Blog
Top Stories
Bombay Chamber and FTI Consulting organises Generative AI Session
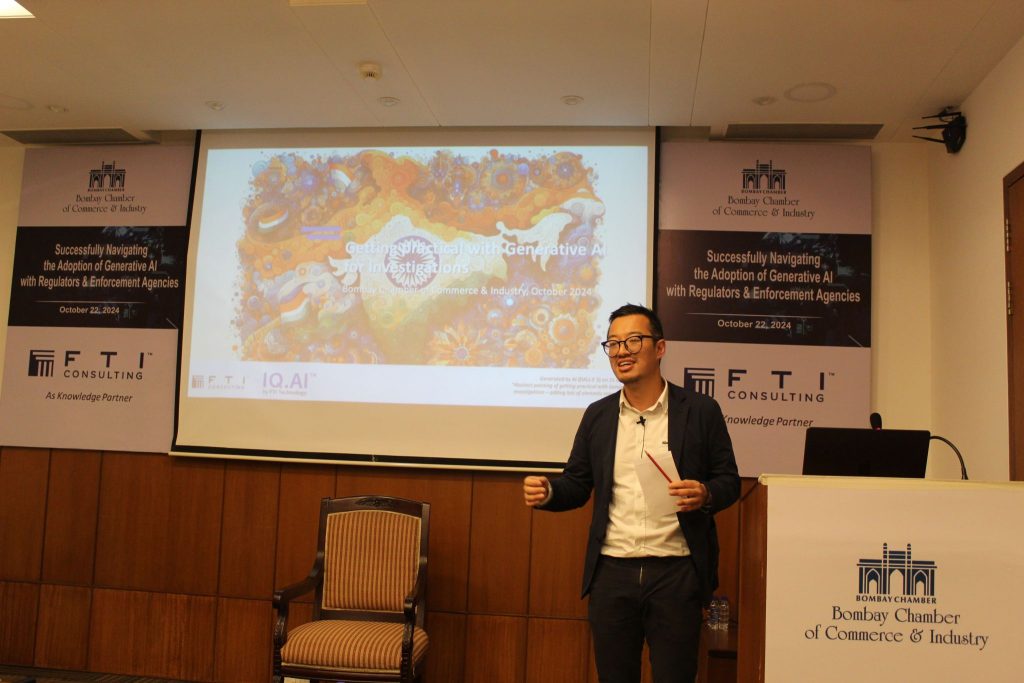

The Bombay Chamber, in association with FTI Consulting as the knowledge partner, conducted a session on Generative AI.
Jon Chan, FTI Consulting’s eDiscovery Innovation and AI leader conducted a 90-minute session titled “Successfully Navigating the Adoption of Generative AI with Regulators and Enforcement Agencies.” This session included an optional 20-minute hands-on labs experience, where attendees utilized laptops and sample data to explore various prompts, models, and concepts, including hallucinations and prompt engineering in an investigative environment.
The session offered practical applications of Generative AI within disputes and investigations, equipping legal, compliance, and investigation leaders with insights on effectively incorporating this technology into their operations. Attendees gained actionable strategies for integrating AI to enhance efficiency and support organisational goals.
Designed for professionals focused on governance, risk, and compliance, the discussion addressed the unique challenges and opportunities posed by Generative AI in regulated environments. FTI’s extensive experiments with this emerging technology provided transparency around associated risks and considerations.
As AI rapidly evolved, organisations learned the importance of navigating uncharted territories, particularly in experimentation and result validation to mitigate risks and support new processes enabled by Generative AI. The session delivered expert perspectives on managing regulatory scrutiny, addressing potential risks, and responsibly leveraging AI to improve operational efficiency while fulfilling legal and compliance obligations.
Following the session, attendees had the opportunity to network during a lunch, fostering discussions around the insights shared and the future implications of Generative AI in their respective fields.
Criminal acquittal cannot revive a dismissed labor dispute, especially when approached after an unreasonable delay – P & H HC
Criminal acquittal cannot revive a dismissed labor dispute, especially when approached after an unreasonable delay – P & H HC
Criminal acquittal cannot revive a dismissed labor dispute, especially when approached after an unreasonable delay
Copy of judgement attached.
India-Germany Partnership in AI, Green Tech, and Semiconductor Sectors to Drive Global Growth: Shri Piyush Goyal
India-Germany Partnership in AI, Green Tech, and Semiconductor Sectors to Drive Global Growth: Shri Piyush Goyal
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry, Shri Piyush Goyal, inaugurated the 18th Asia Pacific Conference of German Business (APK) in New Delhi, highlighting the significant synergy between India and Germany in fields such as artificial intelligence, semiconductors, and green technology. Shri Goyal emphasized that India’s ability to scale, paired with Germany’s expertise in precision engineering, will bring exceptional benefits to the global community.
Shri Goyal highlighted the vast potential in combining Germany’s precision engineering with India’s scaling capabilities across infrastructure sectors—physical, digital, and social. He noted that this partnership could “create something extraordinary for the world.” The Minister emphasized that this collaboration can further drive unprecedented growth in AI adoption, semiconductor innovation, and green technology initiatives, which are central to today’s rapidly evolving global economy.
Speaking on India’s Macroeconomic Strength and Climate Commitments, Shri Goyal stressed that India is on a firm path to exceed its climate change commitments, as outlined at COP21. He remarked that India currently ranks 7th on the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) and is expected to surpass its nationally determined contributions (NDCs) for climate action. “India is committed to combating climate change, on track to meet nationally determined contributions,” Shri Goyal said, reaffirming India’s dedication to sustainable development and responsible environmental practices.
The Union Minister also acknowledged the Asia Pacific Committee of German Business and the Indo-German Chamber of Commerce for organizing the APK conference. He noted that Asia-Pacific, which accounts for 60% of the world’s population, is poised to host two-thirds of the global middle class by 2030. Shri Goyal remarked, “This demographic shift presents a fertile ground for businesses seeking to expand their reach and capitalize on emerging sectors.”
Shri Goyal underscored that the APK conference is instrumental in recognizing emerging trends and addressing global challenges. He pointed out that the conference plays a critical role in facilitating the exchange of best practices, fostering technological advancements, and shaping future industrial policies.
The Minister concluded by quoting German philosopher Arthur Schopenhauer and poet Rabindranath Tagore. Recalling Schopenhauer’s words, “Reading the Upanishads is comforting in my life…,” he encouraged attendees to embrace India’s cultural richness, especially during the festive season from Diwali to Christmas and New Year. Ending on a visionary note, he shared a quote from Tagore: “Reach high, for stars lie hidden in you. Dream deep, for every dream precedes the goal,” encouraging participants to build a future where their innovations and industries leave a global mark.
This strategic alliance marks a significant step forward in both countries’ commitment to global progress through collaborative innovation and sustainable development.
Key Highlights of the 18th Asia Pacific Conference of German Business:
– India-Germany Collaboration: A platform for advancing joint initiatives in AI, semiconductors, and green technologies.
– Climate Change Commitments: India ranks 7th on the CCPI and is set to surpass its climate goals, strengthening sustainable progress.
– Asia-Pacific Market Potential: Asia’s demographic evolution presents opportunities for expansion across emerging sectors.
– Cultural Unity: Shri Goyal celebrated the spirit of India’s rich culture and the synergy of festive seasons across both nations.
This partnership strengthens the longstanding relationship between India and Germany and is a testament to both nations’ pursuit of innovation, sustainability, and economic resilience.
The the onus of proving the nature of employment rests on the person claiming to be a “workman” within the definition of section 2(s) of the I.D. Act – Supreme Court
The the onus of proving the nature of employment rests on the person claiming to be a “workman” within the definition of section 2(s) of the I.D. Act – Supreme Court
The the onus of proving the nature of employment rests on the person claiming to be a “workman” within the definition of section 2(s) of the I.D. Act
Copy of judgement attached.
Maharashtra notifies 20th November 2024 as a public holiday under Representation of People’s Act for Vidhan Sabha Elections
Maharashtra notifies 20th November 2024 as a public holiday.
Maharashtra notifies 20th November 2024 as a public holiday under Representation of People’s Act for Vidhan Sabha Elections.
An aadhar card while can be used to establish identity is not per se proof of date of birth – Supreme Court
An Aadhar card while can be used to establish identity is not per se proof of date of birth.
An Aadhar card while can be used to establish identity is not per se proof of date of birth.
Copy of judgement attached.
Open International Bidding – State Trading Corporation
Open International Bidding – State Trading Corporation
The State Trading Corporation (STC) of Mauritius is inviting bids from eligible bidders for the Supply of Long Grain White Rice for the period covering 01 February 2025 to 30 April 2025.
The Interested Bidders should register by signing up on the e-Procurement System of the Government of Mauritius on https://eproc.publicprocurement.govmu.org in order to participate in the bidding exercise and download the bidding documents, Reference Number STC/IFB/2024/175.
A copy of the Procurement Notice is herewith attached. The deadline for online submission of the Bids on the e-Procurement System is 05 November 2024 up to 14:00 hours (Mauritian Time) at latest.
The Consulate would appreciate if the Procurement Notice could be circulated to the prospective bidders.
D. K. Bucktowar
Officer-in-Charge
Consulate of the Republic of Mauritius
1105, Regent Chambers
11th Floor, Jamnalal Bajaj Marg
208, Nariman Point
Mumbai – 400 021
Tel. : 022 22825421 /22
Fax No. 022 22845468
Industrial Court has no jurisdiction to decide Complaint of unfair labour practices filed under the MRTU & PULP Act)when existence of employer relationship is under dispute. Bom HC
Industrial Court has no jurisdiction to decide Complaint of unfair labour practices filed under the MRTU & PULP Act)when existence of employer relationship is under dispute. Bom HC
Industrial Court has no jurisdiction to decide Complaint of unfair labour practices filed under the MRTU & PULP Act)when existence of employer relationship is under dispute
Bombay HC
Once a workman claims continuous employment, the burden of proof shifts to the employer to disprove the claim with documentary evidence.MP HC
Once a workman claims continuous employment, the burden of proof shifts to the employer to disprove the claim with documentary evidence.MP HC
Once a workman claims continuous employment, the burden of proof shifts to the employer to disprove the claim with documentary evidence.
Copy of judgement attached
Non Compete clause in Master Supply Agreement not be valid post-termination of the agreement – Bombay High Court
Non Compete clause in Master Supply Agreement not be valid post-termination of the agreement – Bombay High Court
Though a non-compete clause can operate validly during the term of the agreement, but it would not be valid post-termination of the agreement as it would result in restraint of trade prohibited by Section 27 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872.
Copy of judgement attached

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin