Blog
Top Stories
Union Minister of Commerce and Industry Shri Piyush Goyal Calls on MedTech Startups to Go Global, Leverage Trade Pacts Covering 70% of World GDP
Union Minister of Commerce and Industry Shri Piyush Goyal today urged medtech startups to look beyond the domestic market, leverage India’s expanding trade agreements covering nearly 70% of global GDP, and scale affordable innovations to serve both India and the world.
Addressing the Pfizer INDovation Startup Showcase Programme in New Delhi, the Minister emphasized that affordable, scalable medical technology can help reach the remotest parts of India and also access global markets across Africa, Latin America, Central Asia, Southeast Asia and developed economies.
He noted that nine Free Trade Agreements concluded in the last three years cover 38 countries with strong per capita incomes, and that most developed markets now have trade arrangements with India. Agreements include the 27-nation EU bloc, four-nation EFTA bloc, the UK, Australia and New Zealand, the United States of America, while Japan and Korea were concluded earlier, along with ASEAN nations. He said India now has market access to 70% of global GDP, in most cases at zero duty for Indian products.
Shri Goyal said startups should not limit themselves to the domestic market and should participate in global fairs and exhibitions. He assured that the Commerce Ministry would support delegations and that India’s missions in over 190 countries are available to assist innovators. He also encouraged collaboration with global companies, present in over 100 countries, to access developed markets.
The Minister highlighted that affordable and scalable medtech products can reduce costs and improve quality through economies of scale. Referring to startups present at the programme, he noted that many had secured CDSCO approvals and some were on the verge of receiving FDA approvals, enabling them to expand internationally.
The Minister stressed that innovation must address India’s day-to-day needs and ground-level imperatives. He underlined the importance of showcasing success stories and urged Startup India, the private sector and the media to encourage entrepreneurs, including those who may not succeed initially.
Stating that failure is not a stigma but a stepping stone to success, Shri Goyal cited the example of Abraham Lincoln, who faced repeated failures in education, business, law practice and elections before becoming President of the United States. He urged young innovators to persevere.
Shri Goyal referred to the Andhra Pradesh MedTech Zone (AMTZ) near Visakhapatnam and expressed interest in establishing a similar facility in North India, possibly in Rajasthan or Uttar Pradesh, or within NICDC (National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation) industrial projects with dedicated land for medical devices and co-working spaces for startups. He also suggested setting up tinkering labs in nearby schools to create a holistic ecosystem.
The Minister stated that over 200,000 startups are registered in India, with many more unregistered, and reiterated the goal of making India a reliable and trusted global partner.
He announced that three more National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs) are being established alongside the upgradation of seven existing NIPERs. A new National Institute of Design (NID) will be set up in East India, with states competing to provide the best proposal. He suggested that NID could assist startups in improving product design, visual appeal and overall quality, possibly through pro bono programmes.
Shri Goyal also highlighted that startups receive an 80% discount on IP-related fees to support genuine innovation while discouraging frivolous applications. He assured that the Ministry’s doors remain open 24×7, supported by a dedicated Startup India team.
Concluding his address, the Minister quoted the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s Independence Day message: “To the youth, bring forward your innovative ideas. I stand with you. I am ready to be your partner in this journey.”
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India, in collaboration with Pfizer, Department of Pharmaceuticals, and NITI Aayog, felicitated the winners of the Pfizer INDovation Program 2025, reinforcing DPIIT’s commitment to building a globally competitive, innovation-driven healthcare and MedTech ecosystem
Through this collaboration, 14 high-potential Indian healthtech startups have been awarded grants of ₹60 lakh each (over ₹8 crore in total) along with 18 months of structured incubation, clinical validation, mentorship, and real-world deployment support. The initiative reflects DPIIT’s ongoing efforts to enable strong public–private partnerships that help startups transition from innovation to impact, accelerating their journey from lab to market.
The selected startups are developing breakthrough solutions across priority healthcare areas including immunization, non-communicable diseases, brain health, oncology, and maternal & child health—sectors critical to strengthening India’s public health systems and improving healthcare access and affordability.
Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal urges Export Promotion Councils and Industry bodies to utilize FTAs to gain greater presence in world markets
Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal urges Export Promotion Councils and Industry bodies to utilize FTAs to gain greater presence in world markets
Union Commerce and Industry Minister Shri Piyush Goyal has urged exporters and industry bodies to take full advantage of the series of Free Trade Agreements signed with developed countries maximise job creation and boost exports of goods and services.
The minister met 35 Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and key Industry Associations representing India’s major export sectors. Industry leaders and association office bearers appreciated the government’s trade-promotion initiatives during their interaction with the minister.
Shri Goyal said the Modi government had signed Free Trade Agreements with developed countries to help India’s farmers, workers, professionals, artisans and MSMEs take advantage of the global market with preferential access. With these trade agreements, India’s traditional medicines and yoga will also get global opportunities, while the interest of India’s agriculture and dairy sectors have been protected.
“Industry must now intensify its efforts to penetrate new markets, upgrade quality and become more competitive to take maximum advantage of trade agreements. India has made its mark in international trade since the ancient era. Our trade deals will accelerate our Viksit Bharat mission and carry forward Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s mantra of ‘Vikas bhi, Virasat bhi’,” Shri Goyal said at a meeting with EPCs and industry bodies.
Industry representatives conveyed their deep gratitude to the Prime Minister and the Minister of Commerce & Industry for the decisive leadership that enabled the successful conclusion of recent trade agreements with the United Kingdom, European Union and the United States of America.
Particular appreciation was expressed for the elimination of the additional 25 % tariff on Indian imports to the United States, as terminated through the United States Executive Order dated 6 February 2026, which is expected to restore competitive market access for Indian exports. Industry noted that the United States is among India’s largest export destinations and that the tariff relief provides significant stability and renewed competitiveness to Indian exporters.
Associations representing sectors earlier impacted by the US tariff measures — including gems & jewellery, textiles and apparel, carpets, leather and footwear, marine products, handicrafts, engineering goods and chemicals — highlighted that the tariff rollback has restored business confidence and safeguarded employment in labour-intensive sectors. Key participating bodies included the Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO); Gem & Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC); Apparel Export Promotion Council (AEPC); Council for Leather Exports (CLE); Engineering Export Promotion Council of India (EEPC India); Basic Chemicals, Cosmetics & Dyes Export Promotion Council (CHEMEXCIL); Cotton Textiles Export Promotion Council (TEXPROCIL); Manmade and Technical Textiles Export Promotion Council (MATEXIL); other major textile EPCs; Carpet Export Promotion Council (CEPC); Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH); agricultural and allied bodies including the Seafood Exporters Association of India (SEAI); Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA); Shellac and Forest Products Export Promotion Council (SHEFEXCIL); Indian Oilseeds and Produce Export Promotion Council (IOPEPC); India SME Forum; Sourcing Consultants Association (BAA); and apex industry chambers including the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI), Associated Chambers of Commerce & Industry of India (ASSOCHAM), National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM) and PHD Chamber of Commerce and Industry (PHDCCI), along with several other leading sectoral associations.
The Ministry also made presentations on the recently concluded trade engagement with the United States, outlining market access opportunities, compliance frameworks and export expansion pathways. Industry welcomed the clarity provided and reaffirmed its commitment to scale exports in priority sectors.
Discussions also highlighted the progress under the Export Promotion Mission (EPM), the Government’s flagship framework to support exporters. Industry welcomed the Interventions already rolled out under the Mission, including enhanced access to trade financethrough Interest Subvention Support for export credit loans, Collateral Guarantee for Export Credit extended to MSMEs and targeted market access support. It was noted that additional measures relating to trade finance, export logistics, export compliances, branding and market diversification are being rolled out shortly, in a phased manner to further strengthen India’s export ecosystem.
The Minister reaffirmed the Government’s commitment to accelerate export growth, deepen global integration and leverage new trade agreements to position India as a trusted global supply partner.
Bombay Chamber post-budget webinar: Navigating India’s economic outlook amidst global uncertainty
Bombay Chamber post-budget webinar: Navigating India’s
economic outlook amidst global uncertainty
The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry organised a Post-Budget Analysis Webinar on 5 February 2026, bringing together economists, industry leaders, and policy experts to examine the Union Budget 2026–27 and its implications for India’s growth trajectory amid an increasingly complex global environment.

Delivering the welcome address, Rajiv Anand, on behalf of the Chamber, emphasised that the Union Budget is not merely an annual financial exercise but a strategic statement of national priorities. He noted that post-budget dialogues play a critical role in interpreting policy intent, assessing real-world impact, and enabling businesses to align their strategies with emerging economic priorities.
He highlighted key signals from the Budget, including the record capital expenditure allocation of ₹12.2 lakh crore to strengthen long-term productive capacity, continued emphasis on manufacturing and MSME growth, enhanced focus on connectivity and urban development, targeted policy reforms to support investment-led growth, and a significant defence allocation of approximately ₹7.8 lakh crore underscoring national security and indigenous capability building.
Anand underscored that while these measures present strong opportunities, they also raise important questions around execution, demand recovery, cost structures, exports, and credit availability. He reaffirmed the Bombay Chamber’s role as a trusted bridge between government and industry, committed to equipping its members with clarity, confidence, and actionable insights through knowledge-driven platforms.
The session was moderated by Dr. Sachchidanand Shukla, Chair, EPRD Committee, Bombay Chamber, and Group Chief Economist, L&T, and featured Navneet Munot, Director, Bombay Chamber, and MD & CEO, HDFC Asset Management Company; Madan Sabnavis, Chief Economist, Bank of Baroda; Rajan Raje, Director, Bombay Chamber, and Founder & CEO, NICHEM Solutions; Dipti Deshpande, Principal Economist, CRISIL; and Rajeshree Sabnavis, Director, Bombay Chamber, and Senior Advisor – Tax, GT Bharat LLP.
Setting the global context, Dr. Shukla observed that the world is entering a phase of heightened uncertainty driven by geopolitical shifts and changing economic assumptions. “We are witnessing a new global disorder, and the Union Budget must be viewed as part of a broader strategy to manage volatility while sustaining growth,” he said.
Providing a macroeconomic assessment, Dipti Deshpande noted that India’s fundamentals remain resilient despite global headwinds. “The macro house is in order, with sustainable growth, moderating inflation, and improved fiscal metrics. This budget extends India’s growth runway through continued capex and structural reforms,” she said.
Explaining fiscal and bond market dynamics, Madan Sabnavis addressed concerns around government borrowing. “The focus should be on net borrowing rather than headline numbers. Fiscal deficit control remains the key anchor, and post-budget market volatility was largely a short-term overreaction,” he said.
From a capital markets perspective, Navneet Munot advised investors to look beyond immediate market movements. “Budget day reactions are often misleading. India’s long-term growth story, supported by strong corporate balance sheets and domestic liquidity, remains firmly intact,” he said.
Addressing taxation and compliance, Rajshree Sabnavis highlighted steps taken to improve predictability and reduce compliance burden. “There is a clear move towards rationalisation, certainty, and lower compliance costs, although customs duty reform remains an area for further progress,” she said.
Focusing on MSMEs, Rajan Raje welcomed the shift from short-term relief to long-term capability building. “The Budget recognises that sustainable MSME growth requires upskilling, integration into formal supply chains, and innovative financing mechanisms,” he said.
The panel also discussed the outlook for the rupee, private sector capex revival, FDI flows, and the balance between public and private investment. Speakers broadly agreed that while the Budget remains capex-led, its success will depend on effective execution and stronger private sector participation.
Budget 2026–27: Record ₹12.2 Lakh Crore Infra Push and Major Boost for MSMEs, Manufacturing
Budget 2026–27: Record ₹12.2 Lakh Crore Infra Push and Major Boost for MSMEs, Manufacturing

Nirmala Sitharaman Outlines Three ‘Kartavya’ Priorities to Drive India’s Growth, Inclusion and Reform Agenda
In her ninth consecutive Union Budget 2026-27, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman delivered a Budget which placed a large emphasis on infrastructure, with the government raising public capital expenditure to ₹12.2 lakh crore for the upcoming fiscal year—an increase of nearly 9 % from the previous year’s allocation and a record high aimed at strengthening national infrastructure across roads, railways, ports, metro projects and logistics networks.
In addition to the infrastructure thrust, the Budget included measures to support industry, including the launch of a ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund to enhance capital access for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, a ₹4,000 crore top-up to the Self-Reliant India Fund, and expanded credit and liquidity mechanisms for smaller businesses. Further manufacturing support was outlined through initiatives such as the expanded Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme with a ₹40,000 crore outlay and continued emphasis on strategic sectors like semiconductors, biopharma, textiles and container manufacturing.
The Budget was anchored around three key “Kartavya” priorities outlined by the Finance Minister—accelerating and sustaining economic growth, fulfilling aspirations and building capacity, and ensuring inclusive access to growth. These priorities were reflected across announcements spanning infrastructure expansion, support for MSMEs and strategic manufacturing sectors, continued reforms to simplify processes and improve efficiency, and people-centric measures aimed at strengthening education, skills and access to essential services.
Reactions from Bombay Chamber Leaders:
Rajiv Anand, President, Bombay Chamber and Managing Director & CEO IndusInd Bank Limited:
“The Union Budget 2026 maintains continuity by focusing on capital expenditure, with a moderate increase in budgetary spending, while keeping the tax code largely unchanged, thereby providing policy stability. Fiscal consolidation anchored in a debt-to-GDP target offers flexibility to pursue countercyclical support, if needed, amid a challenging external environment. A comprehensive review of banking system regulations, development of transport and logistics infrastructure, capital and liquidity support for MSMEs, budgetary support for strategic sectors in manufacturing and services, and initiatives to develop skills will help enhance factor productivity and drive long-term growth.”
Sudhanshu Vats, Sr Vice President, Bombay Chamber and Managing Director, Pidilite Industries Ltd.
The Union Budget 2026–27 reinforces strong confidence in India’s growth trajectory, anchored in manufacturing, infrastructure and consumption. The continued focus on domestic manufacturing across chemicals, electronics and capital goods strengthens supply-chain resilience and supports India’s ambition to be a globally competitive production hub. With public capex at ₹12.2 lakh crore, demand across housing, construction and infrastructure-linked industries will remain robust. It will also dial up tourism and employers . The emphasis on digital infrastructure, Automation & AI-led Customs reforms and trade facilitation will enhance ease of doing business and global integration. Overall, the Budget provides the confidence to invest, innovate and scale alongside India’s long-term economic vision. Onwards to a Viksit Bharat 2047.
Nilesh Shah, Past President, Bombay Chamber and Group President & MD, Kotak Mahindra AMC:
This budget has proposed a capital expenditure of Rs 12.10 lac crore which is more than the net market borrowing of Rs 11.70 lac crore. I pray that a path is laid where one day capital expenditure will be more than the total borrowing including small savings.
Sudhir Kapadia, Past President Bombay Chamber and Senior Advisor, EY
The reform process has continued steadily into 2026, building strongly on the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision. The TCS-related announcements appear globally competitive and send a clear signal of long-term policy intent—possibly the first taxation measure framed with a horizon extending up to 2047. Portfolio investment prospects also look promising. The proposed measures, including support for data centres, are particularly significant given that Indian data centre companies are expected to attract investments of nearly USD 11 billion in the sector.
Key Highlights of the Budget 2026-27
Fiscal and Expenditure Highlights
• Record capital expenditure allocation: ₹12.2 lakh crore for FY 2026–27, up from ₹11.2 lakh crore in the previous year—continuing a strong infrastructure push.
• Defence budget increase: Allocation expanded significantly with around ₹7.8 lakh crore earmarked for defence.
Infrastructure and Connectivity
• Seven new high-speed rail corridors announced connecting major cities such as Mumbai–Pune, Pune–Hyderabad, and Hyderabad–Bengaluru.
• Dedicated freight corridors and rare earth mineral corridors planned in mineral-rich states to support strategic manufacturing and logistics.
• Expansion of 20 national waterways and coastal/service logistics enhancements.
• Introduction of a Seaplane VGF (Viability Gap Funding) Scheme to improve regional connectivity and tourism access.
• Focus on developing Tier II and Tier III temple towns through improved infrastructure and visitor amenities.
Industry, Manufacturing & Investment
• India Semiconductor Mission 2.0 launched with a ₹40,000 crore outlay to boost chip production and tech supply chains.
• New support schemes for Biopharma, textiles, chemicals and container manufacturing to strengthen domestic value chains.
• A ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund to deepen access to capital for MSMEs.
Tax Reforms & Compliance
• Continued simplification of the tax system with an updated Income Tax Act coming into effect from 1 April 2026.
• Reduced TCS (Tax Collected at Source) on overseas travel, education, and medical remittances to 2% under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme.
• Additional procedural ease measures, extended return filing timelines and foreign asset disclosure relief for small taxpayers.
• Customs duty on goods imported for personal use reduced from 20% to 10%.
• Revised rules to enhance baggage allowance for travellers and simplify temporary carriage of goods.
• TCS on overseas tour packages rationalised from 5%/20% to a flat 2%.
• TCS under LRS for education and medical purposes reduced from 5% to 2%.
Social Welfare & Human Capital
• Proposals for one girls’ hostel in every district to improve educational access.
• Expansion of healthcare facilities, multiple AYUSH institutes, and training programmes for allied health professionals.
• Focus on tourism, education-to-employment frameworks, and digital media content labs in schools and colleges.
• Medical tourism to be strengthened through 5 regional hubs.
• National Institute of Hospitality to strengthen training and workforce readiness in the hospitality sector.
• Training of 10,000 tourist guides across 20 sites through a 12-week programme (in partnership with IIMs).
• Creation of a National Destination Digital Knowledge Grid to digitally map and strengthen destination planning and promotion.
• Development of 15 archaeological sites to enhance heritage and cultural tourism.
• Development of Buddhist tourism sites across 6 Northeast states.
• Promotion of trekking and hiking through sustainable trail development.
• Global Big Cat Summit 2026 to support wildlife conservation and eco-tourism.
Macroeconomic Targets
• Fiscal deficit targeted at ~4.3% of GDP, indicating continued fiscal discipline alongside expanded public spending.
India–EU Free Trade Agreement Concluded: A Strategic Breakthrough in India’s Global Trade Engagement
India–EU Free Trade Agreement Concluded: A Strategic Breakthrough in India’s Global Trade Engagement

Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi and European Commission President H.E Ms. Ursula von der Leyen, today jointly announced the conclusion of the India–European Union Free Trade Agreement (India–EU FTA) at the 16th India–EU Summit, held during the visit of the European leaders to India. This announcement marks a historic milestone in India–EU economic relations and trade engagement with key global partners.
The conclusion of this FTA positions India and the European Union as trusted partners committed to open markets, predictability, and inclusive growth. The FTA comes after intense negotiations since the re-launch of negotiations in 2022. The announcement of the FTA today marks the culmination of years of sustained dialogue and cooperation, between India and the EU, demonstrating the political will and shared vision to deliver a balanced, modern, and rules-based economic and trade partnership.
The European Union is India’s one of the largest trading partner, with bilateral trade in goods and services growing steadily over the years. In 2024–25, India’s bilateral trade in goods with the EU stood at INR 11.5 Lakh Crore (USD 136.54 billion) with exports worth INR 6.4 Lakh Crore (USD 75.85 billion) and imports amounting to INR 5.1 Lakh Crore (USD 60.68 billion). India-EU trade in services reached INR 7.2 Lakh Crore (USD 83.10 billion) in 2024.
India and EU are 4th and 2nd largest economies, comprising 25% of Global GDP and account for one third of global trade. Integration of the two large diverse and complementary economies will create unprecedented trade and investment opportunities.
Union Minister for Commerce and Industry, Shri Piyush Goyal, lauded the strategic vision and steadfast leadership of Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi. He stated:
“The conclusion of the India–European Union Free Trade Agreement represents a defining achievement in India’s economic engagement and global outlook. This supports India’s approach to secure trusted, mutually beneficial and balanced partnerships.
Beyond a conventional trade deal, it represents a comprehensive partnership with strategic dimensions and is one of the most consequential FTA. India has secured unprecedented market access for more than 99% of Indian exports by trade value to the EU that also bolsters the ‘Make in India’ initiative. Beyond goods, it unlocks high-value commitments in services complemented by a comprehensive mobility framework enabling seamless movement of skilled Indian professionals. India, powered by a young and dynamic workforce and one of the fastest-growing major economies, stands poised to leverage this FTA to create jobs, spur innovation, unlock opportunities across sectors, and enhance its competitiveness on the global stage.”
The India-EU trade pact covers conventional areas such as trade in goods, services, trade remedies, rules of origin, customs and trade facilitation, as well as emerging areas such as SMEs and digital trade, amongst others. The India–EU FTA gives a decisive boost to its labour-intensive sectors such as textiles, apparel, leather, footwear, marine products, gems and jewellery, handicrafts, engineering goods, and automobiles bringing down tariffs up to 10% on almost 33 bn USD of exports to zero on entry into force of the Agreement. Beyond enhancing competitiveness, it empowers workers, artisans, women, youth, and MSMEs, while integrating Indian businesses more deeply into global value chains and reinforcing India’s role as a key player and supplier in global trade.
On automobiles, calibrated and carefully crafted quota based auto liberalisation package will not only allow EU auto makers to introduce their models in India in higher price bands but also open the possibilities for Make in India and exports from India in future. Indian consumers to benefit from high tech products and greater competition. The reciprocal market access in EU market will also open up opportunities for India made automobiles to access EU market. India’s agricultural and processed food sectors are poised for a transformative boost under the India–EU FTA, creating a level playing field for Indian farmers and agrarian enterprises. Key commodities such as tea, coffee, spices, fresh fruits and vegetables, and processed foods will gain enhanced competitiveness, strengthening rural livelihoods, promoting inclusive growth, and reinforcing India’s position as a trusted global supplier. India has prudently safeguarded sensitive sectors, including dairy, cereals, poultry, soymeal, certain fruits and vegetables, balancing export growth with domestic priorities.
Beyond tariff liberalisation, the FTA provides measures to tackle non-tariff barriers through strengthened regulatory cooperation, greater transparency, and streamlined customs, Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) procedures, and Technical Barriers to Trade disciplines. Through CBAM provisions, commitments have been secured including a forward-looking most-favoured nation assurance extending flexibilities if any granted to third countries under the regulation, enhanced technical cooperation on recognition of carbon prices, recognition of verifiers, as well as financial assistance and targeted support to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and comply with emerging carbon requirements.
Services being dominant and faster-growing part of both economies will trade more in future. Certainty of market access, non-discriminatory treatment, focus on digitally delivered services, ease of mobility will provide boost to India’s services exports. The FTA secures expanded and commercially significant commitments from the EU across key sectors of Indian strength, including IT and IT-enabled services, professional services, education, financial services, tourism, construction, and other business sectors.
India’s predictable access to EU’s 144 subsectors (which includes IT/ITeS, Professional Services, Other Business Services and Education Services) will provide boost to Indian service providers and enable them to provide competitive world class Indian services to EU’s consumers while EU’s access to 102 subsectors offered by India will bring in high tech services, investment into India from EU resulting in a mutually beneficial arrangement.
On mobility, the India-EU FTA provides a facilitative and predictable framework for business mobility covering short-term, temporary and business travel in both directions. These enable professionals to travel between the two economies to provide services under different scenarios. EU and India is providing mobility commitments to each other for Intra-Corporate Transferees (ICT) and Business Visitors, along with entry and working rights for dependents and family members of ICTs. The EU has also offered commitments in 37 sectors/sub-sectors for Contractual Service Suppliers (CSS) and 17 sectors/sub-sectors for Independent Professionals (IP), many of which are sectors of interest to India, including Professional Services, Computer and related Services, Research and Development Services, and Education Services.
India also secured a framework to constructively engage on Social Security Agreements over a five-year horizon, together with framework supporting student mobility and post-study work opportunities. Additionally, India has also secured access for practitioners of Indian Traditional Medicine to work under home title in EU Member States where traditional medical practices are not regulated.
In financial services, the FTA promotes cooperation to advance innovation and secure cross-border electronic payments, while providing India with enhanced market access across several major EU member states. These provisions are expected to deepen financial integration and support the growth of financial services trade. These commitments not only unlock high-value employment opportunities but also reinforce India’s position as a global hub for talent, innovation, and sustainable economic growth.
The FTA reinforces intellectual property protections provided under TRIPS relating to copyright, trademarks, designs, trade secrets, plant varieties, enforcement of IPRs, affirms Doha Declaration and recognises the importance of digital libraries, specifically the Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) project initiated by India. The FTA is expected to facilitate cooperation in critical areas like Artificial Intelligence, clean technologies, and semiconductors, supporting India’s technological advancement.
The FTA is expected to substantially scale up trade, enhance export competitiveness, and integrate Indian businesses more deeply into the European and global value chains. The India–EU FTA marks a new chapter in bilateral economic engagement, strengthening trade, and strategic cooperation between India and the 27-member EU bloc. Cognizant of multifarious objectives placed on trade, dynamic nature of trade, fast evolving technologies and increasing regulatory complexities, the Agreement embeds multiple review, consultation and response mechanisms to deal with new, sudden challenges which emerge in future. The Agreement relies on strong stewardship and trust to deliver gains for both sides.
EU becomes India’s 22nd FTA partner. The Government since 2014 has signed trade deals with Mauritius, UAE, UK, EFTA, Oman and Australia, and announced trade deal with New Zealand. In 2025, India signed trade deal with Oman and UK and announced conclusion of trade deal with NZ. The India-EU trade deal, along with India’s FTA with the UK and the EFTA effectively opens up the entire European market for Indian businesses, exporters and entrepreneurs.
Beyond boosting commerce, it reinforces shared values, fosters innovation, and creates opportunities across sectors and stakeholders from MSMEs, women and skilled professionals to farmers and exporters. Aligned with India’s vision of “Viksit Bharat 2047,” the FTA positions India as a dynamic, trusted, and forward-looking partner on the global stage, setting the foundation for inclusive, resilient, and future-ready growth for both regions.
Source: Press Information Bureau, Government of India.
Chamber Note
As India strengthens its global trade partnerships, the Chamber continues to convene industry leaders and policymakers to deliberate on opportunities in shipbuilding and maritime innovation. These themes will be explored at the upcoming International Conference on Shipbuilding Global Harit Nauka Summit: Trust, Collaborate, Impact
Banking Conclave 3.0 Explores the Future of Banking Amidst Digital Transformation, Consolidation, and Regulatory Change
Banking Conclave 3.0 Explores the Future of Banking Amidst Digital Transformation, Consolidation, and Regulatory Change
January 21, 2026
The Banking Conclave 3.0: Future of Banking, organised by the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, brought together senior bankers, policymakers, fintech leaders, and financial services experts to deliberate on how India’s banking system must evolve to remain resilient, inclusive, and future-ready. Held at the ITC Grand Central Hotel, Mumbai, the conclave examined the structural, technological, and regulatory shifts shaping the next decade of banking.

In his Welcome Address, Sandeep Khosla, Director General, Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, highlighted the Chamber’s long-standing role as a neutral facilitator and an effective bridge between industry and government, fostering constructive dialogue on policy, regulation, and economic priorities. He noted that as the banking and financial services sector navigates rapid technological change, consolidation, and evolving regulatory expectations, such platforms play a critical role in aligning industry perspectives with public policy objectives. Emphasising the Chamber’s commitment to convening thought leadership and enabling informed discourse, he underscored the importance of collaborative engagement to ensure that India’s banking system remains resilient, inclusive, and future-ready.

Delivering the Keynote Address, Rajiv Anand, President, Bombay Chamber and Managing Director & CEO, IndusInd Bank, offered a compelling perspective on the structural transformation underway in global and Indian banking. He observed that the industry is moving beyond a phase where incremental improvements, isolated digital initiatives, or marginal efficiency gains are sufficient to remain relevant. Instead, banking is being reshaped by deeper shifts in how value is created, how trust is earned, and how institutions engage with society.
Anand noted that while banks have traditionally been defined by balance sheets, capital adequacy, branch networks, and regulatory classifications, these dimensions alone are no longer adequate in a world reorganised by technology, data, and changing customer expectations. He emphasised that India’s unique advantage lies in its digital public infrastructure, which has fundamentally altered how citizens participate in the economy. Platforms such as Aadhaar, UPI, Account Aggregator, and the JAM trinity (Jan Dhan–Aadhaar–Mobile) have not merely digitised financial services, but have embedded finance into everyday life, lowered transaction friction, expanded access, and strengthened trust at population scale.
Highlighting India as one of the few countries to have built such infrastructure deliberately and at scale in a short period of time, Anand stressed that technology alone does not transform societies—it only enables transformation. He called upon banks to view themselves not merely as providers of financial products, but as stewards of economic participation, supporting mobility, productivity, and long-term growth. He pointed to the rapid formalisation of enterprises, the digitisation of financial behaviour, the rise of first-generation entrepreneurs, and a young, mobile-first population as defining features of India’s next growth phase.
At the same time, Anand acknowledged that despite progress, credit penetration remains modest, large segments of MSMEs remain underserved, and many households remain vulnerable to income shocks and uncertainty. He underscored the need to rethink how capital is allocated, how risk is assessed, and how customer journeys are designed. He cautioned that merely replicating old banking models on new digital platforms will not deliver meaningful transformation.
He further noted that banking institutions have historically been organised around products—deposits, loans, insurance, and investments—whereas customers experience finance through life goals such as building livelihoods, growing businesses, educating children, caring for families, and preparing for the future. Anand stressed that banks that continue to prioritise internal product structures over customer outcomes risk losing relevance in an increasingly aspiration-driven economy.
Addressing the role of emerging technologies, Anand observed that artificial intelligence represents a fundamental shift—not simply in automation, but in how decisions are made, patterns are detected, risks are assessed, and systems are managed. He emphasised that the future of banking will belong to institutions that combine technological capability with ethical foundations, regulatory responsibility, and a long-term partnership approach to customers.

The first panel discussion, “Changing Face of Banking,” examined how technology, data analytics, and new-age players are redefining the banking landscape. Moderated by Yashraj Erande, India Leader – Financial Services and Global Leader – Fintech, Boston Consulting Group, the panel featured Rajiv Anand, Anirban Mukherjee, CEO, PayU, and Sachin Seth, Regional Managing Director, India and South Asia, CRIF. The discussion focused on the convergence of banks and fintechs, the growing role of alternative data in credit assessment, and the shift towards embedded finance and platform-based banking models.

A key highlight of the conclave was the Fireside Discussion on “The Bank of 2030,” featuring Shri Rajeshwar Rao, Former Deputy Governor, Reserve Bank of India, in conversation with Latha Venkatesh, Executive Editor, CNBC-TV18. The discussion focused on how banks must navigate a rapidly evolving financial ecosystem marked by digital disruption, changing liability structures, the growing role of non-bank players, and increasing interlinkages across the financial system. Shri Rao emphasised the need to balance innovation with stability, underscoring the importance of sound governance, robust risk management, adequate capital and liquidity, and a regulatory framework that remains flexible while safeguarding systemic trust. The conversation offered a forward-looking regulatory perspective on consolidation, competition, and resilience in a technology-driven banking landscape.

The second panel, “Consolidation and Regulation in Banking,” moderated by Abizer Diwanji, Founder, NeoStrat Advisors LLP, featured Prashant Kumar, MD & CEO, YES BANK, Neeraj Makin, Senior Executive Vice President & Group Head – Strategy, Analytics & Venture Capital, Emirates NBD, and Anshul Agarwal, Managing Director and Head – Financial Institutions Group (FIG), Avendus Capital. The panel examined consolidation as a strategic response to scale, competitiveness, and regulatory demands, while underscoring the importance of governance, capital strength, and institutional integration.
The conclave concluded with a Vote of Thanks by Sandeep Khosla, followed by networking. Banking Conclave 3.0 reaffirmed the Bombay Chamber’s role as a convenor of meaningful dialogue between industry and policymakers, and offered a forward-looking perspective on how Indian banking must evolve to serve a dynamic, diverse, and rapidly transforming economy.
Bombay Chamber organises conclave on Reimagining MSME growth: Opportunities in a smart finance era
Bombay Chamber organises conclave on Reimagining MSME growth: Opportunities in a smart finance era
Bombay Chamber recently organised a MSME Conclave that explored innovative financing, trade finance, factoring, and working capital solutions designed to fuel MSME growth in the smart finance era.
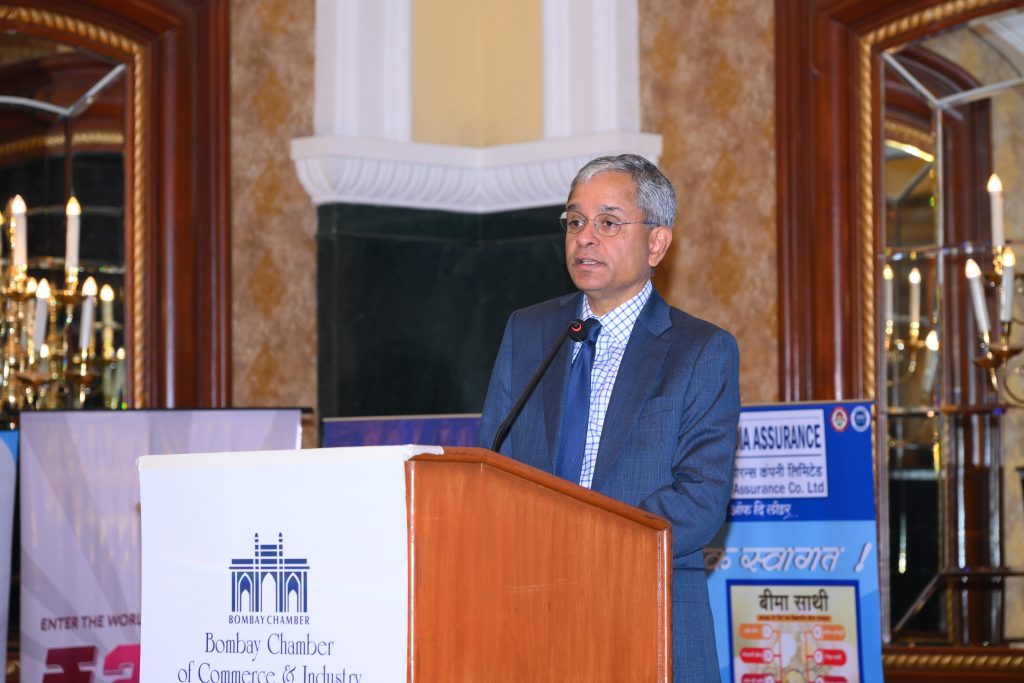

In his welcome address, Rajiv Anand, President, Bombay Chamber & MD & CEO, IndusInd Bank said, “This conclave brings together enterprise leaders, policymakers, financial institutions, and global trade stakeholders to deliberate on the key enablers of MSME advancement. I am confident this conclave will empower MSMEs with the knowledge, resources, and support needed to address challenges in growth, talent management, financing, and internationalisation, enabling them to drive sustainable development and contribute meaningfully to the nation’s economy.”
.
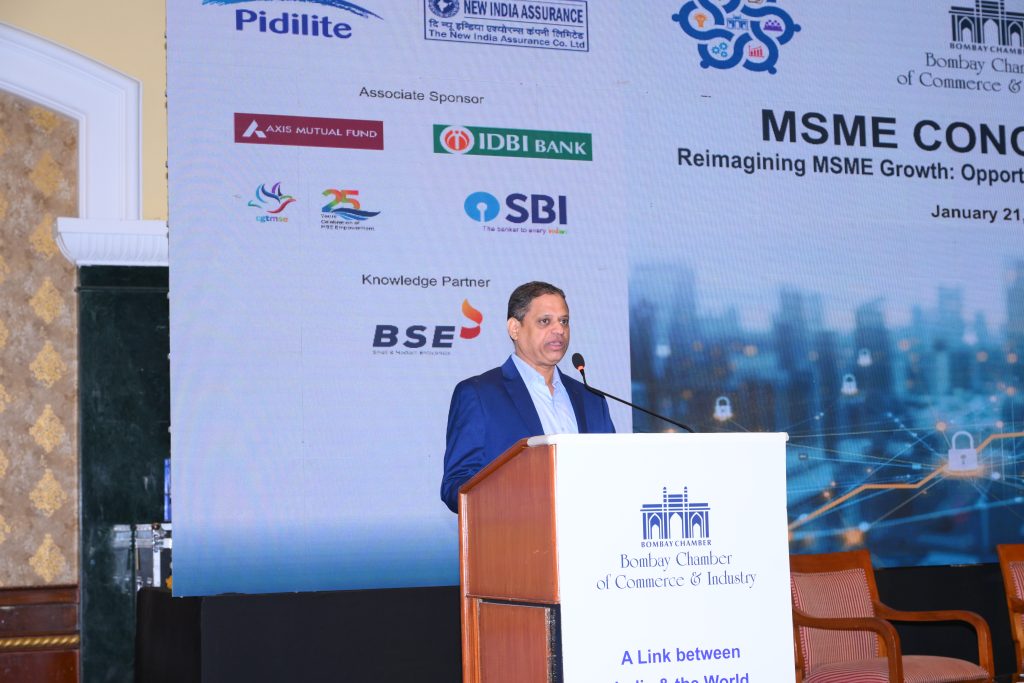

Setting the theme for the conclave, R Srinivasan, Co-Chairperson – MSME Forum, Bombay Chamber & Director, AIRA Consulting, said that at a time when global supply chains are being realigned and digital transformation is reshaping business models, Indian MSMEs are at a critical inflection point. “With access to smart, scalable, and innovative financing solutions, MSMEs have a unique opportunity to enhance competitiveness and integrate more deeply into global value chains,” he added.

In his keynote address, Rajesh Kumar, Deputy Managing Director (Retail – Agri & SME), State Bank of India, stated, “Inclusion of all MSMEs must be intentional. There should be awareness drives for digital offerings from the government, data privacy and ethical use of technology. Technology should not replace human capital; it should co-operate with the existing working
structure.”

This was followed by a Fireside Chat on The Implications of the New Labour Codes on MSMEs covering practical insights into their implications for MSMEs, including compliance, workforce management, and operational efficiency. R. Srinivasan moderated the session with Lancy D’Souza, Advocate & Legal Advisor, Bombay Chamber as the speaker.

The next session was on Country Spotlight: Trade Corridors for Indian MSMEs, where Honourable Consul Generals and Trade Commissioners of Argentina, Finland, Flanders and Alberta Canada shared first-hand perspectives on global business and trade opportunities including sourcing, technology partnerships, market access and export facilitation. H.E. Erik af Hällström, Consul General, Consulate General of Finland, Mumbai; Keith Bradley, Chief Operating Officer Invest Alberta and the Government of Alberta, Canada; Eva Verstraelen, Trade & Investment Commissioner for Flanders (FIT) in Mumbai and Maria Silvina Costa, Head of Economic and Trade Section, Consulate General & Trade Centre of the Argentine Republic in Mumbai made the presentations.

A panel discussion on “Powering India’s Growth Cycle through MSME IPOs,” aimed to familiarise enterprises with the IPO process and highlight how public markets can support long-term expansion. The panelists were Riddhesh Shah, Deputy Vice President, BSE SME & Startups, BSE; Kamal Dharewa, Founder, Ashwath Capital | Capital Markets & SME IPO Expert; Subham Chatterjee, Associate Partner, ALMT Legal and Ajaya Sharma, Senior Vice President- Capital Market Communication Group, Adfactors PR. The panel was moderated by Ajay Thakur, CEO & Managing Partner, TGI SME Capital Advisors LLP.
AYUSH exports climb 6.11% to USD 688.89 Million in 2024–25 amid export facilitation measures and trade agreement inclusion
AYUSH exports climb 6.11% to USD 688.89 Million in 2024–25 amid export facilitation measures and trade agreement inclusion
The Ayush Export Promotion Council (AYUSHEXCIL) observed its 4th Establishment Anniversary today in New Delhi in India’s efforts to promote exports of traditional systems of medicine and wellness products.
Since its formation, AYUSHEXCIL has undertaken several initiatives focused on capacity building of exporters, facilitation of export procedures and regulatory compliance, and the organisation of B2B meetings, international exhibitions, seminars, and outreach programmes in key overseas markets.
Exports of AYUSH and herbal products have registered a growth of 6.11 per cent, increasing from USD 649.2 million in 2023–24 to USD 688.89 million in 2024–25. Following the establishment of AYUSHEXCIL, this growth has accelerated, reflecting enhanced global outreach and rising international demand for India’s traditional medicine and herbal products.
India’s traditional medicine systems (AYUSH) have also received formal recognition in bilateral trade agreements, including the India–Oman CEPA and the India–New Zealand FTA, with dedicated annexes on health-related services and traditional medicine. AYUSHEXCIL has been entrusted with anchoring the Ayush Quality Mark programme of the Ministry of Ayush, launched by the Hon’ble Prime Minister during the 2nd WHO Summit on Traditional Medicine (17–19 December 2025), marking a key milestone in strengthening quality assurance and global recognition of AYUSH products.
As AYUSHEXCIL enters its fifth year, the Council aims to further strengthen international cooperation, leverage opportunities under Free Trade Agreements, promote quality and certification frameworks, and enhance global acceptance of India’s traditional systems of medicine.
The anniversary underscores India’s growing leadership in the global AYUSH and wellness economy, aligned with the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India.
AYUSHEXCIL was registered as a Section 8 company with the Registrar of Companies, New Delhi, on 4 January 2022, and was formally launched by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi during the Global AYUSH Investment and Innovation Summit held in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, on 20 April 2022. Subsequently, the Council was notified by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) on 31 July 2023 as the nodal Export Promotion Council for the AYUSH sector.
The Council functions in consultation with the Ministry of Ayush, with support from the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, to oversee exports of products and services related to Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-Rigpa, Homeopathy, and other Indian traditional healthcare systems.
Bombay Chamber submits Pre-Budget Memorandum on Direct Tax for FY 2026–27
Bombay Chamber submits Pre-Budget Memorandum on Direct Tax for FY 2026–27
Mumbai: The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry, through its Direct Tax Committee, has submitted its Pre-Budget Memorandum on Direct Tax for FY 2026–27.
The memorandum, based on member inputs, is divided into two parts:
Part A – Issues requiring legislative amendments
Part B – Non-legislative issues addressable by CBDT through Rules, Notifications, or Circulars
The Chamber welcomed the Government’s landmark Income-tax Act, 2025, which will replace the Income-tax Act, 1961 from April 01, 2026. The new law simplifies tax provisions, removes redundancies, and presents the statute in clear, accessible language while retaining the core policy framework.
The Chamber noted that the upcoming Budget offers an opportunity to refine the new Act before implementation, with measures to reduce litigation and ease compliance.
Key recommendations aim to:
- Strengthen India’s private investment ecosystem
- Provide tax certainty
- Address procedural challenges
- Minimise litigation
- Enhance ease of doing business
These proposals, aligned with the Government’s policy of moderate progressive tax rates and minimal incentives, are positioned as tax enablers to support India’s vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Don’t resist the AI wave, be a surfer and ride it, says Arundhati Bhattacharya at Bombay Chamber’s 190th Foundation Day
Don’t resist the AI wave, be a surfer and ride it, says Arundhati Bhattacharya at
Bombay Chamber’s 190th Foundation Day
Mumbai: Leverage artificial intelligence and technology as enablers, rather than fear them, was central to the message delivered by Arundhati Bhattacharya, President and Chief Executive Officer of Salesforce South Asia and former Chairperson of the State Bank of India, at the Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry’s 190th Foundation Day on December 17, 2025, in Mumbai.
“AI will change the way we work. It is a change here to stay, not to be resisted. If you resist, it will hit you like a tsunami. Resisting it will disempower you. Leaning in will make you far more powerful than otherwise. Ride AI like a surfer,” Bhattacharya said, addressing an audience comprising business leaders, policymakers, diplomats, and members of the wider corporate community.
Welcoming the audience, Rajiv Anand, President of the Chamber and MD & CEO of IndusInd Bank, reflected on the Chamber’s journey since 1836 and its enduring role in shaping India’s economic and commercial landscape. Anand emphasised that the Foundation Day was not only a commemoration of the Chamber’s past but also a reaffirmation of its commitment to progress and transformation.
He noted that the Chamber’s membership today reflects the breadth of India’s enterprise ecosystem, ranging from some of the country’s largest corporates to a dynamic small and medium enterprise sector that now accounts for two-thirds of its base. “This diversity,” he said, “has been central to the Chamber’s ability to adapt and evolve over nearly two centuries.”
Anand also elaborated on how the Chamber reinforced its role as a trusted bridge between government and industry through an active committee structure, thought leadership initiatives, and effective dispute resolution. Guided by the theme Shaping the Future: Innovation, Inclusion, Impact, its engagements covered priority areas including AI and responsible innovation, arbitration, labour reforms, DEI, MSME development, capital markets, sustainability, agriculture, and infrastructure. The Chamber also strengthened its international footprint through overseas delegations, including India’s first business delegation to Cyprus, while continuing to develop forward-looking knowledge initiatives such as the CSR Year Book and the upcoming CEO’s AI Playbook.
“Together, these initiatives highlight the Chamber’s commitment to progressive business practices, enterprise development and reinforcing Mumbai’s position as a hub of economic leadership, supported by the continued partnership of sponsors and collaborators,” said Anand.
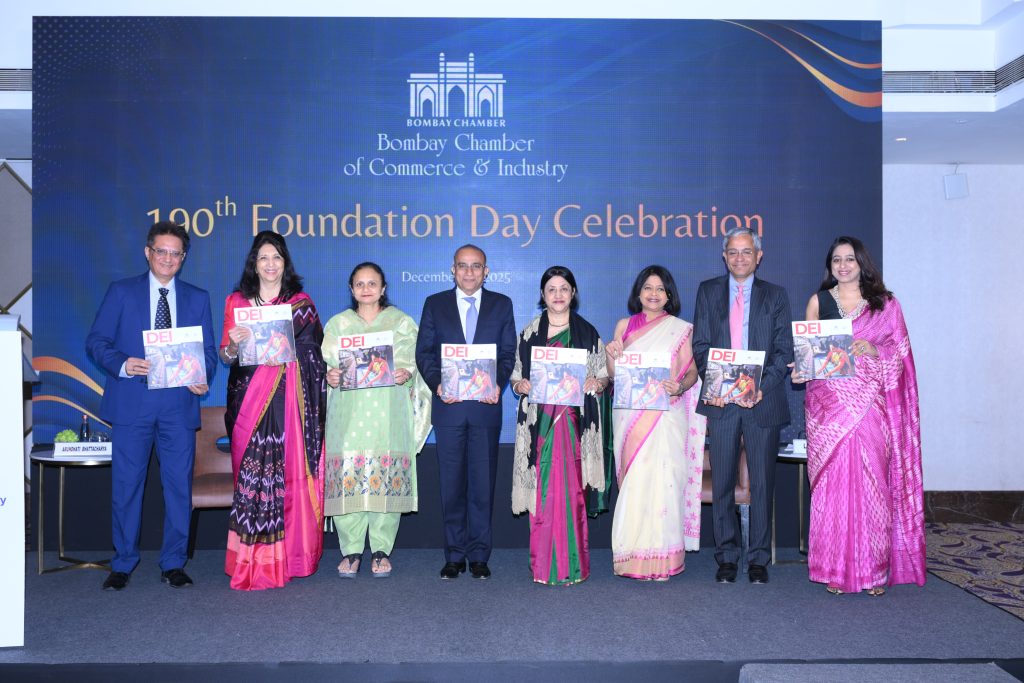

The Foundation Day also saw the unveiling of a book capturing DEI journeys authored by the winners of the third edition of the Bombay Chamber DEI Forum & Awards, held in June. Building on the momentum of the Awards, the initiative seeks to advance DEI conversations by presenting these journeys as practical and inspirational case studies for industry. The book titled DEI Dynamics in India Inc 2025 was unveiled in the presence of Arundhati Bhattacharya, Rajiv Anand, Latha Venkatesh, Executive Editor, CNBC TV18; Sudhanshu Vats, Senior Vice President, Bombay Chamber and Managing Director, Pidilite Industries Ltd.; Meenakshi Priyam, Chair, DE&I Committee, Bombay Chamber and Senior Vice President & Head – Human Resources (Automotive Division), Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.; Pinky Mehta, immediate Past President, Bombay Chamber and CFO, Aditya Birla Capital; Dr Indu Shahani, Founding President & Chancellor, Atlas Skilltech University; and Sandeep Khosla, Director General, Bombay Chamber, reaffirming the Chamber’s commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion as a cornerstone of responsible and future-ready business.
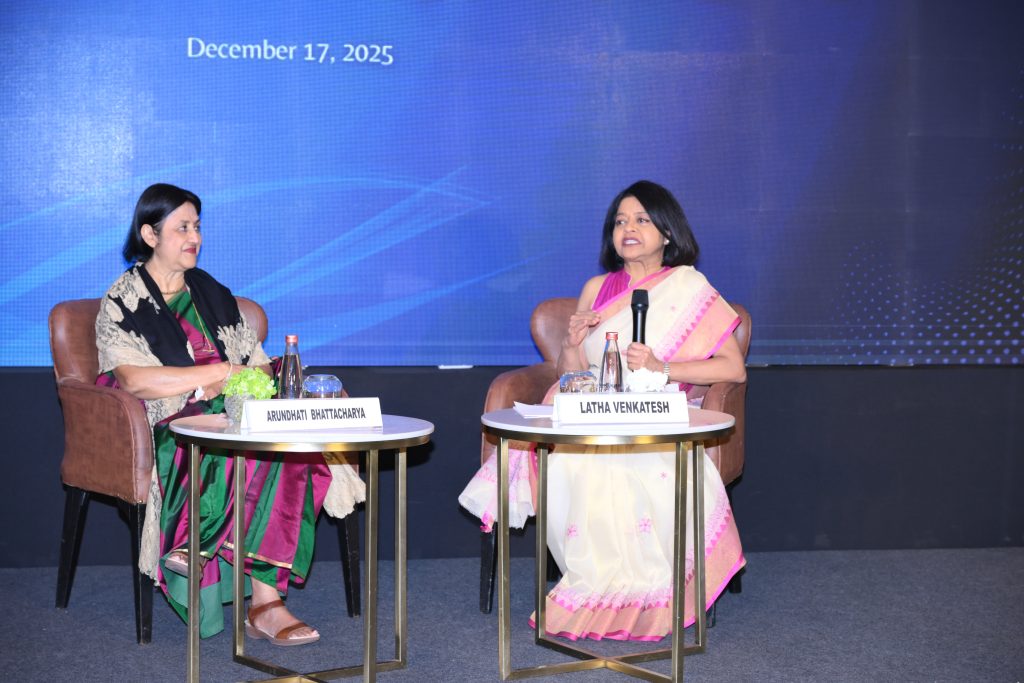

This was followed by a highly illuminating fireside chat that seamlessly blended personal experience with visionary thinking. Bhattacharya, a pioneering leader who has transformed banking and now leads Salesforce South Asia, shared a compelling perspective on technological transformation, with a particular focus on artificial intelligence and its implications for India’s economic landscape. Moderated by Latha Venkatesh, the conversation explored the intersections of technology, banking, and societal progress, anchored in a clear message, “Technological change is not something to fear—it is something to engage with thoughtfully and strategically.”
Addressing concerns around job loss, Bhattacharya reframed the debate and noted, “This is not a question of jobs going away, but of jobs changing.” While acknowledging that transition periods are always painful,” she emphasised the importance of preparedness, adding “What will differentiate people in the future is multidisciplinary capability, experience, and human judgement.” AI, she observed, enhances productivity by enabling faster, more informed decision-making. “Today, AI can point out discrepancies instantly,” she said, citing examples such as loan processing timelines shrinking from two days to thirty minutes. For MSMEs, she noted, “AI can pull data from multiple sources, not just historical financial statements, to enable better and faster access to credit.” In this sense, she stressed that AI will not take away opportunities; it will lead to a burgeoning of opportunities.
Reflecting on the banking sector, Bhattacharya remarked that liquidity is not leaving the system—it is flowing differently because behaviour has changed. This, she argued, requires banks to adapt, with a far deeper understanding of capital markets than ever before.

On the question of public sector banks, Bhattacharya observed that PSBs are delivering with one hand tied behind their back. She underscored that there is no lack of merit or talent, but highlighted the challenges of operating under multiple regulators and diffused priorities. “Privatisation is not the answer,” she said, adding, “What we need is clarity on what we want to achieve, the milestones we want to reach, and the removal of anything that stops institutions from getting there.”
The discussion concluded with a forward-looking call to action – India has the hunger to build, she noted, but we need the right push. Capital, capability, and mindset will be critical, and in an era defined by rapid technological change, she concluded, every organisation must become a learning organisation.
In his vote of thanks, Sudhanshu Vats, reflected on the key themes of the discussion and India’s evolving opportunity landscape. Acknowledging Bhattacharya’s session, he noted how digital adoption and artificial intelligence can help level the playing field, particularly for MSMEs. He also observed that technology is reshaping economic narratives, offering pathways that extend beyond traditional global comparisons.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin