fabric, garments, and made-ups. This is particularly significant for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), which form the backbone of India’s textile ecosystem and are more exposed to fluctuations in raw material costs.
The timing of the waiver is critical. With export competitiveness under strain and inflationary pressures affecting consumer demand, the cost reduction could help manufacturers maintain margins and pricing stability. Lower input costs may also support India’s textile exports, which face stiff competition from countries with more favourable sourcing and duty regimes.
Industry associations have long called for the removal of import duties on cotton, citing the need to align domestic policy with global trade realities. The current exemption responds directly to these concerns, albeit for a limited duration. While the measure is temporary, it signals a willingness to intervene in support of a sector that contributes significantly to employment and foreign exchange earnings. Beneficiaries of the move include spinning mills, fabric producers, garment exporters, and ancillary units that rely on cotton as a primary input. The relief is expected to be most pronounced for SMEs operating in high-volume, low-margin segments, where even modest cost reductions can have a meaningful impact on viability.
The exemption also has implications for price transmission across the supply chain. If cotton prices soften as expected, consumers may see more stable prices for finished textile products, particularly in the domestic market. However, the short duration of the waiver means that its long-term impact will depend on subsequent policy decisions and market responses. The government’s decision reflects a balancing act between protecting domestic producers and ensuring affordability and competitiveness. While cotton farmers may be concerned about the potential impact on domestic prices, the exemption is framed as a short-term measure to address immediate supply and cost challenges.
As the textile sector navigates global headwinds and domestic constraints, the customs duty waiver offers a window of relief. Whether it translates into sustained gains will depend on how quickly manufacturers can leverage the cost advantage and whether the government considers extending or institutionalising similar measures in future.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
PLI schemes and trade hubs reshape India’s export landscape
PLI schemes and trade hubs reshape India’s export landscape

Mumbai: India has rolled out a series of targeted measures to boost exports and reinforce domestic manufacturing, with a clear focus on MSME participation and sectoral competitiveness. The initiatives span production-linked incentives, logistics reforms, trade agreements and grassroots export hubs — forming a multi-pronged strategy to position India as a global supply chain player.
A key highlight is the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, now extended across 14 sectors including electronics, pharmaceuticals, auto components and solar modules. These incentives have led to increased output, job creation and a marked rise in exports. In the medical devices segment alone, 21 projects have begun manufacturing 54 high-end products such as MRI machines, heart valves and CT scanners. In electronics, India has transitioned from being a net importer to a net exporter of mobile phones, with exports rising from ₹1,500 crore in 2014–15 to over ₹2 lakh crore in 2024–25. The country is now the world’s second-largest mobile phone manufacturer.
The pharmaceutical sector has also seen strong gains. Under the PLI scheme, cumulative sales have reached ₹2.66 lakh crore, including ₹1.70 lakh crore in exports over three years. India has reversed its trade position in bulk drugs, moving from a net importer status in FY 2021–22 to a net exporter, with a swing of over ₹4,000 crore.
To support these manufacturing gains, the government has launched the National Logistics Policy and PM Gati Shakti initiative. These aim to streamline the movement of goods, reduce costs and improve coordination across transport networks. The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan is central to developing multimodal infrastructure, ensuring faster transit and better resource utilisation. Complementing this is the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme, which seeks to build globally competitive manufacturing hubs with strong connectivity to domestic and international markets.
Grassroots initiatives are also being scaled up. The Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) programme has identified export-ready products and services across 590 districts, with action plans addressing supply chain bottlenecks and proposing targeted interventions. Institutional mechanisms such as State Export Promotion Committees and District Export Promotion Committees have been set up to drive implementation.
In parallel, the E-Commerce Export Hubs (ECEH) initiative is being piloted to support SMEs and artisans in cross-border trade. These hubs will offer integrated services including customs clearance, packaging, quality certification and warehousing — all at a single location. Five pilot projects have been proposed, with the Directorate General of Foreign Trade inviting detailed submissions.
On the trade diplomacy front, India signed the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the United Kingdom on 24 July 2025, marking a significant step in expanding market access. Talks with the European Union are ongoing, with a deal expected by year-end. These agreements are expected to open new avenues for Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs, in sectors such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Together, these measures reflect a strategic shift in India’s trade and industrial policy — one that blends top-down infrastructure planning with bottom-up export enablement. The emphasis on manufacturing depth, logistics efficiency and market diversification is designed to reduce import dependency and build long-term resilience in India’s export ecosystem.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
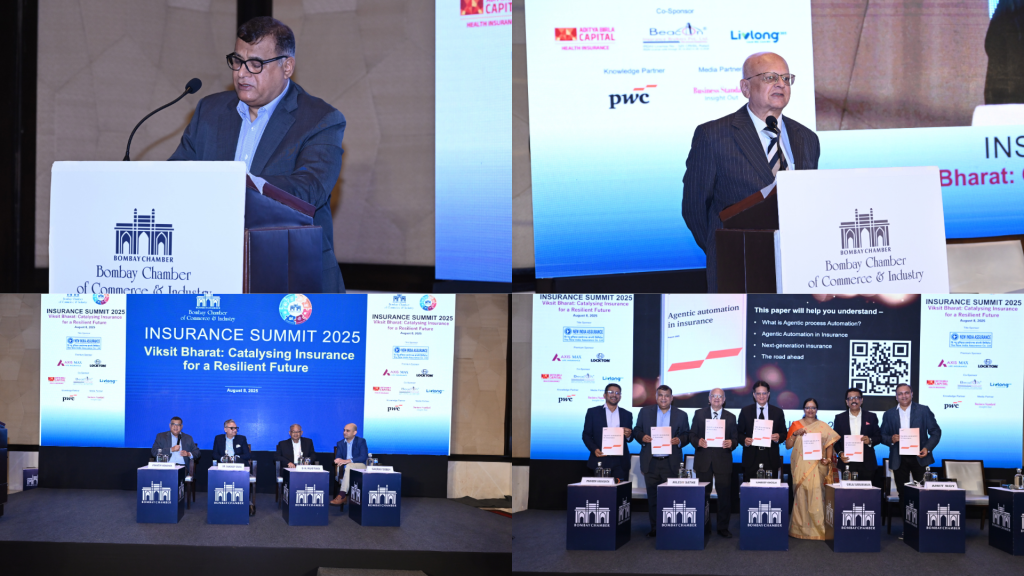
Bombay Chamber Hosts Insurance Summit 2025: Catalysing Insurance for a Resilient Future
Bombay Chamber Hosts Insurance Summit 2025: Catalysing Insurance for a Resilient Future
Mumbai, 8 August 2025 – The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry hosted the Insurance Summit 2025 at the Taj Santacruz, Mumbai, under the theme “Viksit Bharat – Catalysing Insurance for a Resilient Future”. The summit brought together prominent figures from the insurance and reinsurance sectors, policymakers, technology leaders, and financial services experts to explore how insurance can drive inclusive growth and contribute to national development.
Delivering the welcome address, Sandeep Khosla, Director General of the Bombay Chamber, reflected on the Chamber’s 189-year legacy as one of India’s oldest industry bodies. He spoke about its role as a trusted bridge between industry and the government, facilitating dialogue, influencing policy, and supporting sectors in navigating emerging opportunities and challenges.
Setting the context, Praveen Vashishta, Member of the BFSI Committee, Bombay Chamber, Former Co-founder of Howden Insurance Brokers India, and Chairman of Howden Asia, set the tone with a Theme Setting Address that examined the evolving dynamics of the sector and the opportunities on the horizon. His remarks provided a compelling context for the discussions that would follow. He emphasised that achieving Viksit Bharat requires insurance penetration to grow at a pace matching the country’s economic ambitions, highlighting the urgency of closing the protection gap across health, agriculture, climate risk, and infrastructure. He spoke about the twin challenge of under-insurance and low awareness, urging a shift from product-centric to customer-centric models, supported by technology and data-led innovation. Stressing that resilience must be built into the very fabric of India’s development, he called for collaborative action among insurers, regulators, technology providers, and government to create scalable, inclusive, and affordable insurance solutions that reach every citizen.
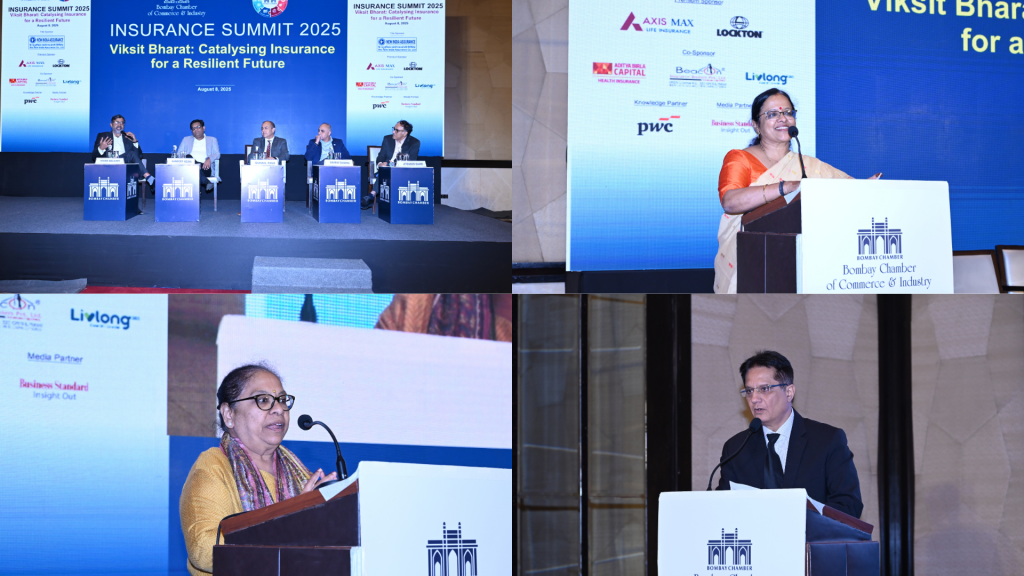
In his Keynote Address, Nilesh Sathe, Former Whole-time Member of IRDAI, reflected on the transformative potential of technology, artificial intelligence, and micro-insurance, and urged the sector to strengthen public-private partnerships in flagship schemes such as PM Jan Arogya Yojana and PM Fasal Bima Yojana. He underscored the need to embrace insurance as a national mission on the path to Viksit Bharat, stressing that climate risk is also a financial risk.
Girija Subramanian, CMD of New India Assurance, shared her vision in a Special Guest Address on Bridging the Protection Gap: Pathways to Inclusion. She emphasised the pressing need to widen access to insurance, noting that nearly half the vehicles on Indian roads remain uninsured, and called for innovative approaches to expand coverage and strengthen resilience.
Gayathri Parthasarathy, India Financial Services Sector Leader and Global Financial Services Technology Leader, PwC India, spoke about the ongoing digital transformation in financial services, highlighting its critical role in building resilience and driving growth.
The event also featured the launch of the PwC Position Paper on Agentic Automation in Insurance, presented by Amit Roy, Partner and Leader – Insurance & Allied Businesses, PwC India, and Mahesh Parab, Partner – Agentic Automation, PwC India. They outlined how autonomous AI agents are transforming operational efficiency, customer engagement, and risk management.
The day progressed with three engaging panel discussions. The first, moderated by Amit Roy, explored the opportunities and implications of the proposed amendments to the Insurance Bill 2025, with contributions from Girija Subramanian, Alok Rungta, MD & CEO of Generali Central Life Insurance and Shanai Ghosh, MD & CEO of Zuno General Insurance. The second panel, led by Praveen Vashishta, examined how the industry can become more customer-centric, featuring insights from Dr. Sandeep Dadia, CEO & Country Head, Asia Board Member, Lockton, India; S. K. Rustagi, CEO of Beacon Insurance Brokers Pvt. Ltd.; and Gaurav Dubey, Founder & CEO of Livlong 365. The third discussion, chaired by Vivek Belgavi, Partner – Financial Services Advisory Leader, PwC India, focused on tech-driven innovation, inclusion, and trust, with perspectives from Sandeep Kedia, CFO of Aditya Birla Health Insurance; Suhail Ghai, Chief Digital Officer & Head of Customer Operations, Axis Max Life; Gaurav Sharma, Deputy General Manager at New India Assurance; and Jitender Bahri, Head of P&C Solutions Operations at Swiss Re.
The summit was supported by Knowledge Partner PwC, Media Partner Business Standard, and sponsors including New India Assurance as Title Sponsor, Premium Sponsors Lockton and Axis Max Life Insurance, and Co-Sponsors Livlong 365, Beacon Insurance Brokers, and Aditya Birla Health Insurance.
The event concluded with a Vote of Thanks by Sandeep Khosla.
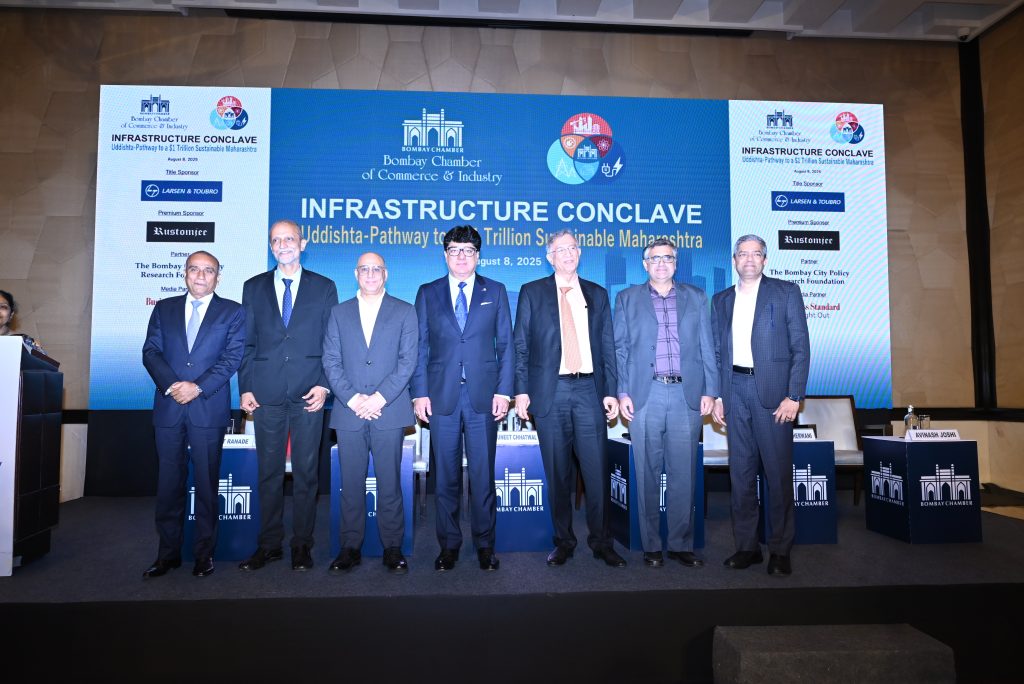
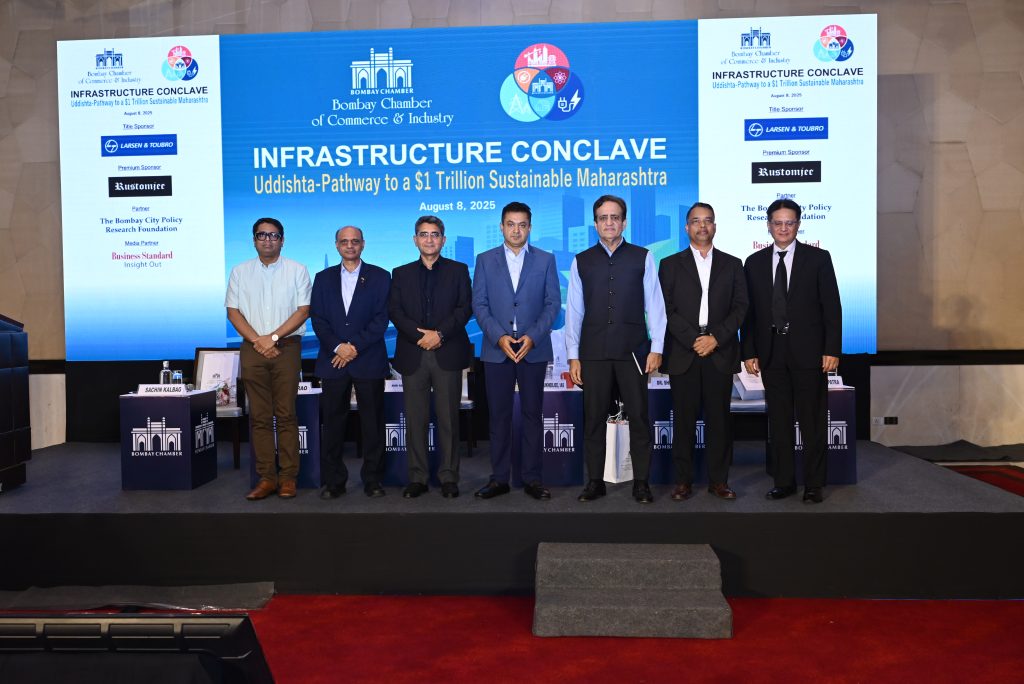
Bombay Chamber Hosts Infrastructure Conclave 2025: ‘Uddishta – Pathway to a $1 Trillion Sustainable Maharashtra’
Bombay Chamber Hosts Infrastructure Conclave 2025: ‘Uddishta – Pathway to a $1 Trillion Sustainable Maharashtra’
Industry leaders and policymakers outline strategies for sustainable, inclusive growth
Mumbai, August 8, 2025: The Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry hosted its flagship Infrastructure Conclave, “Uddishta Pathway to a $1 Trillion Sustainable Maharashtra”, convening a distinguished line-up of leaders from business, policy, and academia to discuss the state’s roadmap to a $1 trillion economy.
Delivering the welcome address, Sudhanshu Vats, Sr. Vice President, Bombay Chamber, set the tone by underlining the Chamber’s commitment to fostering dialogue between industry leaders, policymakers, and stakeholders. “Maharashtra has always been a frontrunner in India’s growth story,” he remarked, “and it is through platforms like this that we can align visions and actions for sustained progress.”
The opening session, “Powerhouses Behind Maharashtra’s Growth”, was moderated by Dr. Ajit Ranade, Senior Fellow at the Pune International Centre, Economist, and member of the Maharashtra Economic Advisory Council. Dr. Ranade stressed that “Mumbai carries the economic burden of the entire state, and skilling and education will be key to inclusive, sustainable and fast economic growth.”
Dhiraj Relli, Managing Director & Chief Executive Officer, HDFC Securities Ltd., observed that “part ownership is now viable, and alternative asset classes are becoming increasingly attractive for investors with instincts for capital appreciation and safety.” He underscored that the $1 trillion target is not a question of if but when, adding, “Implementation is key—we need to unleash the animal spirit through innovation across all sectors.”
From the tourism and hospitality perspective, Puneet Chhatwal, Managing Director & Chief Executive Officer, The Indian Hotels Company Limited, called tourism “one of the brightest opportunities India has been sitting on for a very long time.” He advocated for mission-mode development of destinations such as Sindhudurg as an alternative to Goa and stressed the need to target both business and leisure travellers. “International tourists are as important as domestic,” he said.
Real estate veteran Dr. Niranjan Hiranandani, Managing Director, Hiranandani Group, said that the One trillion goal will happen, while highlighting the need to redevelop all of Mumbai’s slums into affordable housing, address a shortage of two million skilled workers in the sector, and grant infrastructure status to real estate. “We must address small problems like last-mile connectivity when we talk about the big picture,” he added.
Ashish Pherwani, Partner – Media & Entertainment, EY India, pointed out that “India hosts just 1,000 events a year, but we should be doing 1,000 a month,” emphasising the growth potential of the events and entertainment ecosystem.
Avinash Joshi, Chief Executive Officer – India, NTT DATA, called for a shift in perspective, stating, “IT must lead business, not just enable it.”
The second session, “Driving MMR’s Growth Through Strategic Infrastructure Development”, was moderated by Sachin Kalbag, Editor-in-Chief, Mid-Day. Dr. Sanjay Mukherjee, IAS, Metropolitan Commissioner, Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA), outlined MMRDA’s partnership with NITI Aayog, identifying eight policy shifts and seven growth drivers, and securing $40 billion in FDI commitments at Davos. “The key to success is making it simple—breaking down big plans into small, actionable steps. The path towards the trillion-dollar economy has already begun,” he said.
Shri. Rajiv Jalota, Retd. IAS, Former Chairperson, Mumbai Port Authority (MbPA), urged rapid utilisation of Maharashtra’s 300 km coastline and busy inland waterways. He proposed the development of multiple coastal hubs for tourism, logistics, and sector-specific industries such as textiles and automobiles, along with a dedicated state cell for cruise tourism.
Dr. Shirish Sankhe, Director and Founding Partner, ISEG Foundation, stressed that for India to get into the growth trajectory, the GDP growth will have to be raised from 6% to 9–10%, would require “doing things differently.” He also advocated for circular economy models, a climate action plan, and increasing green cover.
Shrinath Rao, Co-Chairman, Power and Infrastructure Committee, Bombay Chamber; Senior Vice President and Head – Special Assignments, L&T Transportation Infrastructure Business, Larsen & Toubro Limited, identified challenges such as lengthy approvals, land acquisition, and utility relocation. He recommended “a single-window clearance system and all due clearances before launch,” along with strong accountability and timely financing to ensure quality, sustainable project delivery.
Prabhat Mahapatra, Chief Operating Officer, Navi Mumbai International Airport, said the new facility would become “the region’s growth engine,” with a projected capacity of 90 million passengers—up from the original plan for 60 million. “Earlier, Mumbai’s limited capacity cost us the No. 1 spot to Delhi. Navi Mumbai will help us reclaim it,” he said.
Amit Kekare, Chairman of the Power and Infrastructure Committee at the Bombay Chamber and Vice President – Head of eMobility at Siemens, concluded the session by highlighting how Maharashtra’s key growth drivers contribute to this milestone, with particular emphasis on strategic infrastructure development, robust financial regulation, and the effective implementation of government initiatives.
India pushes for trade agreements that are MSME-friendly
Centre’s new initiative to connect MSMEs with global market

Mumbai: India is looking to replicate the pro-MSME provisions seen in its recent trade agreement with the United Kingdom across upcoming deals with countries including the United States and the European Union. The aim is to create more favourable terms for Indian micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and ensure these businesses are better positioned to compete globally.
The recent India-UK Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement marked a significant milestone with its dedicated chapter for MSMEs, featuring several support mechanisms. Among these are mutual contact points for MSME-related queries, simplified sharing of regulatory and certification information, and coordinated efforts to promote trade activities such as exhibitions and business networking events.
Under public procurement terms, UK suppliers bidding for Indian contracts will be classified as ‘Class-II local suppliers’ above set thresholds, whereas Indian firms, including MSMEs, retain ‘Class-I’ status, preserving their competitive edge in domestic tenders. Additionally, a technical framework has been established to help MSMEs overcome non-tariff barriers that often hinder access to international markets.
This structured support is viewed as critical for labour-intensive sectors such as textiles, footwear, leather, marine products, toys, sports goods, and jewellery – all of which depend heavily on MSME contribution. These industries have experienced a decline in export share in recent years, reinforcing the need for enhanced access to global markets. Efforts to boost these sectors are also expected to generate positive spillover effects in terms of employment and rural development.
Looking ahead, India is actively trying to incorporate similar MSME carve-outs in ongoing trade negotiations. This approach reflects a broader policy goal of ensuring trade agreements do not disproportionately benefit large firms at the expense of smaller businesses. With talks underway with key partners, there is a concerted push to include practical tools such as training modules, export readiness workshops, and joint promotion of women-led and rural MSMEs.
The Indian government is also pursuing greater collaboration in areas such as sustainability standards and technical skills development, hoping to improve the international competitiveness of domestic MSMEs. By standardising such provisions across multiple trade deals, India is attempting to build a consistent and supportive global framework for its small business sector.
As global trade dynamics evolve, India’s strategic emphasis on MSMEs signals an intent to shape agreements that not only expand market access but also strengthen the foundations of its manufacturing and export ecosystems. While challenges remain, especially with ongoing negotiations, the recent UK agreement is seen as a blueprint for future deals.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
Agriculture & Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) refutes unfounded allegations in Organic Cotton Certification
Agriculture & Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) refutes unfounded allegations in Organic Cotton Certification
Organic Certification under National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) involves a third-party certification, is recognized by European Commission and Switzerland at crop level: APEDA
The National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) was launched in 2001 by the Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt of India for exports of Organic products and APEDA acts as the Secretariat for the implementation of the NPOP. The system of grower group certification was launched in 2005, as it was felt necessary to cater to small and marginal farmers.
Third party certification is a mandatory requirement for export of organic products. The NPOP standards for crop production have been recognized by the European Commission and Switzerland as equivalent to their country’s standards and are also accepted by Great Britain. There is an MRA for organic products with Taiwan.
The system for Organic Certification under NPOP involves a third-party certification system of organic processes and organic produce, which is certified across the supply chain by a certification body (Govt. or private). The accredited Certification Bodies certify organic operators as per their scope of accreditation. At present, there are 37 active Certification Bodies operating in India, which include 14 State Certification Bodies.
Herein, it is clarified that APEDA or the Department of Commerce does not extend any subsidy to farmers taking up Organic cultivation under the NPOP. The figure of Rs. 50,000 per hectare and the further wrongly imputed calculations have no basis.
Organic certification under NPOP is not limited only to Madhya Pradesh but is spread across 31 States/UTs. As per latest records (as on 19.07.2025), there are 4712 active Organic grower groups covering around 19,29,243 farmers certified by the accredited certification bodies under NPOP. These grower groups are involved in production of a wide range of crops including cereals, pulses, oilseeds, tea, coffee, spices and not only cotton.
Thus, the number of Organic grower groups as mentioned in the briefing is incorrect along with the number of farmers, it is also misleading to infer that all the Organic grower groups of India are based in Madhya Pradesh and are producing only Cotton.
It is pertinent to mention that cotton is covered under NPOP only till production level. Thereafter, the post production including ginning, processing etc is done under private certification.
Under NPOP, ICS can be self-managed or managed through a service provider/mandator. As per the NPOP standards, it is mandatory for ICS to carry out internal inspections of all farmers twice annually. Apart from that, the Certification Body (CB) conducts annual audit of each ICS which includes Office audit and farm audits based on a sampling plan. The sampling plan is primarily based on the size of the holdings, number of farmers in the ICS and risk assessment. Certification bodies can carry additional inspections wherever deemed necessary.
In addition to the above, there is a third level of check on the CB by the NAB through APEDA, by undertaking unannounced audits of operators including grower groups (ICS) based on risk assessment/ complaints received, which is conducted by an evaluation committee constituted by the NAB and coordinated by APEDA.
Despite the above stated checks and balances established in the system, there have been reported incidences of malpractices and misuse of Grower Group Certification. These kinds of non-compliances are not unique to India or NPOP but apply to any regulatory system. In this regard the following actions have been taken by the authorities:
- Stringent action has been taken against the cases of willful violation and severe non-conformities of Certification Bodies with the NPOP Standards.
- The NPOP regulations have been revised bringing in more stricter norms in terms of legal entity of grower groups, close monitoring through ICS office in the vicinity of the grower group, and inspection of grower groups through mobile app is going to be started shortly.
- New procedures have been formulated for additional checks for certification of organic cotton production. The procedure also limits the zone of the certification bodies certifying cotton to have a closer monitoring and oversight.
- The process of unannounced inspections has increased many folds. Stringent action has been taken against the grower groups and the defaulting certification bodies.
APEDA is committed to ensure that the Organic certification system under the NPOP is credible, transparent and clear. Wherever credible evidence of non compliances/ wilful violation of organic standards have been brought to light, APEDA had undertaken extensive investigation and taken concrete measures. All such matters are subjected to structured investigation following principles of natural justice. Any Certification Body or operator found violating norms is penalized as per NPOP regulation.
It may be mentioned that in a press briefing by an opposition leader yesterday, unfounded, unsubstantiated and misleading aspersions are being cast against the Organic Certification programme, the National Programme of Organic Production(NPOP).
Generalised allegations against a robust regulatory system of the Country for a particular crop/ region/ group of operators only serve to undermine the credibility of legitimate regulatory institutions and the broader organic movement in India.
Centre’s New Initiative to Connect MSMEs with Global Market
Centre’s New Initiative to Connect MSMEs with Global Market
The Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry Initiative “One District, One Product” (ODOP) aims at fostering balanced regional development across all districts of the country by selection, branding, and promoting one product from each district of the country. The ODOP Initiative aims at attracting investment in the district and boosting manufacturing and exports, thereby generating employment in the district. ODOP is operationally merged with the “Districts as Export Hubs” initiative.
The Developing Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative is a flagship export promotion initiative of Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), with the vision to transform every district into a vibrant contributor to national exports. It builds upon and now incorporates the One District One Product (ODOP) initiative to streamline export potential at the grassroots level. Each district identifies one or more products or services with export potential and creates a District Export Action Plan (DEAP) to support quality, capacity, market access, and infrastructure. A District Export Promotion Committee (DEPC), led by local administration in partnership with DGFT regional authorities, oversees execution. State-level Export Promotion Committees support coordination across districts and the DGFT implements and monitors via a national portal. ODOP products are promoted at international events through engagement with Indian Missions abroad.
The Government facilitates participation of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in International Trade Fairs through the International Co-operation Scheme of the Ministry. The scheme aims to build Capacity of MSMEs for entering export market by facilitating their participation in international exhibitions/ fairs/conferences/ seminar/buyer-seller meets abroad as well as providing them with actionable market-intelligence and reimbursement of various costs involved in export of goods and services. The Scheme provides opportunities to MSMEs to continuously update themselves to meet the challenges emerging out of changes in technology, changes in demand, and emergence of new markets.
The components of training in digital marketing and e-commerce are embedded in schemes like Procurement and Marketing Support and MSME Trade Enablement and Marketing (MSME TEAM) schemes of the Ministry of MSME. Government provides financial incentives/concessions through schemes like Prime Ministers Employment Generation Programme, PM Vishwakarma, Procurement and Marketing Support, International Cooperation, Khadi Gramodyog Vikas Yojana, Coir Vikas Yojana etc, for enterprise creation, capacity building, tool kits, etc. Through the Credit Gaurantee Fund Trust (CGTMSE), Government provides guarantee cover for Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs), with increased cover for women owned enterprises.
This information was given by the Minister of State for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Smt. Sushri Shobha Karandlaje, in a written reply in the Rajya Sabha today.
Cruise Tourism on National Waterways Gains Momentum with Infrastructure Boost
River Cruise Voyages on National Waterways rise by 19.4% in 2024–25; 51 new cruise circuits planned across 14 states and 3 UTs by 2027 under Cruise Bharat Mission
The river cruise tourism sector in India has witnessed notable growth, with the number of river cruise voyages on National Waterways increasing from 371 in 2023-24 to 443 in 2024-25. This 19.4% growth underscores the rising appeal and operational efficiency of river cruises in India’s inland waterways.
Adding to this momentum, Viking Cruises has announced its entry into India’s river cruise market with Viking Brahmaputra, an 80-guest vessel scheduled to begin operations in late 2027, signalling heightened interest and investment in India’s river cruise tourism sector. Viking Brahmaputra, to be indigenously developed by Hooghly Cochin Shipyard Limited in Kolkata, will operate on National Waterway-2.
In line with Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision and guidance of Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is making strides in promoting river cruise tourism and developing sustainable water transport system in India.

The sector has witnessed exceptional growth over the last 11 years. From just five vessels on three waterways in 2013–14, river cruise operations have expanded to 25 vessels across 13 national waterways in 2024–25. This growth is attributed to the proactive efforts of IWAI under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways in enhancing navigational safety and infrastructure on National Waterways. IWAI has facilitated smoother and safer navigation for river cruise vessels by developing terminals, on-shore and off-shore facilities, ensuring adequate depth in waterways, and providing 24-hour navigation aids and pilotage services. These measures have collectively enhanced the passenger experience, improved operational logistics, and boosted operator confidence, contributing to the growth of the sector.
Notably, the MV Ganga Vilas, flagged off by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi in January 2023, undertook the world’s longest river cruise from Varanasi to Dibrugarh, covering 3,200 km through 27 river systems in five Indian states and Bangladesh. This historic voyage earned a place in the Limca Book of Records. Other popular cruise circuits like Sundarbans in West Bengal, Brahmaputra in Assam, and Alappuzha in Kerala are also gaining traction.

IWAI plans to develop 51 new river cruise circuits on 47 national waterways across 14 states and three union territories by 2027. With the launch of the Cruise Bharat Mission, the government aims to increase river cruise passengers from 0.5 million to 1.5 million. The mission focuses on upgrading cruise terminals, ports, and related infrastructure, promoting eco-friendly tourism practices using green vessels, and creating numerous employment opportunities in the cruise industry in the coming two years.
IWAI has recently signed agreements with several state governments to promote cruise tourism on National Waterways, including partnerships with the Governments of Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh for cruise tourism on River Narmada, with the Delhi Government for operating ferries and cruises on the Yamuna River, and with the Government of Jammu and Kashmir for sustainable tourism on the Jhelum, Ravi, and Chenab rivers.
Besides, IWAI is developing dedicated cruise terminals on the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers, with three cruise terminals planned in Varanasi, Guwahati, Kolkata, and Patna. In the Northeast, four more cruise terminals at Silghat, Biswanath Ghat, Neamati, and Guijan are proposed to be developed by 2027.
The Future of Insurance in India: Insights Ahead of Insurance Summit 2025
The Future of Insurance in India: Insights Ahead of Insurance Summit 2025
India’s insurance sector, valued at over USD 140 billion, is undergoing significant transformation. Ranked among the top ten insurance markets in the world, the sector is witnessing momentum fueled by regulatory reforms, digital innovation, and a growing demand for customer-first solutions.
While the life insurance segment continues to experience steady growth, the non-life insurance sectors—including health, motor, property, and liability—are now poised for rapid expansion. This shift reflects India’s evolving risk landscape, changing consumer expectations, and stronger public-private policy alignment.
At the centre of this evolution lies a vital question:
Is India’s insurance industry actively preparing for this transformation, or merely hoping it will unfold on its own?
Catalysts for Sectoral Change
The government’s “Insurance for All by 2047” vision, championed by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI), has placed the insurance sector on an ambitious course. Several recent and upcoming developments will play a decisive role in shaping this path forward:
- The Insurance Bill Amendment 2025 is set to redefine how insurers raise capital, handle solvency requirements, and operate under a modernised regulatory structure. This could have far-reaching implications for IPO-readiness and governance transparency across the industry.
- The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission aims to launch a national health claims exchange, designed to digitise and simplify the claims settlement process across insurers, third-party administrators, and hospitals. This move is expected to drastically reduce paperwork, speed up approvals, and improve the policyholder experience.
- Insurtech firms and legacy insurers are collaborating to co-develop products that meet the specific needs of diverse populations — from urban centres to semi-urban and rural markets. These collaborations are also enabling the expansion of microinsurance and embedded insurance services.
- Today’s insurance consumers are demanding more than just coverage. They are seeking transparency, trust, and personalised service. This behavioural shift is compelling insurers to rethink their models — from transaction-driven to relationship-based.
Introducing Insurance Summit India 2025
To address these developments, the Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI) Committee of the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry will host:
Insurance Summit India 2025 – Viksit Bharat: Catalysing Insurance for a Resilient Future
Date: August 8, 2025
Time: 1:00 PM Onwards
Venue: Hotel Taj Santacruz, Mumbai
Organiser: Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, BFSI Committee
This high-impact summit will convene key stakeholders from across the insurance ecosystem — including senior regulators, CEOs, actuaries, underwriters, legal experts, technology leaders, brokers, TPAs, and insurtech founders.
🤝 Supported by Industry Leaders
The Insurance Summit India 2025 is supported by some of the most respected names in the insurance and financial services industry:
- Title Sponsor: New India Assurance
- Premium Sponsors: Axis Max Life Insurance | Lockton
- Co-Sponsors: Beacon Insurance Brokers Pvt. Ltd. | Aditya Birla Capital Health Insurance
- Knowledge Partner: PwC India
Their collaboration reflects the shared commitment toward building a more resilient, inclusive, and tech-enabled insurance ecosystem. To explore the full agenda and speaker lineup, visit the official event page.
What to Expect at the Summit
The Summit will open with a high-impact plenary session featuring a keynote address by Mr. Deepak Sood, Member (Non-Life), IRDAI, who will share the regulator’s vision and roadmap for driving innovation while upholding consumer protection and financial stability. The session will also include special addresses by Mr. Nilesh Sathe, Former Whole-time Member, IRDAI, and Ms. Girija Subramanian, CMD, New India Assurance.
Participants can look forward to three high-value panel discussions:
- Panel 1: Opportunities and Impact of the Proposed Insurance Bill Amendment 2025 — featuring leaders from Zuno Insurance, Universal Sompo, and Future Generali.
- Panel 2: Enhancing Customer-Centricity — featuring experts from Lockton and Beacon Insurance Brokers, among others.
- Panel 3: Tech-Driven Innovation, Inclusion and Trust — with insights from Aditya Birla and Axis Max Life Insurance, among others.
Each session is designed to foster actionable dialogue on how innovation, regulation, and consumer engagement can jointly enable India’s transition into a resilient insurance economy.
The Summit also offers structured networking opportunities, including a curated networking lunch and post-event dinner with cocktails — allowing professionals to connect meaningfully across domains.
Why This Summit Matters
Insurance has evolved from being a financial product to becoming a pillar of economic resilience. In today’s India, it is a critical lever for inclusive growth, social stability, and institutional trust.
The Insurance Summit India 2025 is not just another industry event — it is a strategic forum for collaborative problem-solving, innovation sharing, and long-term ecosystem building.
If you are involved in insurance, fintech, legal advisory, regulatory policy, health administration, or capital markets, this Summit offers unparalleled insights and access.
Register Now
Participation is limited and registration is filling quickly.
To confirm your seat and gain access to this flagship event,
Click here to register for Insurance Summit India 2025
For queries or institutional participation, contact:
Utkarsha Joshi:
+91 22 6120 0271
utkarsha.joshi@bombaychamber.com
Priya Singh:
+91 22 6120 0238
GST invoice management system evolves for smarter tax compliance
GST invoice management system evolves for smarter tax compliance


Mumbai: When the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Invoice Management System (IMS) went live on October 1, 2024, it arrived as a quiet revolution in the nation’s GST architecture. Introduced with the promise of real time visibility into business-to-business (B2B) transactions, the system is currently optional – a testing ground rather than a mandate. Yet within months, it became obvious to tax professionals and corporate leaders alike that IMS would reshape not only compliance routines but the very dynamics of trust and transparency across the supply chain.
As Komal Sampath, Director – Indian Tax Practice at Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu India LLP, explained at a recent webinar organised by the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, the true turning point comes with the decision to freeze outward liability in the GSTR 3B return from the July 2025 tax period onwards. At that juncture, any rejection of credit notes by the customers under their IMS may no longer directly be corrected under summary returns of GSTR 3B – a deadline that demands urgent attention from every taxpayer.
On the surface, the GSTN Portal itself presents a deceptively simple layout. Vendors upload their B2B transactions as soon as they are issued, and these records appear in the recipient’s dashboard that allows them to cross-verify entries against their own available records. Yet behind this simplicity lies an intricate choreography of data feeds and validation checkpoints. As transactions initially populate in the ‘No action’ section, recipient may take appropriate action and digital cut-throughs ensure near-instantaneous updates of both the supplier’s and the recipient’s IMS dashboards.
Filters by GSTIN, invoice number, and month enable finance teams to monitor high-value transactions and identify potential discrepancies. Furthermore, for quarterly filers, GSTR-2B is not generated during the first two months of the quarter, permitting them to undertake necessary actions on a quarterly basis.
It is in the dance between acceptance and rejection that the system’s power becomes evident. Should a recipient recognise a transaction as legitimate, a click of the accept button seamlessly authorises the corresponding input tax credit. If the transaction appears spurious or mis-addressed, rejection becomes an immediate deterrent against fraud – alerting both vendor and tax authority to the anomaly.
And where doubts persist, the pending status allows additional scrutiny, perhaps triggering an internal audit or a supplier follow-up. This triage of invoices not only curtails credit claims on counterfeit documents but also strengthens the integrity of each firm’s self-assessment.
Yet practical experience has also revealed obstacles, Karthik Gandhi, Head – Indirect Tax at Siemens India, shared at the same webinar that integration between IMS and legacy ERP systems remains a thorny issue for multinational groups. “We are dealing with multiple entities, each on a different digital platform,” he noted. “Ensuring that transactions captured in one system synchronise accurately with IMS, without duplications or time lags and requires intensive coordination between finance and vendor support teams,” said Gandhi.
Additionally, many practitioners believe further refinements are still required, particularly for taxpayer registered PAN India where tax documents are received at multiple offices and it may delay verification of tax documents by weeks. Calls for extended timelines for taking action on credit notes are already being tabled by industry associations, though any reprieve will need to balance ease-of-use with the government’s broader objectives of plugging revenue leakages.
For businesses large and small, the strategic implications of IMS extend far beyond compliance. Real time invoice matching can accelerate working capital cycles by giving suppliers confidence that credits will be honoured without delay subject to fulfilment of provision of GST law.
Conversely, any backlog in reconciliation can put pressure on cash flows, as the freeze on outward liability could leave invoices in limbo and credits unclaimed. Financial controllers thus find themselves at the nexus of legal compliance, treasury management and supplier relations – a role that demands both technical acumen and diplomatic finesse.
At its heart, the IMS represents a step towards a more transparent, accountable commercial ecosystem. No longer can shell companies hide behind fabricated invoices or delay reporting without immediate consequence. Simultaneously, genuine traders gain the reassurance of on-demand verification, reducing the friction of inter-company settlements. The transformation may be gradual – after all, the initial phase remains optional – but with each month of voluntary participation, taxpayers refine their processes in anticipation of the mandatory horizon.
As the IMS evolves, so too will the skills demanded of India’s tax professionals. Tomorrow’s finance teams/tax professionals will need data analytics expertise to monitor dashboard metrics, legal insight to interpret emerging advisories and change-management know-how to embed new procedures across dispersed operations.
The freeze effective July 2025 is not merely a technical adjustment; it is a signal that digital compliance has arrived irreversibly. Firms that adapt swiftly will not only avoid penalties but stand to gain a competitive edge in the increasingly data-driven marketplace.
In the end, India’s journey towards real time invoice reporting is a microcosm of its aspirations for a fully digitised economy. By merging technology with regulatory intent, the government seeks to construct a fiscal architecture that is both resilient against fraud and conducive to growth. The road ahead will doubtless present further challenges, from system enhancements to policy fine-tuning, but the direction of travel is clear.
For those who embrace the change, the IMS offers a pathway to greater efficiency, stronger compliance and deeper collaboration across the supply chain. And when the next chapter of India’s tax story is written, it will surely be defined by the lessons learned from the first months of IMS in action.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin