Blog
Top Stories
When commercial dispute resolution matters choose your fight wisely
Mumbai: In today’s increasingly complex commercial landscape, disputes are inevitable. But the method you choose to resolve them can shape not just the outcome, but the time, cost, and relationships along the way. Arbitration and mediation, often bundled under the banner of alternative dispute resolution, differ as much in strategy as they do in spirit.
Arbitration is inherently adversarial. It imposes a formal structure reminiscent of courtroom litigation. The process is governed by procedure and results in a binding decision – an award – that can be executed like a court decree.
This makes it particularly useful where parties need finality, enforcement, and a framework capable of absorbing complex evidence and legal argumentation. But it also comes at a price. Arbitrator fees, lengthy timelines, and procedural layers can make it a costly affair, with durations often stretching beyond two years and expenses creeping into seven to ten per cent of the dispute value. As many professionals have observed, arbitration serves best when the stakes are high – often above ₹1 crore – and the issues require detailed adjudication.
Mediation, however, takes a different path. It is fluid, collaborative, and anchored in consent. Rather than imposing a judgment, it offers a facilitated space for parties to communicate, find common ground, and reach a solution of their own making.
A well-handled institutional mediation can resolve matters within three months, at a fraction of the cost of arbitration. In practice, a typical mediation may cost under ₹76,000 and produce outcomes that cannot be challenged under Section 34, provided the terms are formalised as part of an arbitration award or under Section 30(4) of the Arbitration Act.
What makes mediation particularly powerful is its emphasis on preserving relationships. In business disputes, where future collaboration might still be on the table, this becomes a strategic edge. And while the Mediation Act is still in the process of full notification, professionals are already making adjustments – treating direct resolutions as ‘conciliation’ where required by law, but maintaining the spirit and structure of mediation.
Interestingly, the future may not belong exclusively to one approach. Institutions and arbitrators are already embedding mediation within arbitration proceedings. When the arbitrator also holds mediation training, the shift between forums is seamless.
Parties may pause arbitration, engage in structured mediation, and return—if successful—with a binding resolution converted into an award. It is here that the strategic blend reveals its strength, offering the enforceability of arbitration with the consensual power of mediation.
For professionals and institutions alike, the real challenge lies in knowing when to pursue which path. Arbitration is a hammer; precise, powerful, but not always appropriate. Mediation is a bridge – faster, lighter, and often more enduring. In a world where legal efficiency is currency, the best strategy may be to ask not which tool is better, but which moment calls for which instrument.
Dispute Resolution @ Bombay Chamber (DR@BC) is an initiative of the Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry, India’s oldest operating chamber of commerce. Established in response to the growing need for efficient, business-friendly alternatives to litigation, DR@BC provides a structured platform for Mediation, Arbitration, Conciliation, and Neutral Evaluation. Contact us for a free initial consultation: https://adr.bombaychamber.com/contact-us/
₹1000 crore ADEETIE scheme to empower MSMEs with clean energy investment
₹1000 crore ADEETIE scheme to empower MSMEs with clean energy investment
Mumbai: The Ministry of Power, Government of India has launched a nationwide initiative to accelerate industrial energy efficiency, with the Union Minister for Power and Housing & Urban Affairs, Manohar Lal, officially rolling out the ₹1000 crore ADEETIE scheme in Panipat, Haryana. Designed to support Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), the scheme offers financial and technical assistance to promote the adoption of energy-efficient technologies across 14 energy-intensive sectors.
The Assistance in Deploying Energy Efficient Technologies in Industries & Establishments (ADEETIE) programme is being implemented by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency and aims to reduce the carbon footprint of Indian industry, improve the power-to-product ratio, and enhance competitiveness through sustainability. MSMEs can avail themselves of interest subvention on loans – 5 percent for micro and small enterprises, and 3 percent for medium enterprises – alongside end-to-end handholding from energy audits to post-implementation monitoring.
Officials expect the scheme to mobilise ₹9,000 crore in investment, including ₹6,750 crore in prospective MSME lending, and boost the country’s progress towards international climate commitments.
Speaking at the launch, Lal described the scheme as a transformative movement aligned with the Viksit Bharat vision, stating that it empowers industries to reduce energy consumption by up to 50 percent. Early success stories, Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signings and commendations for pioneering MSMEs added momentum to the event, which marked a milestone in India’s clean energy transition.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)

Union Cabinet approves transformative scheme for farming districts
Union Cabinet approves transformative scheme for farming districts

Mumbai: In a major push to revitalise agriculture and allied sectors, the Union Cabinet has approved the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, a first-of-its-kind initiative aimed exclusively at accelerating development across 100 districts. The scheme has an outlay of Rs 24,000 crore per year and will be implemented over the next six years.
Drawing inspiration from NITI Aayog’s Aspirational District Programme, the scheme promises a data-driven, outcome-focused approach to raise agricultural productivity, promote sustainable practices and improve rural livelihoods.
Target districts will be selected using key indicators such as low crop yield, minimal cropping intensity and limited access to agricultural credit. Each state will see at least one district included, with final selections reflecting the distribution of India’s net cropped area and operational holdings.
The plan’s implementation will rely on the convergence of 36 existing central schemes across 11 departments, alongside complementary state initiatives and private sector participation. A three-tier governance structure – national, state and district – will oversee planning and execution, with each district guided by its own Dhan-Dhaanya Samiti, comprising officials and progressive farmers.
District-level plans will align with national goals, emphasising crop diversification, conservation of natural resources and the promotion of organic farming. Progress will be tracked monthly via a digital dashboard against 117 key performance indicators, with NITI Aayog offering guidance and monitoring support.
As outcomes in the chosen districts improve, officials expect national agricultural metrics to rise correspondingly. By enhancing productivity, storage, irrigation and financial access, the scheme aspires to foster greater self-reliance and value addition within India’s agricultural ecosystem, anchoring the broader vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
GST webinar highlights practical insights for tax and finance professionals
GST webinar highlights practical insights for tax and finance professionals


Mumbai: The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry, under the aegis of its Indirect Tax Committee, hosted an informative webinar on the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Invoice Management System (IMS). The session provided participating tax professionals and finance teams with timely updates and practical guidance on the evolving invoice reconciliation framework.
The session centred on operational and strategic implications of the IMS, introduced by the GSTN and also discussed updates effective July 2025. The system is designed to enable recipient taxpayers to reconcile purchase invoices in real time, with functionality to accept, reject, or defer invoices – ultimately streamlining the Input Tax Credit (ITC) claim process.
The webinar was led by two eminent speakers viz. Kartik Gandhi, Head of Indirect Tax at Siemens Ltd., and Komal Sampat, Director in the Indirect Tax practice at Deloitte Tohmatsu India LLP. Drawing from more than 15 years in the domain, Gandhi elaborated on technological integrations and practical workflows in managing indirect taxes. Sharing nuanced insights from over a decade of experience in indirect tax advisory and compliance, Sampat highlighted real-world applications and sectoral impact across industries such as energy, TMT, pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, and small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
Participants gained a clear understanding of the IMS structure, from invoice submission by suppliers to the recipient’s actions and the cascading effects on GSTR-2B and GSTR-3B filings. The session offered a comprehensive walkthrough of the IMS dashboard, invoice tracking capabilities, and the communication loop between supplier and recipient. The presenters also navigated scenarios involving invoice exceptions and discussed best practices for streamlining compliance efforts in light of recent regulatory amendments. Legal updates and their implications for IMS usage were thoroughly reviewed, ensuring participants left with actionable clarity.
The webinar concluded with an interactive Q&A session, where participants sought clarification on individual queries. Attendees were encouraged to share additional practical challenges related to GST IMS directly with the Bombay Chamber and were assured of timely support and guidance from GST experts.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
With DR@BC, Bombay Chamber reinforces its role as a neutral partner in business conflict resolution
With DR@BC, Bombay Chamber reinforces its role as a neutral partner in business conflict resolution
Mumbai: The Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, India’s oldest operating chamber of commerce, has launched a dedicated website for its alternative dispute resolution services – Dispute Resolution @ Bombay Chamber (DR@BC) – a milestone that reinforces the Chamber’s role in shaping India’s evolving dispute resolution landscape.
As India’s economy continues to expand, the rise in complex business transactions demands mechanisms that are swift, confidential, and commercially sound. Traditional litigation – often burdened with delays and backlogs – has highlighted the need for robust alternatives that uphold the integrity of commercial relationships while delivering timely outcomes.
DR@BC addresses this need head-on, providing an institutional platform for Mediation, Arbitration, Conciliation, and Neutral Evaluation. The newly launched website enhances access to these services – enabling corporates, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), professionals, and other stakeholders to understand procedures, initiate matters, and browse profiles of DR@BC’s distinguished panel of arbitrators and mediators.
In alignment with contemporary business expectations, DR@BC offers flexible formats for resolving disputes. Depending on preference and context, parties can opt for online hearings via secure virtual platforms, in-person proceedings at DR@BC’s Mumbai facility, or hybrid models – ensuring convenience without compromising on procedural integrity.
The centre is equipped with a dedicated meeting / conference room for arbitration and mediation discussions, and infrastructure designed for confidentiality and efficiency. A team of trained support professionals ensures seamless coordination for both physical and digital sessions.
Commenting on the alternative dispute resolution services offerings, Sandeep Khosla, Director General, Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, said, “With the DR@BC website, we reaffirm our commitment to empowering India’s business community with dispute resolution avenues that are timely, confidential, and globally aligned. As commerce becomes more dynamic, the ability to resolve conflicts efficiently is vital to economic resilience and stakeholder trust.”
The initiative reflects the Chamber’s broader mission to enhance India’s business climate by easing judicial burdens and promoting collaborative, commercially viable solutions. For more information or to submit a query, please visit the Dispute Resolution @ Bombay Chamber (DR@BC) page at https://adr.bombaychamber.com.
India-U.S. interim trade deal nearing completion amid agricultural deadlock
India-U.S. interim trade deal nearing completion amid agricultural deadlock
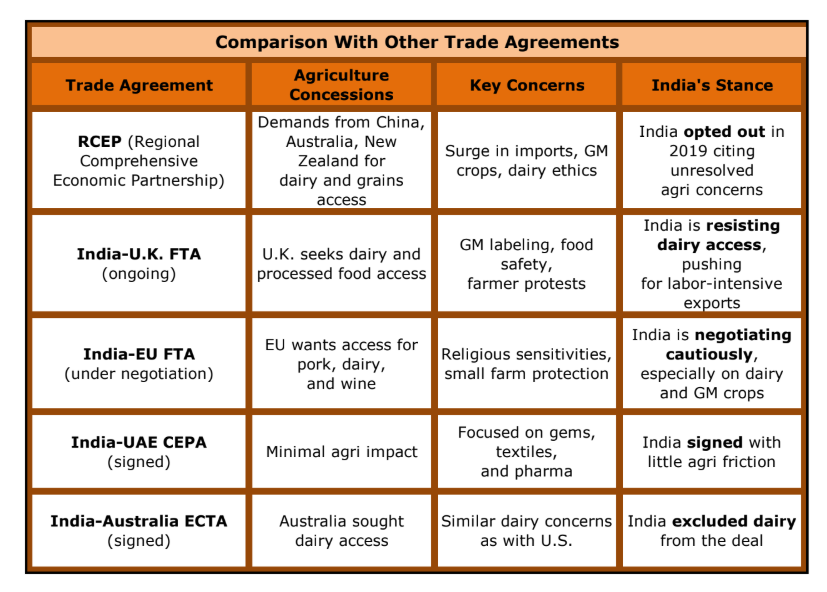
Mumbai: India and the United States are on the cusp of finalising an interim trade agreement, expected to be signed soon. The deal is aimed at pausing the reciprocal tariffs imposed during the Trump administration, with July 9 set as a critical deadline.
Negotiators from both nations have made substantial progress, but a decisive hurdle remains: India’s staunch refusal to fully open its agriculture and dairy markets to American imports. Officials from the Indian delegation have described agriculture as a “non-negotiable” pillar of national interest – both economically and culturally.
While the U.S. seeks wider access to Indian markets for genetically modified crops, dairy products, and ethanol, India has cited domestic sensitivities and structural constraints. Concerns over food safety, smallholder farm vulnerabilities, and ethical dietary norms have driven New Delhi’s resistance to American agricultural standards.
India’s Ethanol Blended Petrol program — which relies on sugarcane and grains — is another sticking point. Importing U.S. ethanol could undercut domestic production and compromise energy security.
Balancing Trade Ambitions and Rural Realities
Agriculture sustains nearly half of India’s population. Experts warn that an influx of subsidised U.S. goods could destabilise rural livelihoods and reignite tensions reminiscent of the 2021 farmer protests. There are also fears that tariff concessions may erode India’s Minimum Support Price (MSP) framework, a key safety net for its farming community.
The asymmetry in farm scale and tariffs adds complexity. American farms average over 180 hectares, operate with advanced mechanisation, and enjoy low trade barriers — unlike India’s predominantly manual, micro-scale farming landscape, where tariffs range up to 150%.
Instead of making concessions in agriculture, India is pushing for expanded access for labour-intensive sectors like textiles and manufacturing, which fuel employment and export growth. The interim deal, if sealed, could potentially boost bilateral trade to $500 billion and lay the groundwork for broader economic cooperation.
India’s protective stance on agriculture mirrors its approach in other trade agreements — including the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), which it exited in 2019, and ongoing negotiations with the UK and European Union. Dairy and genetically modified (GM) crops remain consistent red lines.
As talks enter their final phase, all eyes are on whether Washington and New Delhi can bridge differences — or if agriculture will once again be the dealbreaker.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
Indian diamond industry braces for downturn amid tariffs and shifting demand
Indian diamond industry braces for downturn amid tariffs and shifting demand
Mumbai: India’s cut and polished diamond (CPD) industry is confronting another challenging year, as export volumes are expected to decline by up to 10 percent on a year-on-year basis to about $12 billion in FY2026. Industry sentiment remains subdued following the steep 17 percent contraction to $13 billion in FY2025, driven by global economic headwinds, heightened competition from lab-grown diamonds (LGDs), and a pronounced drop in demand across key markets including the United States and China.
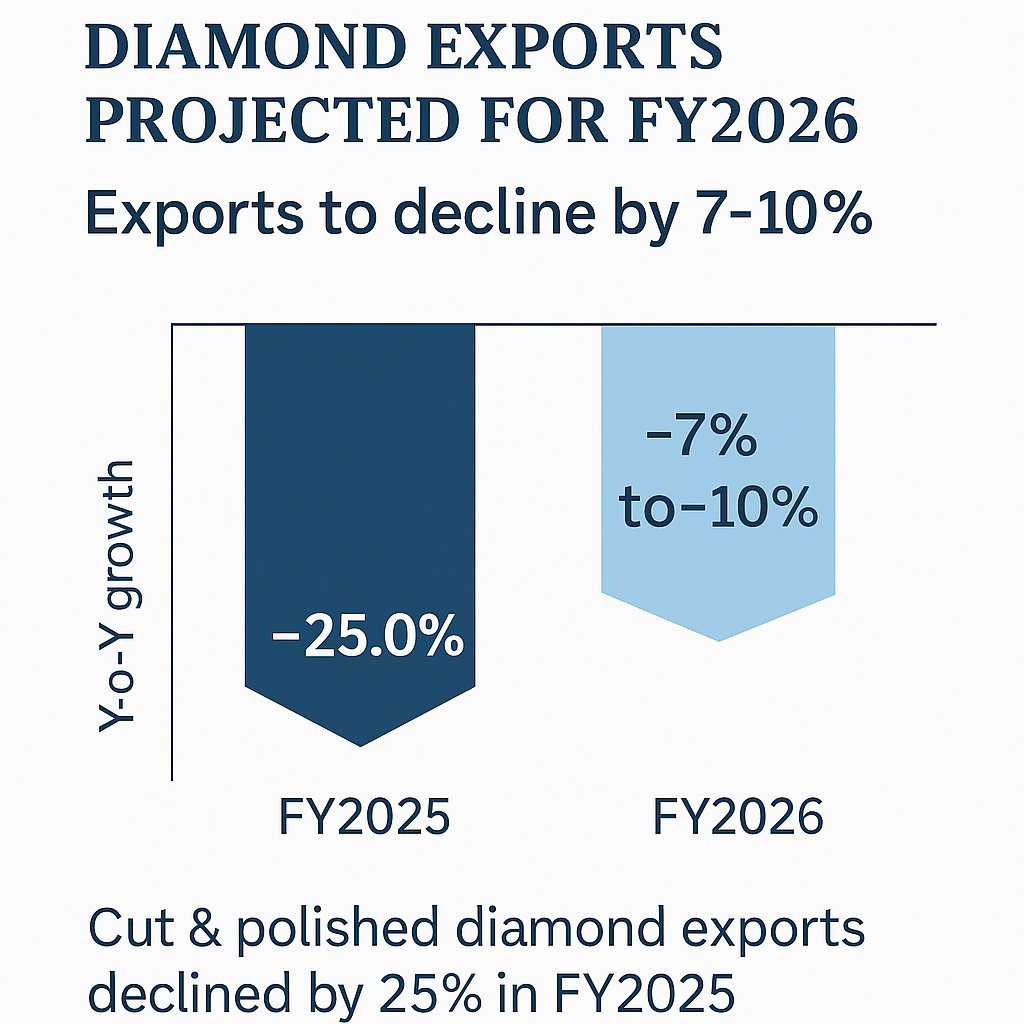
ICRA, in its latest report, has maintained a negative outlook for the sector, cautioning that the imposition of US tariffs and ongoing preference for LGDs may further erode profitability. A baseline tariff of 10 percent currently applies to Indian CPD exports to the US — a pivotal market accounting for over a third of outbound shipments. Diamantaires are exploring rerouting options through regions such as Dubai, Belgium, and Israel to offset tariff burdens and retain competitiveness.
While demand for LGDs continues to climb, capturing 8 percent of India’s polished diamond export value in FY2025, the sharp price correction — driven by technological advances and new market entrants — has squeezed margins. In contrast, fancy coloured diamonds (FCDs) have demonstrated relative price stability, offering a buffer for companies dealing in niche, high-quality stones.
Polished diamond prices reached historic lows in the second half (H2) of FY2025 and are expected to remain range-bound through the first half (H1) of FY2026. Meanwhile, rough diamond imports have declined sharply, reflecting cautious inventory management and weak global appetite. Despite reductions in procurement and extended seasonal closures, working capital cycles remain stretched, and operating margins for ICRA-rated entities are forecast to dip further to around 3.6-3.7 percent.
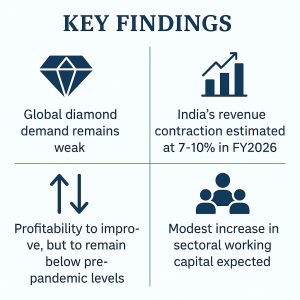
Survey responses from leading CPD players indicate muted optimism. Over 75 percent expect export volumes to be impacted by tariffs, while nearly 90 percent anticipate re-routing through favourable trade hubs. Most diamantaires predict stagnant rough prices, and volume degrowth exceeding 10 percent remains a concern.
As the industry recalibrates its strategies, success hinges on balancing cost controls with evolving consumer preferences. With bridal jewellery and luxury spending showing early signs of recovery in select markets, companies are watching closely for a demand revival in H2 FY2026.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
Corporate India redefines diversity through wellness, inclusion, and empathy
Corporate India redefines diversity through wellness, inclusion, and empathy
Mumbai: The landscape of workplace diversity is undergoing a profound transformation, revealing complex layers of challenges and innovative solutions across corporate India. At the heart of this evolution lies a nuanced understanding that diversity extends far beyond gender representation, encompassing mental wellness, infrastructure, cultural mindsets, and systemic barriers.

At the recently concluded Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) Forum & Awards 2025, hosted by the Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry, participating organisations discussed in detail the idea that true inclusion requires a holistic approach. Companies like Novo Nordisk India are pioneering initiatives that strategically recruit talent from tier-two cities, creating pathways for women who might otherwise be overlooked. Similarly, Aditya Birla Capital has achieved a remarkable 30 percent diversity rate by implementing comprehensive wellness programmes that address not only professional challenges but also personal health concerns such as menopause, hormonal changes, and mental well-being.
The conversation around diversity is increasingly intersectional, moving beyond binary gender discussions to embrace LGBTQ+ representation. Companies like Crompton Greaves and Raymond Ltd have taken a groundbreaking approach by integrating LGBTQ+ professionals into design departments, demonstrating how diverse perspectives can be transformative. This approach challenges traditional workplace structures and unlocks innovative potential.
Infrastructure has emerged as a critical yet often overlooked aspect of inclusion. Speakers at the DEI Forum & Awards 2025 highlighted the stark reality that many operational roles remain inaccessible to women due to inadequate sanitation and hygiene facilities. This infrastructure gap reflects deeper systemic challenges that require deliberate, organisation-wide commitment to change.
Cultural transformation is equally crucial. Participants candidly discussed how deeply ingrained societal norms perpetuate gender inequalities—from childhood conditioning that prioritises male needs to workplace environments that expect women to silently endure challenges. Breaking these cycles demands conscious effort at individual, organisational, and societal levels.
Mental wellness has emerged as a pivotal dimension of inclusive workplaces. Stockholding Corporation’s comprehensive approach—which includes counselling sessions, flexible work policies, and extensive health coverage—represents a progressive model of employee support that transcends traditional diversity metrics.
Particularly compelling was the discussion around Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), where invisible barriers such as the ‘glass ceiling’ and ‘sticky floor’ significantly impede women’s professional growth. These organisations require targeted interventions to create equitable opportunities.
Speakers emphasised that diversity cannot be an HR-driven initiative alone—it must be embraced by business leadership. The most successful approaches integrate diversity strategies into the core organisational DNA, viewing inclusion as a strategic imperative rather than a compliance exercise.
Innovative companies are extending their diversity efforts beyond corporate boundaries. Aditya Birla Capital’s collaboration with UN Women to conduct financial literacy programmes in rural areas exemplifies how organisational commitment can drive broader societal transformation.
The emerging narrative is clear — diversity, equity, and inclusion are not static concepts but dynamic, evolving strategies that require continuous learning, adaptation, and genuine commitment. Success lies not in tokenistic representation, but in creating environments where every individual, regardless of gender, background, or ability, can thrive and contribute meaningfully.
As organisations navigate this complex landscape, the key lies in fostering a culture of empathy, understanding, and genuine respect — transforming workplaces from mere employment spaces into platforms for human potential and collective growth.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
From Bricks to Blocks: Bombay Chamber Explores the Future of Real Estate Investments through REITs: Asset Tokenisation Conclave 2025
From Bricks to Blocks: Bombay Chamber Explores the Future of Real Estate Investments through REITs: Asset Tokenisation Conclave 2025
Mumbai, June 25, 2025 – The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry hosted the REITS – Asset Tokenisation Conclave 2025: From Bricks to Blocks at ITC Grand Central, Mumbai, bringing together senior regulators, policy influencers, industry pioneers, and legal experts to discuss the shifting contours of real estate investment in India. As the sector moves towards greater digitisation, accessibility, and transparency, the Conclave served as a timely platform to spotlight how fractional ownership and tokenisation are reshaping the real estate investment landscape.
The event began with a welcome address by Sandeep Khosla, Director General of the Bombay Chamber, who underscored the Chamber’s role in taking forward critical conversations that influence industry thinking and regulatory evolution. He emphasised that the Chamber remains committed to being a forum that not only reflects business sentiment but also actively steers emerging discussions—especially those at the intersection of innovation, finance, and policy.

Setting the thematic foundation, Sanjay Dutt, Director at Bombay Chamber and MD & CEO of Tata Housing Development Company, traced the arc of India’s real estate sector from a modest 750 million square feet of office space in 2000 to its projected expansion to 1.3 billion square feet in the next few years. He called attention to the sector’s growing complexity and promise, with emerging segments such as data centers, logistics, warehousing, co-working spaces, and senior living. He described the sector as “a supernova”—brilliant and explosive in its growth—and highlighted how new investment tools like REITs, SM REITs, and tokenisation are unlocking access to a broader investor base and building a new category of mid-ticket capital.

In his keynote address, G.N. Bajpai, Former Chairman of LIC and SEBI, examined the global financial environment and its implications for Indian investors. Speaking to a room filled with institutional stakeholders, millennials, and professionals, he emphasised that in today’s inflation-prone and uncertain world, democratising investment through technology is no longer aspirational but essential. He argued that tokenisation, backed by strong regulatory support, has the power to transform real estate into an accessible and liquid asset class for the common investor—not just the ultra-wealthy.

Shri Pramod Rao, Executive Director at SEBI, delivered a special address focusing on the regulatory view of fractional ownership and tokenisation. He offered a nuanced distinction between regulated products like REITs and unregulated financial innovations like tokenised real estate. Highlighting SEBI’s openness to learning from sandbox approaches and pilot projects, he called for thoughtful differentiation between these instruments and urged industry players to prioritise investor protection. He also pointed to the significant monetisation potential in government and municipal assets and shared his optimism on how technology and regulatory engagement could bridge investment gaps.

The first panel, moderated by Neil Borate, Deputy Editor of LiveMint, brought together Shiv Parekh, Founder & CEO, hBits, Vivek Mimani, Partner- Investment Funds Practice Group, Khaitan & Co; and Saurabh Rathi, Managing Director & Co-Head of Real Estate, Motilal Oswal, to explore the current state and future potential of fractional ownership and SM REITs. The discussion delved into key market triggers—from faster licensing and simplified processes to investor education and institutional viability. The panellists also addressed the importance of platform credibility, noting that investor confidence will grow when there are clear skin-in-the-game mechanisms and greater governance frameworks.

The second panel, moderated by Jyoti Tandon, Compliance Consultant and Co-Founder of FinCrimeExpert, featured Manish Kumar, Co- Founder & CEO, RealX; Anand Narayanan, Co- Founder & CEO, Alt DRX; Prasanth Kalangi, Founder & CEO, Zoniqx, and Anil Choudhary, Partner, Finsec Law Advisors. This panel navigated the layered dimensions of real estate tokenisation—touching upon the technology stack, financial implications, and legal frameworks. The panelists shared insights into how smart contracts, cybersecurity, and interoperable platforms are foundational to scaling tokenisation.
As the event drew to a close, Sandeep Khosla delivered the vote of thanks, reiterating the Bombay Chamber’s commitment to providing a platform for forward-looking, inclusive, and solutions-oriented engagement at the intersection of industry, innovation, and regulation.
CEO NITI Aayog B.V.R Subrahmanyam delivers impactful message at Bombay Chamber’s 189th AGM; Rajiv Anand takes over as Chamber president
CEO NITI Aayog B.V.R Subrahmanyam delivers impactful message at Bombay Chamber’s
189th AGM; Rajiv Anand takes over as Chamber president
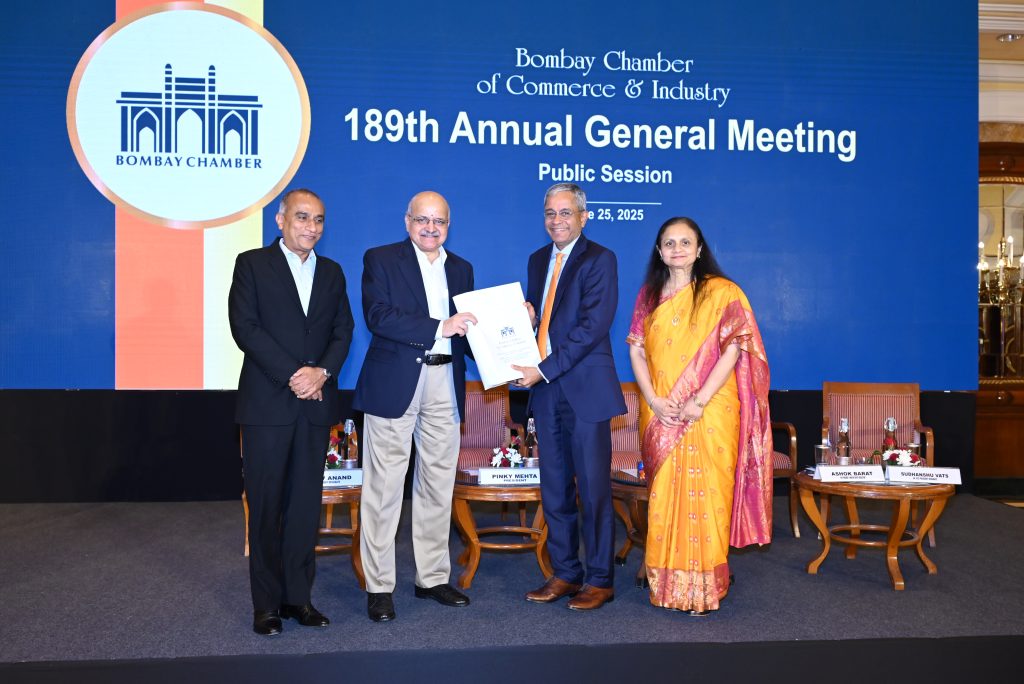
Mumbai, June 25, 2025: The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry held its 189th Annual General Meeting in Mumbai, bringing together eminent business leaders, policymakers, and members of the Chamber for an evening of reflection, renewal, and forward-looking dialogue. Rajiv Anand, Deputy Managing Director, Axis Bank took over as the Bombay Chamber President while Sudhanshu Vats, Managing Director, Pidilite Industries, became Sr Vice President of the Chamber.
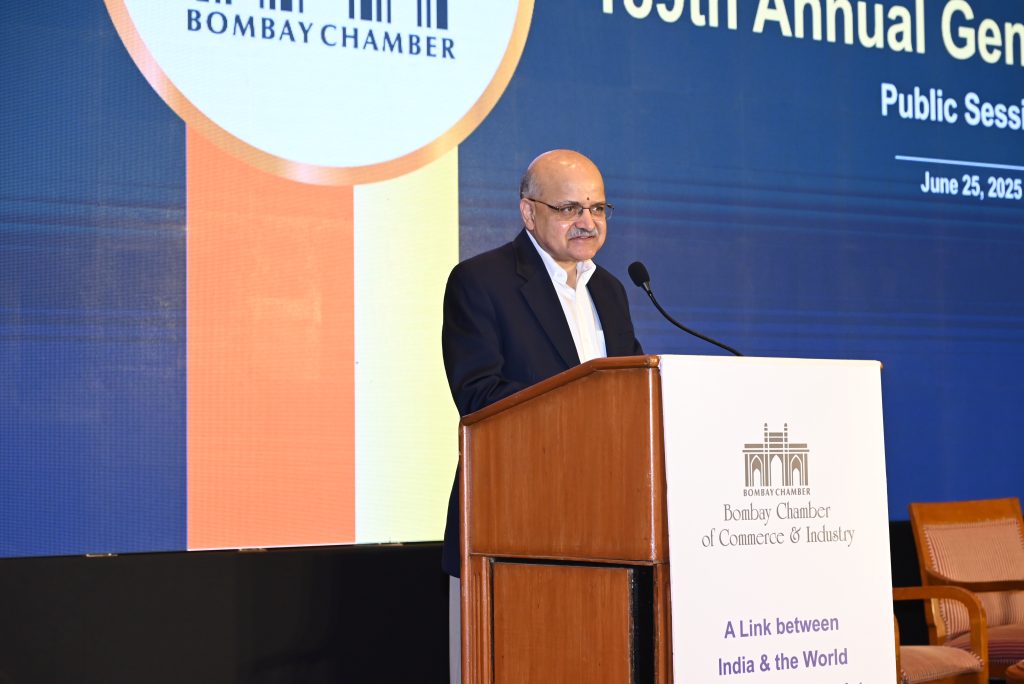

In his keynote address, B.V.R. Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, delivered an inspiring vision for India future, highlighting the nation remarkable transformation since independence. “In 1947, many doubted India’s ability to survive – today we have emerged as a potential economic powerhouse, projected to become the third-largest economy by 2027.”
Subrahmanyam emphasised the critical role of the Bombay Chamber in driving India growth, highlighting Mumbai potential as a global economic hub. While taking note of the vision shared by the incoming president, he appreciated the Chamber efforts and stressed on the need to frequently engage with the government to implement Mumbai’s economic plan, focus on micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), and drive innovation and sustainability. Additionally, the Chamber should leverage Mumbai position as a hub of industry, finance, and talent to drive India leadership in frontier technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and biotechnology.
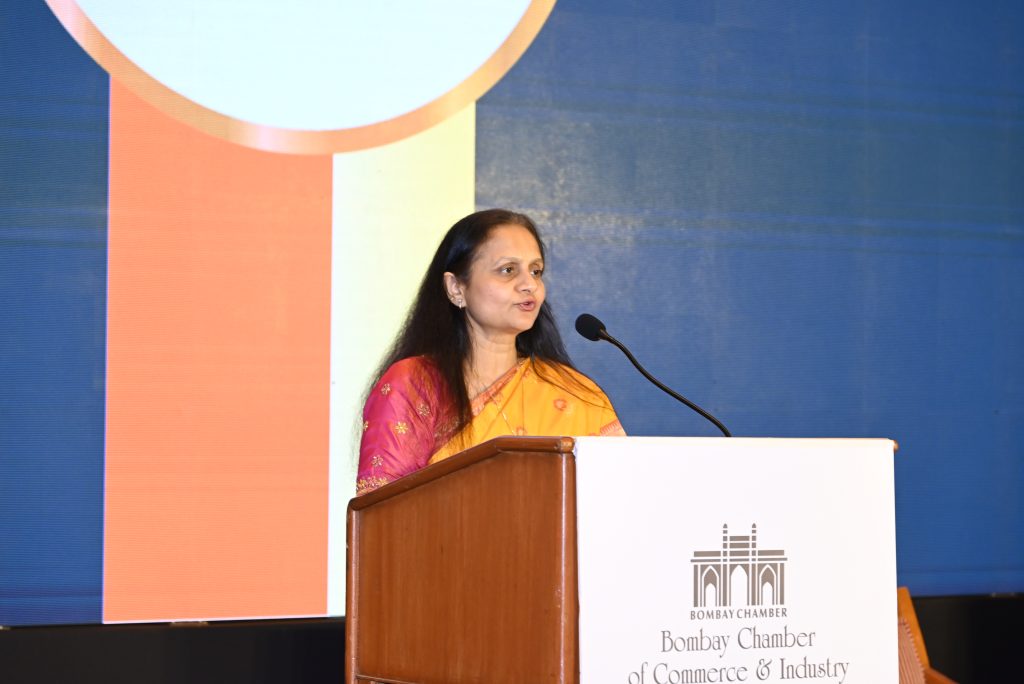

The AGM started with Pinky Mehta, outgoing President Bombay Chamber and Director, Aditya Birla Sun Life Insurance Co Ltd. & CFO, Aditya Birla Capital Ltd. welcoming the members and sharing her reflections on the Chamber’s impactful journey over the past year. Under her leadership, the Chamber championed four key pillars—Digitalisation, ESG & Sustainability, Ease of Doing Business, and Diversity, Equity & Inclusion—hosting over 100 knowledge-led events that advanced innovation, sustainability, and inclusive growth. She highlighted global engagements such as the Indian delegation to Cyprus during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the country, thought leadership at the International Agri Hackathon, the third edition of the Chamber’s DEI Forum and Awards, and dialogues with diplomats and regulators. She also reaffirmed the Chamber’s digital and green commitments through initiatives like the CSR in the Digital Era Conclave, the Green Growth Forum, and the Smart City Leaders’ Conclave.
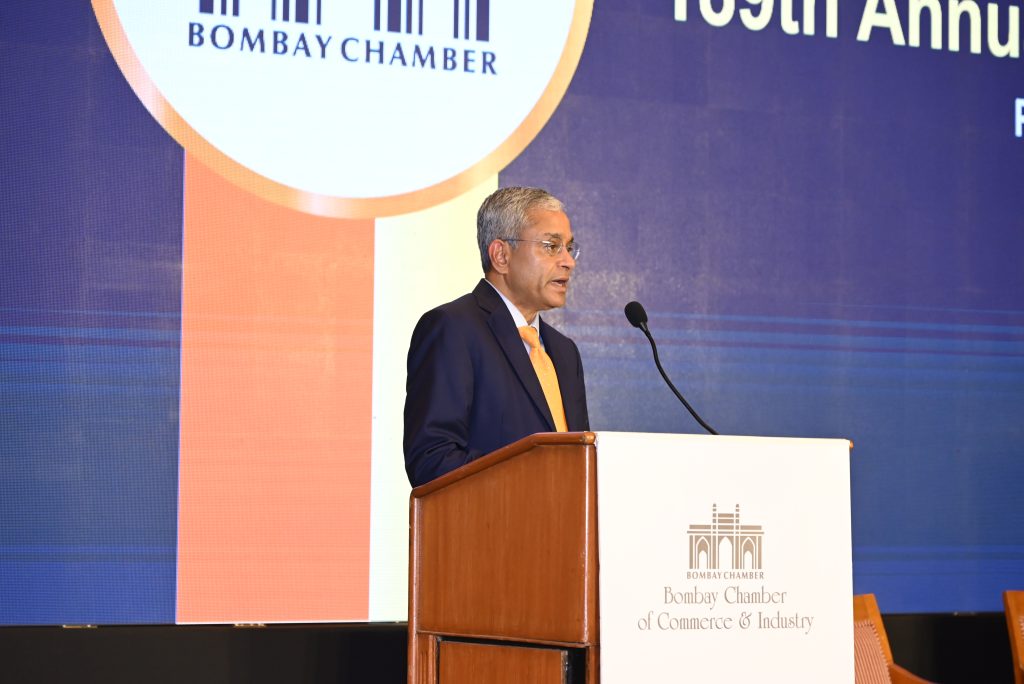

Following this, Rajiv Anand, President Designate, Bombay Chamber and Deputy Managing Director, Axis Bank, shared his vision for the year ahead under the theme ‘Shaping the Future: Innovation, Inclusion, Impact.’ He outlined five strategic priorities for 2025–26: catalysing sustainable economic growth, driving technology and innovation through the launch of a Centre for Emerging Technologies, empowering human capital with a focus on women and youth deepening public–private partnerships, and modernising the Chamber for the next generation. He stressed the Chamber’s mission to align closely with national priorities such as Atmanirbhar Bharat and Viksit Bharat@2047, and work in tandem with NITI Aayog on entrepreneurship, energy transition, and inclusive development.
In his keynote address, the NITI Aayog CEO also spoke about India ambitious goal to become a developed nation by 2047, with a targeted gross domestic product (GDP) of $30 trillion and a per capita income of $14,000. He said that this transformation isn’t just an economic target, but a national movement that requires participation from every citizen. He also stressed on India’s rise as a friendly, non-threatening power with relevance for developing regions worldwide.

Subrahmanyam shared critical viewpoints focusing on several strategic areas. He spoke extensively on human capital development covering aspects like leveraging India demographic dividend (median age of 29), expanding higher education to 9 crore students, increasing women workforce participation and comprehensive skilling programs.
On the economic transformation front he spoke about expanding manufacturing from half a trillion to $8-10 trillion, becoming a global services hub, developing agriculture beyond traditional cereal crops and creating global-standard financial and banking systems.
Urban development, Subrahmanyam said, needs special focus wherein cities have to be prepared to accommodate 50% of population by 2047, creation of economic growth hubs and developing comprehensive urban infrastructure.
Subrahmanyam called for business and industry leaders to be agents of change, working together to achieve a bold and inclusive vision for India’s future.
The evening also saw the launch of the “Dispute Resolution @ Bombay Chamber” website, an initiative focused on mediation as a structured and efficient tool for resolving commercial disputes. The launch was presented by Ashok Barat, Past President, Bombay Chamber and Mentor, Dispute Resolution @ Bombay Chamber & Director, Bata India, who emphasised the need for industry-led mechanisms to ease legal burdens and promote amicable solutions.
Concluding the evening, Sudhanshu Vats, Sr Vice President Designate, Bombay Chamber and Managing Director, Pidilite Industries, delivered the vote of thanks, expressing gratitude to the speakers, members, and stakeholders for their continued support and commitment. He reiterated the Chamber’s vision to serve as a forward-thinking, solutions-oriented platform for business leadership and policy engagement, dedicated to building an inclusive and prosperous future for Mumbai and India.

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin