Supreme Court asks Union Govt. to consult all stakeholders on model Menstrual Leave Policy.
Judgement attached.
Copy of judgement attached
Top Stories
Supreme Court asks Union Govt. to consult all stakeholders on model Menstrual Leave Policy.
Judgement attached.
Copy of judgement attached
Union Civil Aviation Minister, Shri Kinjrapu Rammohan Naidu has announced the implementation of a uniform IGST rate of 5% on all aircraft and aircraft engine parts, effective from 15th July 2024. This decision marks a significant milestone for the domestic Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) industry, aimed at making India a global aviation hub.
Commenting on this development,Shri Naidu, said, “The introduction of a uniform 5% IGST rate on MRO items is a major boost for the aviation sector. Previously, the varying GST rates of 5%,12%, 18%, and 28% on aircraft components created challenges, including an inverted duty structure and GST accumulation in MRO accounts. This new policy eliminates these disparities, simplifies the tax structure, and fosters growth in the MRO sector.”
The Union Minister further emphasized the role of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s visionary leadership in making this change possible. “Under the guidance of Prime Minister Modi, we are committed to the Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiative. His support for transforming India into a leading aviation hub has been crucial in driving this policy forward,” he added.
Union Minister applauded the efforts of the Ministry of Civil Aviation,Ministry of Finance and other stakeholders who have worked diligently to achieve this policy adjustment recommended by the GST Council in its 53rd meeting on 22nd June 2024, the uniform 5% IGST rate aims to reduce operational costs, resolve tax credit issues, and attract investment.
Highlighting the future prospects, Shri Rammohan Naidu stated, “Our vision is to transform India into a leading aviation hub. The Indian MRO industry is projected to become a $4 billion industry by 2030. This policy change is a crucial step towards building a strong ecosystem for MRO services, driving innovation, and ensuring sustainable growth.”
The Ministry is confident that this move will significantly enhance the competitiveness of the Indian MRO sector, fostering innovation and efficiency, and creating a robust and efficient aviation sector.
The Delhi HC has held that such clauses in employment contracts may in fact be necessary for the health of the employer institution as it provides the required stability and strength to the employer institution and its framework. Lock-in periods in employment contracts are especially prevalent at the executive levels in the trade and industry and are considered necessary for the purpose of stability and continuance of the employer organization. It also reduces the employee attrition levels.
Copy of judgement attached
The J & K High Court has held that where a principal employer engaged a Contractor for execution of some works, he is liable to compensate to any employee engaged by the Contractor for doing his work.
Copy of judgement attached.

Shri Goyal discusses deeper economic ties and FTAs with EU and UK on sidelines of G7 meeting. Shri Goyal calls for collaboration to reinforce global supply chains in critical minerals, semiconductors, pharma and green energy. Shri Goyal highlights need for robust partnerships in the face of 3 Cs – Covid, Conflicts and Climate Change
Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Shri Piyush Goyal, attended the G7 Trade Ministers’ meeting held at Villa San Giovanni, Reggio Calabria, Italy. The meeting served as a pivotal platform for discussions on enhancing global trade relations and economic cooperation. On the sidelines of the meeting, Shri Goyal engaged in several high-level bilateral meetings with his international counterparts, reflecting India’s commitment to fostering stronger economic partnerships globally.
During discussions with Antonio Tajani, Italy’s Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, both the Ministers agreed to enhance bilateral trade and investments, industrial co-production, and cooperation in clean technologies. Minister Goyal congratulated Mr. Tajani for hosting a productive G7 Trade Ministers’ meeting.
Discussions with Valdis Dombrovskis, Executive Vice President of the European Commission focused on promoting India-EU trade and economic collaborations, including ongoing FTA negotiations. Both sides explored opportunities to strengthen cooperation in various areas of mutual interest.
Shri Goyal in talks with New Zealand’s Trade Minister, Mr. Todd McClay explored opportunities to enhance bilateral trade and investment ties for mutual growth. The discussions aimed at giving further impetus to the existing strong trade relationship between India and New Zealand.
Shri Goyal congratulated Mr. Jonathan Reynolds, UK Secretary of State for Business and Trade on his appointment and discussed deepening bilateral economic relations. The conversation included plans to take forward the discussions on Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between India and the UK.
Shri Goyal in conversation with Dr. Robert Habeck, Federal Minister for Economic Affairs & Climate Action, Germany discussed opportunities to elevate the growing Indo-German trade and economic partnership. The discussions focused on the upcoming Inter-Governmental Consultations and the Asia-Pacific Conference of German Businesses in Delhi.
These bilateral engagements are expected to pave the way for significant advancements in India’s trade relations with key international partners.
Shri Goyal’s participation in the G7 Trade Ministers’ meeting underscores India’s proactive approach in engaging with global economies to foster trade and economic cooperation.
During this session, Shri Goyal thanked Mr. Antonio Tajani for the invitation and highlighted the importance of analyzing global supply chains’ robustness in times of crisis, referencing the Covid-19 pandemic, Ukraine-Russia conflict, and Red Sea crisis.
He emphasised the efforts of various countries to build resilient supply chains under platforms like the G20 Generic Framework for Mapping GVCs, the 14 Member IPEF association, Trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI), and India-EU TTC.
He discussed India’s initiatives with strategic partners such as the US, GCC countries, and the EU, including the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) to strengthen supply chains, and highlighted India’s domestic measures to enhance multimodal connectivity for a seamless supply chain integrated with markets, distribution systems, and logistics.
The minister proposed collaboration among trusted partners to reinforce global supply chains in critical areas such as critical minerals, semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, and green energy; and advocated public-private partnerships, investments in critical infrastructure, innovation, and consistent regulatory frameworks across G7 countries and partner nations.
He addressed the impact of the 3 Cs – Covid, Conflicts, and Climate change – on global value chains, emphasizing the necessity for robust partnerships and cooperation. He also introduced the concept of the 3 Fs – fragmented, fragile, and fraught with uncertainties – characterizing the current global context and urged for greater alignment of investment, trade, environment, and energy policies to fortify global supply chains.
He emphasised the need for resilient supply chains that endure beyond the current generation.

Committee aims to ensure comprehensive development of maritime and waterways transport across the country. Meeting will focus on preparation of a State specific Maritime and Waterways Transport Master Plan, Maritime Sector Policies, Green Initiatives, Waterways Development, Cruise Tourism, Urban Water Transportation, Development of Lighthouses
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), Government of India, will convene the State Maritime & Waterways Transport Committees (SMWTC) meeting on 16th July 2024 at 10:00 AM via video conferencing, chaired by Shri TK Ramachandran, Secretary, MoPSW.
The committee aims to ensure comprehensive development of maritime and waterways transport across India, expanding its reach to include the remaining states. The meeting will focus on the preparation of state-specific Maritime and Waterways Transport Master Plans, formulation of Maritime Sector Policies, Green Initiatives, Waterways Development, Cruise Tourism, Urban Water Transportation, and the Development of Lighthouses.
Recognising the need for a unified approach to manage and integrate the waterways transportation sector, the Ministry has established SMWTCs to coordinate various initiatives and schemes within each state. These committees will be pivotal in consolidating efforts and providing focused leadership in the maritime and waterways sector. Each SMWTC will be headed by the Chief Secretary or Additional Chief Secretary and include representatives from major ports, maritime boards, state PWD, Inland Waterways, Department of Tourism, Department of Fisheries, Railways, NHAI, Customs, etc.
Currently, SMWTCs have been constituted in 13 states, including Andhra Pradesh, Mizoram, Himachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Puducherry, Rajasthan, Bihar, Assam, Goa, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Lakshadweep, with plans to establish them in all 30 coastal and waterways states and UTs of India.
The agenda for the meeting includes reviewing the progress made by already constituted SMWTCs, discussing the issues faced by different states along with discussion on implementation of Sagarmala Programme, development of National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) at Lothal, opportunities in Ro-Ro / Ro-Pax / Ferry / Urban Water Transportation, Sagarmala Shipbuilding Clusters, Harit Nauka (Green Transition) Scheme for Inland Waterways, Cargo Promotion Scheme, MoUs with States for Coastal and River Cruise Tourism and support for State Inland Waterway Transport.
Chief Secretaries and Additional Chief Secretaries, as Chairpersons of SMWTCs, will present progress in their states, SMWTC initiatives, state-specific issues, and required support from the Ministry, aiming to review progress, address issues, and foster collaborative solutions to enhance maritime and waterways transport in India.
Disputes relating to lock-in periods that apply during the subsistence of employment contracts are arbitrable under the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996.
Copy of judgement attached.

Tata Group Airlines have concluded the harmonisation of the operating procedures across its key functions, including harmonisation of the supporting manuals across all four carriers, reaching an important milestone in the merger of four airlines into two.
Over the last 18 months, a team of more than 100 members have worked to align on the best practices and adopting common operating procedures. The result of this will be two separate manuals for the full-service carrier and the low-cost carrier.
“This is an important milestone in the merger of the Tata Group airlines and we are grateful for the support received from the Ministry of Civil Aviation in terms of timely clearances for the merger process. We are also grateful to DGCA for their continuous guidance, systematic review and approval of the harmonized operating manuals. DGCA has guided our teams with a safety-first change management approach which is congruent with the safety-first priorities of the TATA Group. The live tracker created by the Flight Standards Directorate of DGCA with a dedicated team for continuous monitoring of the progress of the harmonisation process has been instrumental in achieving the challenging task in a time bound manner,” said Campbell Wilson, Chief Executive Officer & Managing Director, Air India.
Air India and group companies are initiating the necessary crew training to action the harmonized processes, which will be another step in the direction towards building the new Air India and Air India Express.
After 69 years as a government-owned enterprise, Air India and Air India Express were welcomed back into the Tata group in January 2022. Air India is navigating through a major five-year transformation roadmap under the aegis of Vihaan.AI, with an ambition to become a world class airline with an Indian heart. The first phase of this transformation, the taxi phase was recently concluded, and focused on fixing the basics. These included bringing back to service many long grounded aircraft, addition of talent across flying and ground functions, rapid upgradation of technology and strengthening of customer care initiatives amongst others.
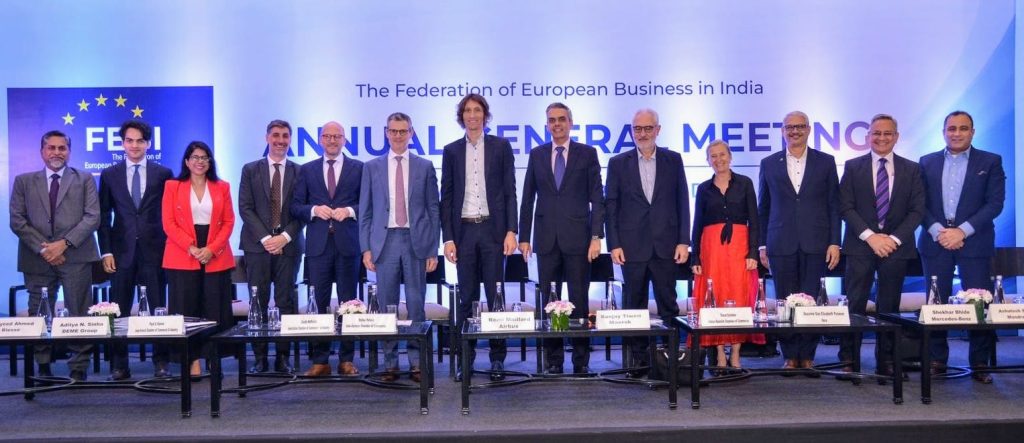

New Delhi, July 8, 2024: The Federation of European Business in India (FEBI), the official Chamber of EU businesses in India, supported by EU Delegation in India and the Embassies of the EU Member States, has held its first Annual General Meeting, marking a significant milestone in its new journey. The meeting formalised the Board of Directors with 14 elected members and confirmed key office bearers.
Mr. Rémi Maillard (President and Managing Director of Airbus in India and South Asia) will lead FEBI as its first President, with Mr. Sanjay Tiwari (Public Affairs Advisor to Maersk India Pvt. Ltd.) and Mr. Oscar Esteban (President, Indo-Spanish Chamber of Commerce), elected as Vice-President and Treasurer respectively. The inaugural AGM was held in New Delhi on July 4, 2024.
Mr. Hervé Delphin, Ambassador of the EU to India and Honorary President of FEBI said: “EU-India relations have been on an ascending trajectory, with a growing economic footprint. Over 4500 European companies are present in India, providing 6.5 million direct and indirect jobs. The EU is India’s largest trading partner in goods, with trade amounting to EUR 123 billion in 2022-23, and ranks among the top three investors in India. Ongoing negotiations for a Free Trade Agreement between the EU and India hold promise to enhance trade flows and economic cooperation significantly. FEBI will bring a very much needed business perspective that will contribute to the further expansion and bringing together of the EU-India economic and trade eco-system. It will be a true force multiplier.”
FEBI will maintain close and constructive relations with Indian and European authorities, acting as a credible intermediary between government and businesses and an advocacy place for pro-business policies and solutions. Currently, FEBI boasts a membership of 73 companies representing a diverse cross-section of EU Member States across 10 sectors in India, including Aerospace, Automotive, Agri-food Products, Chemicals & Pharma, Consumer & Luxury Goods, Finance & Insurance, Telecom & ICT & Digital Trade, Machinery & Capital Goods, Energy & Renewables, and Transportation & Logistics. More companies are in the process of joining FEBI.
“It is as much an honour as a responsibility to helm FEBI as its inaugural president. FEBI will serve as a bridge between Europe and India to deepen bilateral trade and investment. India’s rapid expansion holds significant potential for European companies to grow here in a symbiotic way. We will work with our Indian and EU stakeholders and industrial partners to ensure that trade opens more opportunities, thereby helping both regions to grow and thrive together. I thank my colleagues at FEBI for putting their trust and confidence in me,” said Mr. Rémi Maillard after his confirmation as President of FEBI.
FEBI’s Board of Directors include –
– Rémi Maillard, President and Managing Director, Airbus in India and South Asia
– Sayeed Ahmed, CEO/ Director, Biesse India Pvt. Ltd.
– Aditya Narain Sinha, Vice President & Director, ALAR Group, Business Development, International Seaport Dredging Pvt. Ltd. (DEME Group Belgium)
– Stefan Leser, Managing Director, Groz Beckert Asia Private Limited
– Susanne Gun Elisabeth Pulverer, CEO and Chief Sustainability Officer, IKEA India Pvt. Ltd.
– Sanjay Tiwari, Public Affairs Advisor to Maersk India Pvt. Ltd.
– Shekhar Bhide, VP–Customer Services & Corporate Affairs, Mercedes-Benz India Pvt. Ltd.
– Ashutosh Sharma, Executive Director, Mondragon Corporation, India,
– Deepak Sharma, Managing Director & CEO, Schneider Electric India Private Limited,
– Payal S. Kanwar, Director General, Indo-French Chambers of Commerce and Industry (IFCCI)
– Stefan Halusa, Director General, Indo-German Chamber of Commerce (IGCC)
– Claudio Maffioletti, Secretary General, Indo-Italian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (IICCI)
– Oscar Esteban, President, Indo-Spanish Chamber of Commerce, CEO of SIS-Prosegur and Business Director of Prosegur for Asia
– Kamal Bali, President & Managing Director, Volvo Group in India, Chairman, Swedish Chamber of Commerce India (SCCI).
About FEBI: The Federation of European Business in India (FEBI) is the official Chamber of EU businesses in India, supported by EU Delegation in India and the Embassies of the EU Member States. FEBI’s mission is to articulate the collective business business interests of EU companies in India and facilitate the growth in trade and investment between the EU and India.
The Government of Karnataka has published the draft Karnataka Platform based Gig Workers Social Security and Welfare Bill, 2024 calling for comments.
Copy of public notice attached.

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin