Blog
Top Stories
PLI scheme changes to ease textile investment and hiring

Mumbai: The Ministry of Textiles has announced a series of amendments to the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for textiles, aimed at making it easier for companies to invest and expand operations in India’s man-made fibre (MMF) and technical textiles sectors. The revisions, notified on October 09, 2025, are expected to lower entry barriers, reduce compliance burdens, and support job creation across the value chain.
Under the revised guidelines, companies will no longer be required to set up new entities to qualify for incentives. Instead, they can establish project units within existing firms. This move is likely to benefit mid-sized and established players who were previously deterred by the additional costs and administrative hurdles of creating new corporate structures.
The government has also halved the minimum investment thresholds for new applicants from August 01, 2025. For the Part-1 category, the requirement has been reduced from ₹300 crore to ₹150 crore, while for Part-2, it has been lowered from ₹100 crore to ₹50 crore. These changes are expected to attract a broader pool of investors, particularly from the micro, small and medium enterprises (MSME) segment, which has often cited high capital requirements as a barrier to entry.
In a further relaxation, the incremental turnover requirement for claiming incentives has been reduced from 25% to 10% from the second year of operations, starting FY 2025–26. This adjustment acknowledges the challenges faced by manufacturers in scaling up production rapidly and aligns the scheme more closely with ground realities.
The scope of eligible products has also been expanded. Eight new Harmonised System of Nomenclature (HSN) codes have been added for MMF apparel and nine for MMF fabrics. This expansion is intended to reflect evolving market demand and technological advancements in textile manufacturing.
The application window for the scheme has been extended until December 31, 2025, giving companies additional time to assess the revised terms and submit their proposals. Industry observers believe this extension, coupled with the relaxed norms, could lead to a fresh wave of investment in the sector.
The original PLI scheme for textiles, launched in 2021, was aimed at boosting domestic manufacturing and exports in high-value segments such as MMF and technical textiles. However, uptake had been slower than anticipated, with stakeholders citing stringent eligibility criteria and high investment thresholds as key concerns.
The MMF and technical textiles sectors are seen as critical to India’s ambitions of increasing its share in global textile trade. While India has traditionally been strong in cotton-based textiles, MMF accounts for a growing share of global demand. Technical textiles, used in sectors ranging from healthcare to infrastructure, are also gaining traction due to their specialised applications.
By easing the investment and operational requirements under the PLI scheme, the government hopes to unlock new capacity, attract technology partners, and generate employment in both urban and semi-urban areas. The focus on MMF and technical textiles is also aligned with broader policy goals, including import substitution and value addition in manufacturing.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
The Future of Insurance in India: Insights Ahead of Insurance Summit 2025
The Future of Insurance in India: Insights Ahead of Insurance Summit 2025
India’s insurance sector, valued at over USD 140 billion, is undergoing significant transformation. Ranked among the top ten insurance markets in the world, the sector is witnessing momentum fueled by regulatory reforms, digital innovation, and a growing demand for customer-first solutions.
While the life insurance segment continues to experience steady growth, the non-life insurance sectors—including health, motor, property, and liability—are now poised for rapid expansion. This shift reflects India’s evolving risk landscape, changing consumer expectations, and stronger public-private policy alignment.
At the centre of this evolution lies a vital question:
Is India’s insurance industry actively preparing for this transformation, or merely hoping it will unfold on its own?
Catalysts for Sectoral Change
The government’s “Insurance for All by 2047” vision, championed by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI), has placed the insurance sector on an ambitious course. Several recent and upcoming developments will play a decisive role in shaping this path forward:
- The Insurance Bill Amendment 2025 is set to redefine how insurers raise capital, handle solvency requirements, and operate under a modernised regulatory structure. This could have far-reaching implications for IPO-readiness and governance transparency across the industry.
- The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission aims to launch a national health claims exchange, designed to digitise and simplify the claims settlement process across insurers, third-party administrators, and hospitals. This move is expected to drastically reduce paperwork, speed up approvals, and improve the policyholder experience.
- Insurtech firms and legacy insurers are collaborating to co-develop products that meet the specific needs of diverse populations — from urban centres to semi-urban and rural markets. These collaborations are also enabling the expansion of microinsurance and embedded insurance services.
- Today’s insurance consumers are demanding more than just coverage. They are seeking transparency, trust, and personalised service. This behavioural shift is compelling insurers to rethink their models — from transaction-driven to relationship-based.
Introducing Insurance Summit India 2025
To address these developments, the Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI) Committee of the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry will host:
Insurance Summit India 2025 – Viksit Bharat: Catalysing Insurance for a Resilient Future
Date: August 8, 2025
Time: 1:00 PM Onwards
Venue: Hotel Taj Santacruz, Mumbai
Organiser: Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, BFSI Committee
This high-impact summit will convene key stakeholders from across the insurance ecosystem — including senior regulators, CEOs, actuaries, underwriters, legal experts, technology leaders, brokers, TPAs, and insurtech founders.
🤝 Supported by Industry Leaders
The Insurance Summit India 2025 is supported by some of the most respected names in the insurance and financial services industry:
- Title Sponsor: New India Assurance
- Premium Sponsors: Axis Max Life Insurance | Lockton
- Co-Sponsors: Beacon Insurance Brokers Pvt. Ltd. | Aditya Birla Capital Health Insurance
- Knowledge Partner: PwC India
Their collaboration reflects the shared commitment toward building a more resilient, inclusive, and tech-enabled insurance ecosystem. To explore the full agenda and speaker lineup, visit the official event page.
What to Expect at the Summit
The Summit will open with a high-impact plenary session featuring a keynote address by Mr. Deepak Sood, Member (Non-Life), IRDAI, who will share the regulator’s vision and roadmap for driving innovation while upholding consumer protection and financial stability. The session will also include special addresses by Mr. Nilesh Sathe, Former Whole-time Member, IRDAI, and Ms. Girija Subramanian, CMD, New India Assurance.
Participants can look forward to three high-value panel discussions:
- Panel 1: Opportunities and Impact of the Proposed Insurance Bill Amendment 2025 — featuring leaders from Zuno Insurance, Universal Sompo, and Future Generali.
- Panel 2: Enhancing Customer-Centricity — featuring experts from Lockton and Beacon Insurance Brokers, among others.
- Panel 3: Tech-Driven Innovation, Inclusion and Trust — with insights from Aditya Birla and Axis Max Life Insurance, among others.
Each session is designed to foster actionable dialogue on how innovation, regulation, and consumer engagement can jointly enable India’s transition into a resilient insurance economy.
The Summit also offers structured networking opportunities, including a curated networking lunch and post-event dinner with cocktails — allowing professionals to connect meaningfully across domains.
Why This Summit Matters
Insurance has evolved from being a financial product to becoming a pillar of economic resilience. In today’s India, it is a critical lever for inclusive growth, social stability, and institutional trust.
The Insurance Summit India 2025 is not just another industry event — it is a strategic forum for collaborative problem-solving, innovation sharing, and long-term ecosystem building.
If you are involved in insurance, fintech, legal advisory, regulatory policy, health administration, or capital markets, this Summit offers unparalleled insights and access.
Register Now
Participation is limited and registration is filling quickly.
To confirm your seat and gain access to this flagship event,
Click here to register for Insurance Summit India 2025
For queries or institutional participation, contact:
Utkarsha Joshi:
+91 22 6120 0271
utkarsha.joshi@bombaychamber.com
Priya Singh:
+91 22 6120 0238
GST invoice management system evolves for smarter tax compliance
GST invoice management system evolves for smarter tax compliance


Mumbai: When the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Invoice Management System (IMS) went live on October 1, 2024, it arrived as a quiet revolution in the nation’s GST architecture. Introduced with the promise of real time visibility into business-to-business (B2B) transactions, the system is currently optional – a testing ground rather than a mandate. Yet within months, it became obvious to tax professionals and corporate leaders alike that IMS would reshape not only compliance routines but the very dynamics of trust and transparency across the supply chain.
As Komal Sampath, Director – Indian Tax Practice at Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu India LLP, explained at a recent webinar organised by the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry, the true turning point comes with the decision to freeze outward liability in the GSTR 3B return from the July 2025 tax period onwards. At that juncture, any rejection of credit notes by the customers under their IMS may no longer directly be corrected under summary returns of GSTR 3B – a deadline that demands urgent attention from every taxpayer.
On the surface, the GSTN Portal itself presents a deceptively simple layout. Vendors upload their B2B transactions as soon as they are issued, and these records appear in the recipient’s dashboard that allows them to cross-verify entries against their own available records. Yet behind this simplicity lies an intricate choreography of data feeds and validation checkpoints. As transactions initially populate in the ‘No action’ section, recipient may take appropriate action and digital cut-throughs ensure near-instantaneous updates of both the supplier’s and the recipient’s IMS dashboards.
Filters by GSTIN, invoice number, and month enable finance teams to monitor high-value transactions and identify potential discrepancies. Furthermore, for quarterly filers, GSTR-2B is not generated during the first two months of the quarter, permitting them to undertake necessary actions on a quarterly basis.
It is in the dance between acceptance and rejection that the system’s power becomes evident. Should a recipient recognise a transaction as legitimate, a click of the accept button seamlessly authorises the corresponding input tax credit. If the transaction appears spurious or mis-addressed, rejection becomes an immediate deterrent against fraud – alerting both vendor and tax authority to the anomaly.
And where doubts persist, the pending status allows additional scrutiny, perhaps triggering an internal audit or a supplier follow-up. This triage of invoices not only curtails credit claims on counterfeit documents but also strengthens the integrity of each firm’s self-assessment.
Yet practical experience has also revealed obstacles, Karthik Gandhi, Head – Indirect Tax at Siemens India, shared at the same webinar that integration between IMS and legacy ERP systems remains a thorny issue for multinational groups. “We are dealing with multiple entities, each on a different digital platform,” he noted. “Ensuring that transactions captured in one system synchronise accurately with IMS, without duplications or time lags and requires intensive coordination between finance and vendor support teams,” said Gandhi.
Additionally, many practitioners believe further refinements are still required, particularly for taxpayer registered PAN India where tax documents are received at multiple offices and it may delay verification of tax documents by weeks. Calls for extended timelines for taking action on credit notes are already being tabled by industry associations, though any reprieve will need to balance ease-of-use with the government’s broader objectives of plugging revenue leakages.
For businesses large and small, the strategic implications of IMS extend far beyond compliance. Real time invoice matching can accelerate working capital cycles by giving suppliers confidence that credits will be honoured without delay subject to fulfilment of provision of GST law.
Conversely, any backlog in reconciliation can put pressure on cash flows, as the freeze on outward liability could leave invoices in limbo and credits unclaimed. Financial controllers thus find themselves at the nexus of legal compliance, treasury management and supplier relations – a role that demands both technical acumen and diplomatic finesse.
At its heart, the IMS represents a step towards a more transparent, accountable commercial ecosystem. No longer can shell companies hide behind fabricated invoices or delay reporting without immediate consequence. Simultaneously, genuine traders gain the reassurance of on-demand verification, reducing the friction of inter-company settlements. The transformation may be gradual – after all, the initial phase remains optional – but with each month of voluntary participation, taxpayers refine their processes in anticipation of the mandatory horizon.
As the IMS evolves, so too will the skills demanded of India’s tax professionals. Tomorrow’s finance teams/tax professionals will need data analytics expertise to monitor dashboard metrics, legal insight to interpret emerging advisories and change-management know-how to embed new procedures across dispersed operations.
The freeze effective July 2025 is not merely a technical adjustment; it is a signal that digital compliance has arrived irreversibly. Firms that adapt swiftly will not only avoid penalties but stand to gain a competitive edge in the increasingly data-driven marketplace.
In the end, India’s journey towards real time invoice reporting is a microcosm of its aspirations for a fully digitised economy. By merging technology with regulatory intent, the government seeks to construct a fiscal architecture that is both resilient against fraud and conducive to growth. The road ahead will doubtless present further challenges, from system enhancements to policy fine-tuning, but the direction of travel is clear.
For those who embrace the change, the IMS offers a pathway to greater efficiency, stronger compliance and deeper collaboration across the supply chain. And when the next chapter of India’s tax story is written, it will surely be defined by the lessons learned from the first months of IMS in action.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
47 New National Waterways (NWs) to be operational by 2027; Cargo volume to rise up to 156 MTPA by 2026”: Sarbananda Sonowal
47 New National Waterways (NWs) to be operational by 2027; Cargo volume to rise up to 156 MTPA by 2026”: Sarbananda Sonowal

Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, today chaired a meeting of the Consultative Committee on Inland Waterways Transport in Mumbai, where it was revealed that 76 waterways are targeted to be made operational by 2027, with cargo volume expected to surge by 156 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) by end of FY 2026. The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), the nodal agency under the Ministry, presented a comprehensive review of major projects, future projections, and the roadmap ahead. Members of Parliament attending the meeting acknowledged and appreciated the progress made and supported increased budgetary allocations to boost the sector’s growth.
The footprint of inland water transport is expected to expand significantly—from 11 states in FY 2024 to 23 states and 4 Union Territories by FY 2027. To support this growth, projects worth ₹1,400 crore were launched or announced during the Inland Waterways Development Council (IWDC) meeting held on January 10, 2025. Additionally, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is conducting 10,000 km of longitudinal survey each month to assess Least Available Depth (LAD) for improved navigability. Cargo Volume is likely to make an incremental growth up to 156 MTPA by March, 2026 inching closer towards the Maritime India Vision 2030 target of 200 MTPA.
Speaking on the occasion, the Union Minister Shri Sarbananda Sonowal said, “Inland waterways are emerging as the watershed moment in India’s logistics and transport ecosystem. Under the visionary leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi ji, we are witnessing a transformational shift with policy interventions like the National Waterways Act, 2016, the Inland Vessels Act, 2021 and supplemented by multiple programmes like Jal Marg Vikas Project, Arth Ganga, Jalvahak scheme, Jal Samriddhi scheme, Jalyan & Navic among others. Through Maritime India Vision 2030 and the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047. These roadmaps are not just policy documents—they are catalysts driving India toward becoming a global maritime powerhouse. Today’s meeting with esteemed Members of Parliament reflects a unified commitment to boost infrastructure and unlock the immense economic potential of our rivers and coasts. With enhanced budgetary support and cooperative federalism, we are building a greener, more efficient, and future-ready waterway network across the country.”
The Regional Waterways Grid aims to boost economic activity by ensuring seamless vessel movement from Varanasi to Dibrugarh, Karimganj, and Badarpur via the IBP route, creating a 4,067 km economic corridor. A traffic study and DPR for renovating the Jangipur navigation lock are underway. The project’s cargo potential is estimated at 32.2 MMTPA by 2033.
On NW 1 (Ganga), a dedicated waterway corridor spanning 1,390 km is being developed to enable seamless movement of vessels, enhancing the efficiency of inland transport. As part of this initiative, capacity augmentation of NW-1 is underway to support the navigation of 1,500–2,000 DWT vessels, alongside the creation of key cargo handling facilities at Varanasi (MMT), Kalughat (IMT), Sahibganj (MMT), and Haldia (MMT).

Inland Waterways has major projects in the Northeast. A ₹5,000 crore roadmap is planned over the next five years. On NW-2 (Brahmaputra), four permanent terminals—Dhubri, Jogighopa, Pandu, and Bogibeel—and 13 floating terminals are supported by fairway and navigation upgrades. A ₹208 crore ship repair facility at Pandu and a ₹180 crore alternative road are set for completion by 2026 and 2025, respectively. On NW-16 (Barak), terminals at Karimganj and Badarpur are active, while NW-31 (Dhansiri) is being developed to support NRL’s expansion.
Adding further, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal said, “In line with the Harit Nauka Guidelines, the Inland Waterways Authority is committed to green and sustainable transport solutions, including the procurement of electric catamarans and hydrogen fuel cell-powered vessels. By strengthening urban water transport through water metro projects and promoting eco-friendly cruise tourism, we are paving the way for a cleaner, greener future in inland waterways transportation. The Regional Waterways Grid aims to seamlessly connect Assam and the Northeast with the rest of India through an integrated network of inland waterways. This will boost regional trade, tourism, and connectivity while unlocking economic potential across the Brahmaputra and Barak River systems. Government is also working on a ₹5,000 crore roadmap for Inland Waterways Development in Northeast Over Next 5 Years.”
The committee also reviewed the ongoing works on NW -1 (river Ganga), NW 2 (Brahmaputra) among other states like Odisha, Jammu & Kashmir, Goa, Kerala, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
India’s river cruise tourism is witnessing robust growth, with 15 river cruise circuits now operational across 13 National Waterways (NWs) spanning nine states. The number of NWs supporting river cruises has risen from just three in 2013-14 to 13 in 2024-25, while luxury river cruise vessels have increased significantly from three to 25 during the same period. To further boost inland water-based tourism, 51 additional cruise circuits have been identified on 47 NWs for development by 2027. Three World class river cruise terminals are also planned, with construction underway at Kolkata. Feasibility studies for terminals at Varanasi and Guwahati are being conducted by IIT Madras, while four more terminals at Silghat, Bishwanath Ghat, Neamati, and Guijan are set to be developed by 2027.
Speaking on the occasion, Minister of State for Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Shri Shantanu Thakur said, “Special efforts are underway to advance river cruise tourism across India by developing modern cruise terminals and related infrastructure. Through strategic partnerships and MoUs with private enterprises, we are boosting luxury river cruises on the Ganga and Brahmaputra, while also expanding cruise tourism on the Yamuna, Narmada, and key rivers in Jammu & Kashmir. These initiatives not only promote tourism but also contribute to sustainable economic growth in the regions we serve.”

The Consultative Committee meeting was chaired by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal while Minister of State for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Shantanu Thakur was also present. The meeting was attended by Shatrughan Prasad Sinha, Lok Sabha MP (Asansol, West Bengal), Bibhu Prasad Tarai, Lok Sabha MP (Jagdispur, Odisha), Hibi Eden, Lok Sabha MP (Ernakulum, Kerala), M.K. Raghavan, Lok Sabha MP (Kozhikode, Kerala), Naba Charan Majhi, Lok Sabha MP (Mayurbhanj, Odisha), Abhimanyu Sethi, Lok Sabha MP (Odisha) and Seema Dwivedi (Rajya Sabha MP from Uttar Pradesh).
India Participates in 9th BRICS Industry Ministers’ Meeting in Brasília
India Participates in 9th BRICS Industry Ministers’ Meeting in Brasília

India participated in the 9th BRICS Industry Ministers’ Meeting held under the Chairship of Brazil on 21st May 2025 at the Itamaraty Palace, Brasília – Federal District. The overarching theme of the meeting was “Strengthening Global South Cooperation for More Inclusive and Sustainable Governance”.
The meeting witnessed the presence of Industry Ministers and representatives from all BRICS member countries including Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, as well as newly inducted members Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The Joint Declaration adopted at the meeting reaffirmed the collective commitment to fostering an open, fair, and resilient global environment, strengthening the multilateral system, and enhancing economic and social resilience amid rapid global transformations.
As a key initiative, India launched the BRICS Startup Knowledge Hub on 31st January 2025, under the aegis of the BRICS Start-Up Forum. This is the first-of-its-kind dedicated platform for BRICS nations, aimed at enhancing cross-border collaboration and strengthening startup ecosystems across member countries. India extended an invitation to all BRICS nations to contribute to and derive benefits from this platform through the exchange of policy insights, innovations, and best practices.
In line with the Joint Declaration, India also emphasized the critical role of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the national and global economy. India highlighted that with 5.93 crore registered MSMEs employing more than 25 crore individuals, the sector contributed 45.73% of the country’s total exports in 2023–24.
The Ministers underscored the need to deepen industrial cooperation and promote sustainable and inclusive growth across BRICS nations. The Joint Declaration emphasized the pivotal role of innovation and digital technologies under Industry 4.0 as key drivers of sustainable development. India, in its intervention, articulated its vision for a future-ready industry that is inclusive, innovative, and digitally empowered, aligning with the objectives of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
It was noted that India’s Digital India campaign has transformed the country into the world’s largest digitally connected democracy. The number of internet users in India increased significantly from 251.59 million in 2014 to 954.40 million as of March 2024.
India concluded its remarks by calling upon BRICS members to be guided by the principles of Sahyog (Collaboration), Samanjasya (Harmony), Samagrata (Inclusiveness), and Sarvasammati (Consensus) in all cooperative endeavours going forward.
India-UK FTA to enhance bilateral trade, create new job avenues, and boost economic growth
India-UK FTA to enhance bilateral trade, create new job avenues, and boost economic growth
In a landmark move marking a new chapter in global commerce, India and the United Kingdom have successfully concluded a Free Trade Agreement (FTA), bringing an end to years of negotiations. The deal, hailed as a ‘historic milestone’ by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, is expected to significantly enhance bilateral trade, create new job avenues, and boost economic growth.
For India, the agreement presents both opportunities and challenges. While it opens doors for increased exports and foreign investment, it also raises concerns about domestic industries facing heightened competition. The deal is expected to catalyse trade, investment, and innovation, but its long-term impact on India’s economy remains to be seen.
One of the most significant advantages of the FTA is the elimination or reduction of tariffs on a wide range of goods and services. Indian exporters, particularly in labour-intensive sectors such as textiles, footwear, and automobile components, stand to benefit immensely. The UK has agreed to eliminate tariffs on these products, making Indian goods more competitive in the British market.
Additionally, the agreement includes provisions for increased mobility of skilled Indian professionals to the UK, particularly in sectors such as information technology (IT) and healthcare. The Double Contribution Convention, a social security pact, ensures that Indian workers in the UK and their employers are exempt from paying social security contributions for three years, reducing financial burdens and enhancing employment opportunities.
The pharmaceutical and medical device industries are also expected to see a surge in exports, as the UK lowers tariffs on these products. With India being a global leader in generic medicines, this move could significantly boost revenue for Indian pharmaceutical firms.
While the agreement offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges for certain Indian industries. The reduction of tariffs on British whisky and gin, for instance, has raised concerns among domestic beverage manufacturers. Indian tariffs on these products will be halved from 150% to 75%, and further reduced to 40% over the next decade. This could lead to increased competition for Indian liquor brands, potentially impacting local businesses.

Similarly, the automotive sector faces mixed outcomes. While Indian manufacturers will benefit from reduced tariffs on exports, the influx of British automobiles at lower duties could pose a challenge for domestic carmakers. The UK has negotiated a tariff reduction from 100% to 10% under a quota system, which may lead to increased imports of British vehicles.
Agriculture remains another sensitive area. India has excluded certain agricultural products, such as dairy, apples, and cheese, from duty concessions to protect its farmers. However, concerns persist about the potential impact of increased competition from British agricultural exports.
The FTA is expected to have a positive impact on India’s gross domestic product (GDP) growth, with projections indicating a substantial increase in bilateral trade. The British government estimates that trade between the two nations will rise by £25.5 billion annually from 2040 onwards. This surge in trade is likely to contribute to India’s economic expansion, fostering job creation and investment.
Moreover, the agreement strengthens India’s position as a global trade partner, reinforcing its commitment to economic liberalisation. By opening up key sectors and reducing trade barriers, India is positioning itself as a flexible and attractive destination for foreign investment.

(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
Private equity, venture capital market in India surges to $43 billion as buyouts dominate
Private equity, venture capital market in India surges to $43 billion as buyouts dominate
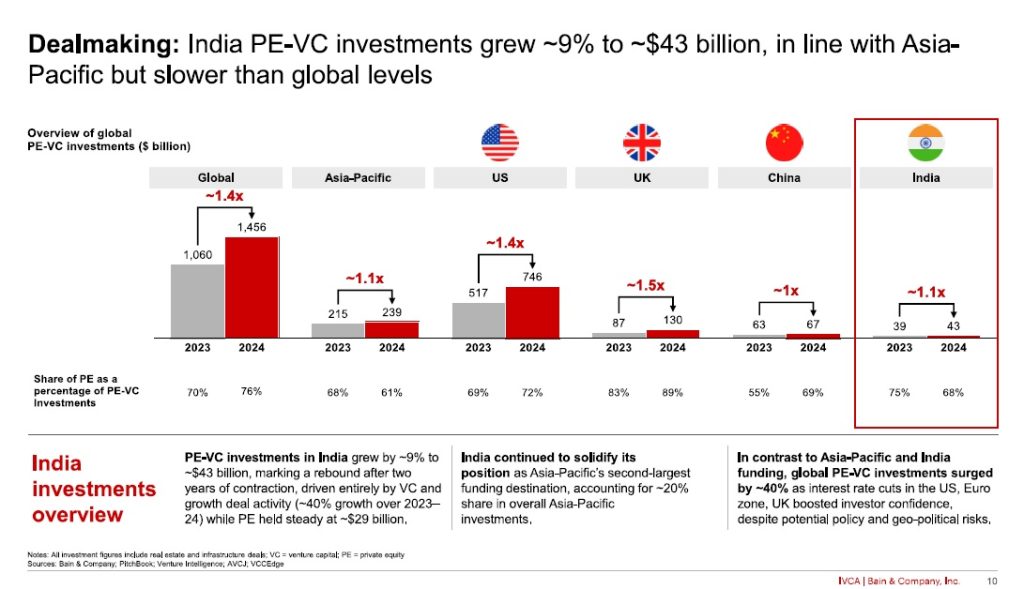
India’s private equity and venture capital (PE-VC) market rebounded strongly in 2024, reversing two years of contraction with a 9% rise in investments to reach $43 billion across 1,600 deals. As Asia-Pacific’s second-largest PE-VC hub, India continues to attract global capital, signalling renewed investor confidence in its macroeconomic stability and long-term growth potential.
According to Bain & Company’s ‘India Private Equity Report 2025’, published in collaboration with the Indian Venture and Alternate Capital Association (IVCA), while growth-stage investments drove much of the resurgence, private equity remained steady at $29 billion. A major shift towards buyouts was evident, with their share of total PE activity surging to 51% from 37% in 2022. Investors are increasingly securing control positions in high-quality assets, leveraging record dry powder reserves to pursue scalable opportunities.
Real estate and infrastructure emerged as standout performers, collectively accounting for 16% of total PE-VC funding, with deal values soaring by 70% compared to the previous year. Financial services also experienced robust growth of 25%, particularly within non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), driven by affordable housing finance, micro-lending, and MSME financing. Large transactions in companies such as Shriram Housing Finance and Aavas Financiers underscore investor confidence in high-yield, asset-secured businesses.
The healthcare sector maintained strong momentum, with an 80% increase in deal volume. Investments in medical technology, pharmaceutical outsourcing, and single-specialty hospitals – particularly in areas like eyecare, oncology, and IVF – highlighted a strategic push towards underpenetrated categories.
Meanwhile, IT-enabled services saw remarkable expansion, with deal activity tripling. Notable transactions such as Perficient’s $3 billion deal, Altimetrik’s $900 million investment, and GeBBS’s $865 million acquisition reinforced the sector’s growing dominance in digital transformation and revenue cycle management.
India also led the Asia-Pacific region in private equity exits, with exit values reaching a record-breaking $33 billion across 360 deals, marking a 16% year-over-year increase. Public market exits gained prominence, making up 59% of total exit value compared to 51% in 2023, as strong IPO activity fuelled investor optimism. The IPO landscape expanded significantly, with 33 listings in 2024 – up from 23 the previous year – driven largely by consumer-focused sectors.
Domestic fundraising hit new highs, further strengthening India’s private capital ecosystem. Kedaara Capital closed a landmark $1.7 billion fund, while ChrysCapital raised a record $2.1 billion. Global funds also intensified their presence, with Blackstone announcing plans to double its India-based assets under management from $50 billion to $100 billion, reflecting growing international confidence in India’s economic trajectory.
The private equity and venture capital market in India rebounded in 2024 and the outlook for 2025 remains positive. However, sustaining the momentum will require funds to navigate shifting economic and market conditions. Investors with strong operational capabilities, sector-specific expertise, and a focus on sustainable value creation will be best positioned to capitalise on opportunities. As the market tilts towards traditional industries and domestic fundraising reaches new highs, India’s PE-VC landscape looks set for a steady and long-term growth.
(Write to us at editorial@bombaychamber.com)
Bombay Chamber Hosts Conclave on Future of Fund Management: AIFs in GIFT City
Bombay Chamber Hosts Conclave on Future of Fund Management: AIFs in GIFT City
The Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry hosted its PEVC Conclave on the theme “Future of Fund Management: AIFs in GIFT City.” The event brought together fund managers, policymakers, regulators, and industry experts to explore the growing significance of GIFT City and its role in shaping India’s financial services landscape.
The conclave opened with a welcome address by Sandeep Khosla, Director General of the Bombay Chamber, who outlined the Chamber’s wide-ranging initiatives and reaffirmed its longstanding role as a bridge between industry and government. He emphasised the importance of fostering collaborative dialogue to support India’s evolving financial ecosystem.
Setting the theme of the Conclave, Ashith Kampani, Chair of the PE&VC Committee at the Bombay Chamber and Chairman of CosmicMandala15 Securities highlighted the Chamber’s focus on collaborative development toward a Viksit Bharat, grounded in digitalisation, ESG integration, ease of doing business, and inclusive growth—principles reflected throughout the day’s discussions. Kampani underscored how these pillars are directly relevant to the evolving financial landscape in GIFT City, India’s first operational smart city and International Financial Services Centre (IFSC). He highlighted the momentum GIFT City has gained, with over 80 fund managers operating within its ecosystem and more than $20 billion in fund commitments, as evidence of its growing prominence. He also noted that the progressive regulatory framework, especially following the introduction of the Fund Management Regulations in 2022, offers unparalleled flexibility in fund structuring, cross-border investments, and tax incentives—making GIFT City a highly attractive jurisdiction for global capital and investment innovation.

Swati Khemani, Founder and CEO of Carnelian Asset Management & Advisors, delivered the keynote address. She emphasised that GIFT City represents a transformational shift in India’s financial sector, offering regulatory transparency, tax incentives, and infrastructure that rival global standards. With over $36 billion in assets under management and 124 registered fund units as of March 2024, GIFT City is becoming a preferred destination for asset and wealth managers worldwide.
Khemani also connected GIFT City’s evolution with the government’s broader vision under Amrit Kaal, projecting India’s share in global trade to rise from 12 percent to 16 percent and targeting per capita income of $18,000. She noted the city’s multi-currency capabilities, favorable tax treatment, and appeal for non-resident investors as key differentiators, positioning GIFT as a global center for financial innovation.

The first panel discussion, titled GIFT AIFs: Unlocking Inbound and Outbound Investment Potentials, was moderated by Tejas Desai, Co-Chair of the PE&VC Committee at the Bombay Chamber and Partner at Ernst & Young. The panellists included Pavan Shah, General Manager, International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA); Mitul Mehta, Chief Financial Officer, Blume Ventures; Lakshmi Iyer, CEO – Investment & Strategy, Kotak Alternate Asset Managers; Clarence Anthony, Managing Partner, Clarence & Partners; and Niutpol Handique, Assistant Vice President – International Business Development, Mirae Asset Management Company.

The session addressed the game-changing nature of 100 percent NRI-focused funds, the challenges faced by domestic SEBI AIFs in making offshore investments, and how the FEMA non-resident status of GIFT AIFs offers a compelling solution. The discussion also covered recent amendments to the Fund Management Entity Regulations and the tax advantages of launching asset-specific funds through GIFT City, especially for investing in Indian mutual funds.
The second panel, Dual Listing in GIFT City, moderated by Jyoti Vineet Tandon, Compliance Consultant and Co-Founder of FinCrimeExpert, featured Pradeep Ramakrishnan, Executive Director, International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA); Vijay Krishnamurthy, Managing Director and CEO, India INX; Siddharth Shah, Partner, Khaitan & Co.; and Veenit Surana, Partner, Ernst & Young. The panellists provided insights into IFSCA’s regulatory vision, the readiness of market infrastructure institutions, and the broader ecosystem required to make dual listings a viable and attractive route for Indian and global market participants.

The event concluded with a vote of thanks from Sandeep Khosla who underscored the value of the discussions and the Chamber’s ongoing efforts to support industry-policy collaboration.

- To learn more about Bombay Chamber’s initiatives, visit our Events Page
- Explore more about our Private Equity & Venture Capital Committee
- Visit Our LinkedIn Page
For More Details Contact: Priya Singh at priya.singh@bombaychamber.com OR 022 61200238
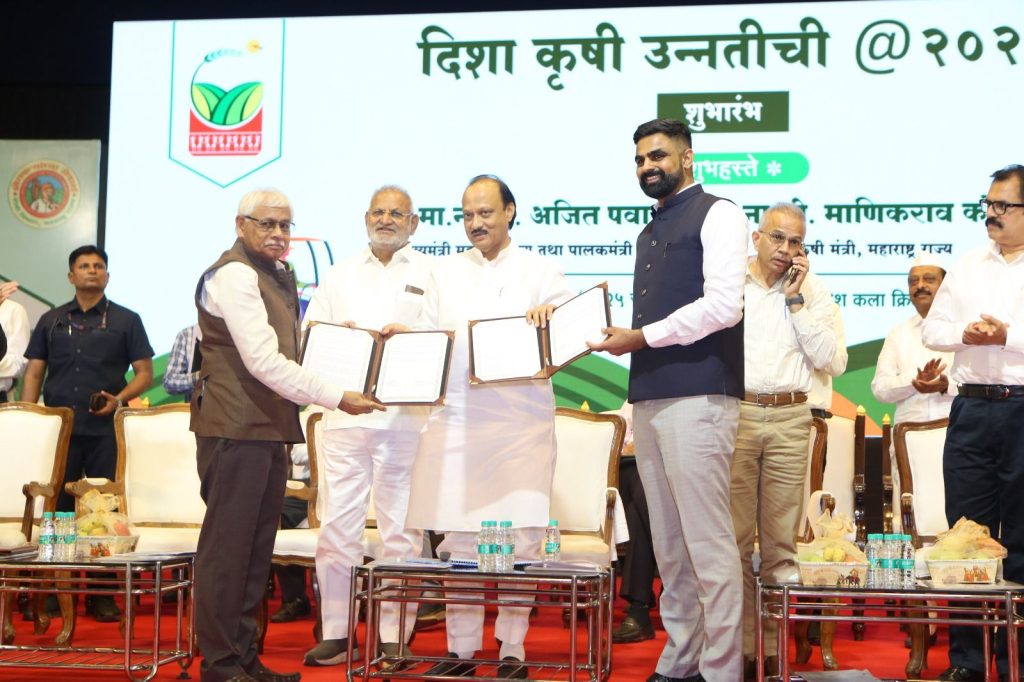
Pune to Host India’s First-Ever International Agritech Hackathon
Pune to Host India’s First-Ever International Agritech Hackathon
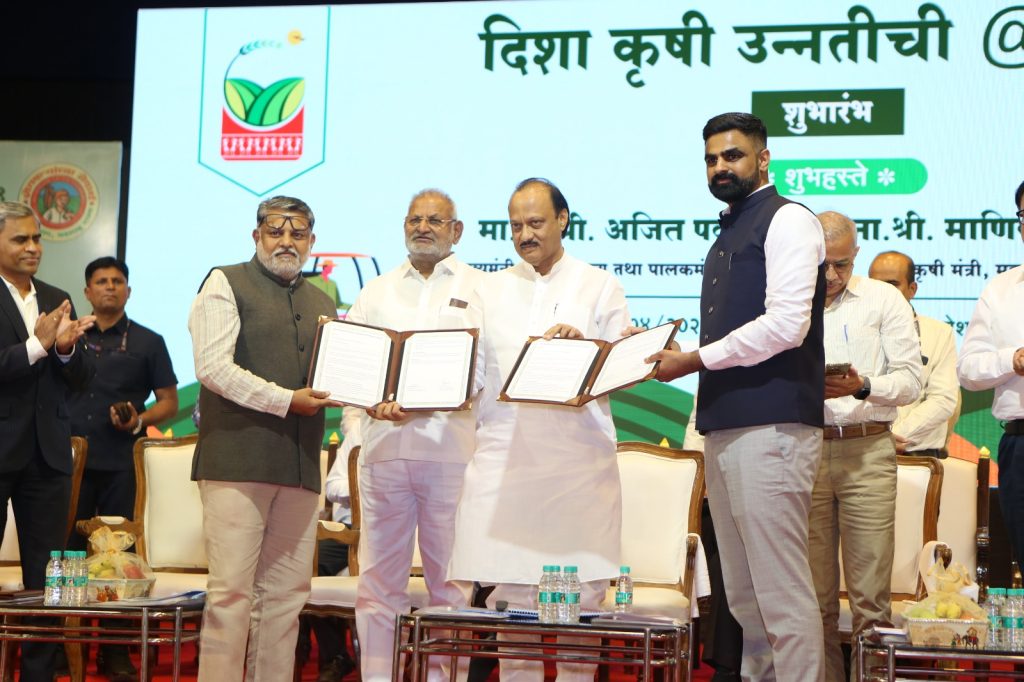
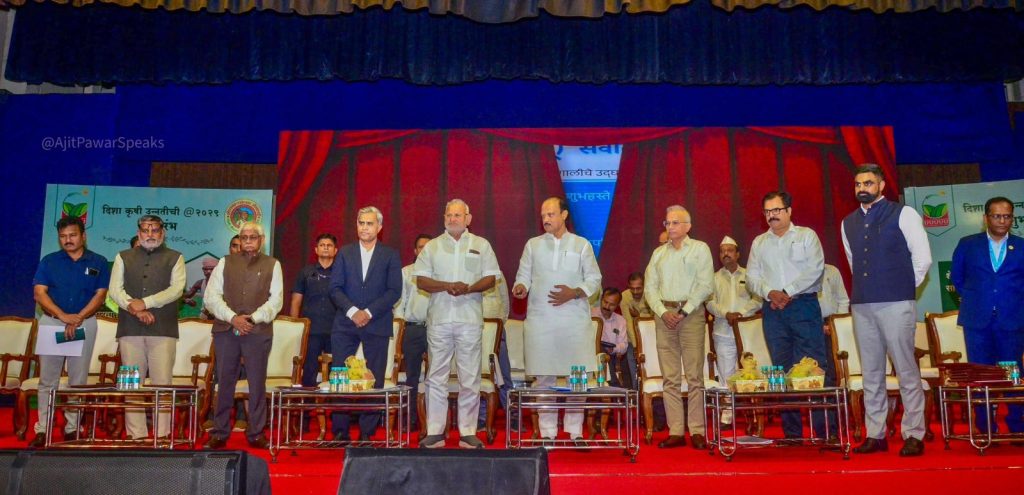
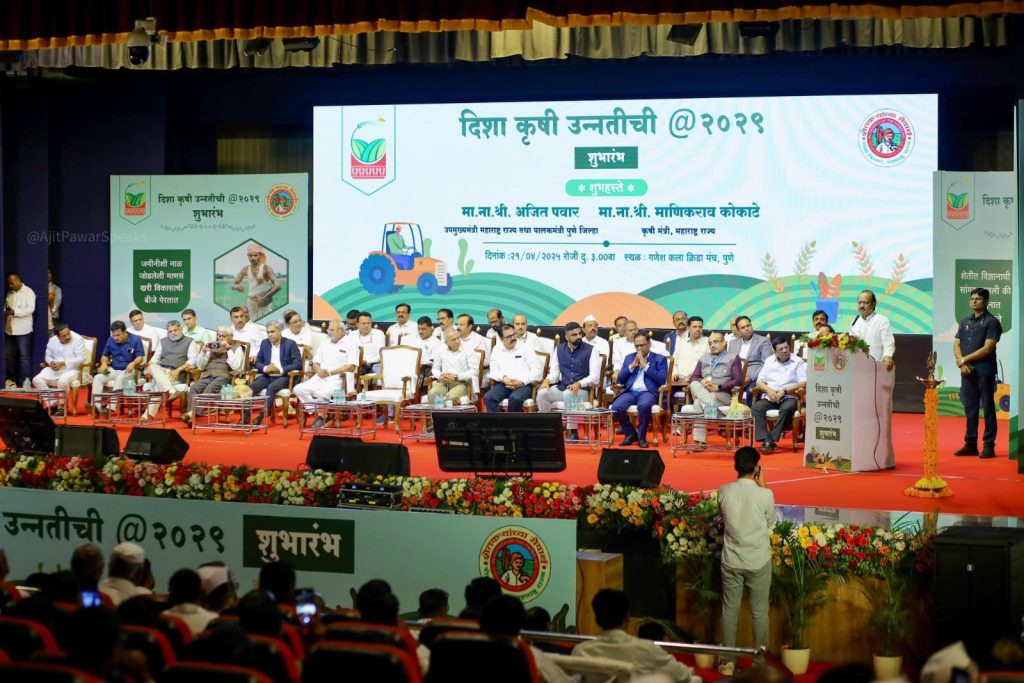
Pune, April 21, 2025 – In a landmark initiative to revolutionize the agriculture sector through innovation and technology, Pune will host the country’s first-ever International Agritech Hackathon. The event was officially launched on 21st April 2025 by Hon’ble Guardian Minister (Pune) and Deputy Chief Minister of Maharashtra State, Shri Ajit Dada Pawar, at Ganesh Kala Krida Manch, Pune.
The International Agritech Hackathon is a collaborative effort between the District Administration, Pune, and the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry. During the launch, a MoU was signed by Mr. Jitendra Dudi, District Collector, Pune and Chief Organizer of the Hackathon, Mr. Rajan Raje, Chairperson, Agriculture & Food Processing Committee – Bombay Chamber and CEO, Nichem Solutions and Mr. Chetan Dedhia, Expert Committee Member, Agriculture & Food Processing Committee – Bombay Chamber and Managing Partner, J.J.Overseas.
Through this MoU, the Bombay Chamber has extended full support to the district administration to ensure the successful execution of the Hackathon.
The International Agritech Hackathon aims to bring together students, startups, developers, researchers, and innovators from diverse backgrounds, all driven by a shared goal — to transform the future of agriculture through cutting-edge technology.
Registrations are now open, and interested participants can register via the official website: https://www.puneagrihackathon.com/







Bombay Chamber and SOFOFA sign landmark MoU to strengthen India-Chile trade relations
Bombay Chamber and SOFOFA sign landmark MoU to strengthen India-Chile trade relations
The Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry and SOFOFA, the Chilean Federation of Industry, have formally entered into a historic Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aimed at deepening economic engagement between India and Chile. The agreement was signed by Rosario Navarro, President of the Chilean Federation of Industry, and Pinky Mehta, President of the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry and CFO of Aditya Birla Capital, during a networking meeting organised by the Bombay Chamber in collaboration with the Chile Business Forum on April 03, 2025.

The signing ceremony was attended by several eminent dignitaries, including Jose Miguel Benavente H. Vice Presidente Ejecutivo, Corfo; Viraj Kulkarni, Chairman of the International Trade and Commerce Committee of the Bombay Chamber; Ivan Marambio, President of the Chilean Chapter of the Chile-India Business Council; Nandan Mehta, Corporate Affairs-EMEA, Tata Consultancy Services; and Siddhartha Roy, Business Head-New Country Development, Marico and other esteemed guest from Chile & India.

A key pillar of the MoU is to establish a strategic commitment by both organisations to support their respective governments in the negotiation of a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) between Chile and India. Through technical insights and industry perspectives, both parties aim to contribute constructively to the advancement of trade discussions.

Additionally, should a CEPA be successfully concluded, the Bombay Chamber and SOFOFA will collaborate to facilitate its effective implementation, monitor emerging business opportunities, and drive private sector participation through trade missions, industry briefings, and sectoral collaboration initiatives.
Established in 2020, the Chile-India Business Council aims to double trade volumes between India and Chile by 2026, with a focus on food and beverage exports. “To facilitate this growth, the Council is actively engaging Indian business partners, leveraging industry expertise and market insights to create structured trade opportunities. The Council is focused on transforming trade discussions into measurable business outcomes, ensuring long-term commercial success between Chile and India,” said Marambio.

Speaking at the event, Siddhartha Roy, Business Head-New Country Development, Marico, reflected on Chile’s rich cultural legacy and the strong commercial ties between both nations. “Over the years, India and Chile have demonstrated resilience and dynamism. Chile’s mining industry has thrived, and Indian companies are actively exploring greenfield and brownfield investments. Likewise, Indian IT firms have established a strong presence in Chile,” he said.

India-Chile bilateral trade has witnessed remarkable expansion, rising from $1.5 billion in 2020 to $3.8 billion in 2024. Investment opportunities are evolving beyond traditional sectors, with agriculture, digital services, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles emerging as areas for enhanced cooperation.
Viraj Kulkarni, Chairman of the International Trade and Commerce Committee of the Bombay Chamber, emphasised Mumbai’s economic prominence, citing its gross domestic product (GDP) of over $600 billion and its pivotal role as India’s financial centre. “Mumbai is a gateway to East Asia, just as Santiago could serve as a strategic hub for India’s presence in Latin America. This MoU ensures structured collaboration, enabling businesses to leverage the immense opportunities before them,” he said.

This MoU marks a significant step taken by the Bombay Chamber and SOFOFA, laying the groundwork for structured commercial growth. Both organisations have pledged to support CEPA negotiations and drive cross-border cooperation through sustained industry engagement.


It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin