Blog
Top Stories
The 7th Annual Economic Outlook Survey 2024-25
Survey Content:
We are thrilled to announce the launch of the 7th Annual Economic Outlook Survey 2024-25, conducted by the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry. This survey has become a vital platform for collecting insights and data from both member and non-member organisations, allowing us to deliver a comprehensive macroeconomic analysis of the Indian economy.
In keeping with our role as a bridge between the industry and the Government, we have shared findings from our previous Surveys with key authorities, including the RBI, Ministry of Finance, and Regulatory Bodies. These insights have contributed to a deeper understanding of the economic landscape and influenced policies aimed at fostering a conducive business environment in the country.
The Economic Outlook Survey plays a crucial role in understanding the pulse of the industry across the spectrum – from Large corporations to Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). By capturing the diverse challenges, opportunities, and trends experienced by businesses of all sizes, the Survey offers a balanced view of the economic landscape, providing invaluable insights that cater to both ends of the industry.
In this spirit of collaboration and nation-building, we invite you to participate in the 7th Economic Outlook Survey. By taking just a few minutes to share your perspectives, you can play an active role in shaping the future of our economy.
Your feedback is crucial and will help inform policy decisions that drive sustainable development.
For further queries, contact:
Priya Singh: 022 6120 0238; Utkarsha Joshi: 022 6120 0271
Email Id: priya.singh@bombaychamber.com ;Utkarsha.Joshi@bombaychamber.com
Bombay Chamber Mutual Fund Conclave says industry needs a North Star to guide towards long term financial security for all
Bombay Chamber Mutual Fund Conclave says industry needs a North Star to guide towards long term financial security for all
Bombay Chamber organised its annual Mutual Fund Conclave yesterday at the St Regis Hotel, Mumbai. The theme of the Conclave was India’s growth funded by Indians.

In her welcome address, Pinky Mehta, President, Bombay Chamber and CFO, Aditya Birla Capital, said, “The Assets Under Management (AUM) of India’s mutual fund industry rose by an impressive 40.70% over the past year, climbing from ₹46.94 lakh crore in August 2023 to ₹66.04 lakh crore in August this year, as reported by the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI). Recognising this expanding market, SEBI has introduced a simplified regulatory framework for launching passive mutual fund schemes, known as MF Lite. This initiative aims to reduce compliance burdens and encourage new entrants into the mutual fund space.”

Setting the theme for the Conclave, Nilesh Shah, Past President, Bombay Chamber & Group President and Managing Director, Kotak Mahindra AMC said, “The MF industry represents a sustainable model where distributors, manufacturers, and investors come together to drive economic freedom. It is unique in aligning the interests of all three stakeholders. The industry’s primary responsibility is to safeguard investor trust, which has remained strong thanks to regulatory oversight.”
He further added, “Currently, 93% of household savings in India go into instruments like bank savings and fixed deposits, which do not keep pace with inflation. The remaining 7%, invested in equities and mutual funds, offers inflation-beating returns. This imbalance means most Indians are not financially secure. A greater push, such as through initiatives like Jan Nivesh, is needed to direct savings toward real-return products. The younger generation must also be engaged – 18 crore Indians traded in cryptocurrencies and lost money, with many of these being young investors. The MF industry needs a North Star, to guide these efforts toward long-term financial security for all.”

The Keynote Speaker, Manoj Kumar, Executive Director, SEBI, said, “With 60 lakh crore AUM, the regulator should work fast too. There is no meaning to whatever has been built if trust is eroded. Our objective is to help everyone. We are making changes to MF to match the pace of growth of the industry. We actively consult with everyone for these changes – the industry, the distributors and gain a holistic view. The recent introduction of MF Lite was in keeping pace with the needs of the industry and investors. To reduce compliance burden and make it lighter, while also ensuring compliance standards are adhered to. Similarly, the new asset class for HNIs. With a lot of unauthorised activities that happen at the lower end of the market, we need to take action and adopt a development approach to the same. Since there is a need in the market, we address it by bringing it into the regulatory framework. The structure we are trying to create is that all PMS and AIF players should be facilitated in MF Lite and the new asset class. “

In a Fireside Chat on Guardrails for a Growing Mutual fund industry, between Navneet Munot, Board Member, Bombay Chamber and Chairman, AMFI and MD & CEO, HDFC AMC and Anil Singhvi, Managing Editor, Zee Business, the two speakers shared insights on reaching the 5 crore unique investors and cautioned that the industry still has a long way to go.

The Conclave also saw two panel discussions. The first which was on ‘The journey from 4 cr to 40 cr investors’ was moderated by Latha Venkatesh, Executive Editor, CNBC TV18 and the panelists included Nilesh Shah; Swarup Anand Mohanty, Vice-Chairman and CEO, Mirae Asset Investment Managers (India); Lalit Keshre, Co-Founder & CEO, Groww and D P Singh, DMD, SBI Mutual Fund.

The second panel moderated by Nisha Poddar, Managing Editor, Times Experiences included panelists Soumya Rajan, Founder & CEO, Waterfield Advisors; Karan Bhagat, Founder, MD & CEO, 360 ONE; Sudhir Variyar, Deputy CEO, Multiples Alternate Asset Management; Ashish Gupta, Chief Investment Officer, Axis Mutual Fund and Vishal Agarwal, Partner & National Leader – Transaction Tax and PE Channel, Grant Thornton Bharat LLP. The panel discussed about wealth creation through AIFs and PMS.
Webinar on LEADERSHIP ACCELERATOR
Webinar on LEADERSHIP ACCELERATOR
The Young Bombay Forum of the Bombay Chamber organized a six-part Leadership Accelerator webinar series in September 2024. Ms. Shruti Rathod, representing the Bombay Chamber, extended a warm welcome to the speaker and participants, highlighting the rich legacy and accomplishments of both the Bombay Chamber and the Young Bombay Forum. The event saw participation from professionals across various industries.
The webinar featured two expert coaches:
- Ms. Monica Divekar, Founder of The Mind Coaching Academy, Author, Behavior Specialist, ICF Certified Coach with expertise in Neuroscience and Emotional Intelligence (EI), Master NLP Practitioner, EI Certified Assessor, Facilitative Trainer, and Visiting Faculty at S.P. Jain Institute of Management & Research.
- Ms. Varsha Chitnis, Founder of The Mind Coaching Academy, Author, ICF Certified Coach specializing in Brain-Based Intuitive & Solution-Focused Coaching, Certified Behavior Trainer, Certified in Facilitation, Certified Assessor BAT 5, and Visiting Faculty at We School and Tata Institute of Social Sciences.
The webinar addressed key challenges faced by many talented leaders that often hinder their progression into senior positions or critical roles. Common hurdles discussed included confidence gaps, self-doubt, lack of self-awareness, and the need for proactive engagement and relationship-building. By identifying these challenges and offering actionable insights, the webinar aimed to help leaders unlock their full potential and advance in their careers, benefitting both individuals and their organizations.
The Leadership Accelerator initiative was designed to equip participants with the tools and strategies needed to overcome leadership obstacles. The series focused on various topics, including:
- Self-Awareness and Growth: Tools and techniques to foster self-awareness and overcome self-doubt.
- Confidence and Focus Building: Exercises aimed at boosting self-confidence and strengthening leadership presence.
The program’s structure included:
- Six online sessions, each lasting 60-90 minutes
- Four weeks of ongoing support via WhatsApp
- Focus group discussions (FGD) with participant sponsors
- Participant orientation and assessments, followed by group feedback sessions
- Interactive sessions for introducing tools and techniques, with continuous review and feedforward
- Certification upon completion
Participants also benefited from continuous support and practice exercises through WhatsApp, reinforcing the concepts learned during the sessions.
Key Takeaways:
- Improved self-awareness and recognition of gaps holding leaders back
- Greater belief in their ability to step into leadership roles
- Practical, actionable insights ready for immediate implementation
The feedback from attendees was overwhelmingly positive, with many highlighting the webinar’s relevance and effectiveness. The interactive format and practical focus made it a valuable and enriching experience for all involved.
Thought Leadership Session by Dr. VS Parthasarathy
Thought Leadership Session by Dr. VS Parthasarathy
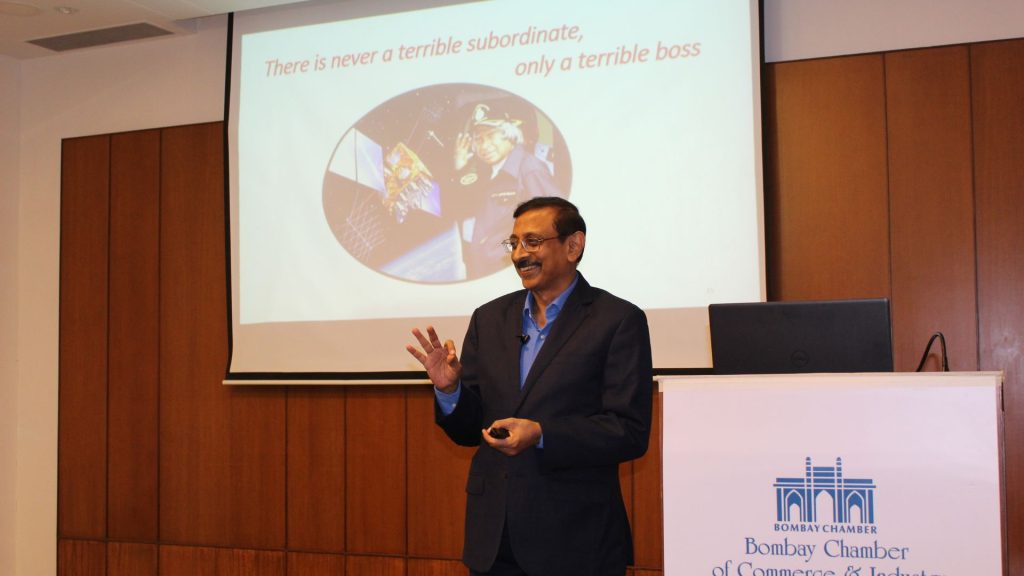

The Young Bombay Forum of the Bombay Chamber organized a dynamic Thought Leadership Session on September 25, 2024, featuring Dr. VS Parthasarathy, a distinguished coach, mentor, and social entrepreneur. Dr. Parthasarathy, known for his roles with SEWA, LIC, NIIT, Cloud9, and other prominent organizations, delivered an enriching session at The Ruby, Mumbai, that attracted professionals eager to gain insights from his extensive leadership experience.
The session began with a warm welcome by Ms. Shruti Rathod from the Bombay Chamber, followed by introductory remarks by Mr. Ashith Kampani, Chairman of the Young Bombay Forum and Managing Director of CosmicMandala 15 Securities Pvt. Ltd. Mr. Kampani reflected on the historical milestones of both the Bombay Chamber and the Young Bombay Forum, setting the stage for an engaging discussion.
Dr. Parthasarathy captivated the audience with his insightful address on leadership, emphasizing both professional and personal development. His talk was inspiring, practical, and interactive, encouraging active participation from the attendees. He offered actionable advice on enhancing leadership skills, grounded in his philosophy of perseverance, passion, and purpose—the “three Ps” that he believes are essential for success.
He shared key mantras for excellence and leadership, focusing on empathy, understanding others, and the importance of consistent practice. Dr. Parthasarathy challenged the common belief that success is solely about strategy and execution. He argued that true success also requires perseverance. He illustrated this with a powerful metaphor: “When you plant a seed and water it, the results aren’t immediately visible. It takes time and perseverance for the plant to grow.”
Dr. Parthasarathy also spoke about the significance of creating a familial atmosphere in the workplace. Given the long hours professionals spend at work, he suggested treating colleagues like family to achieve better work-life balance. He emphasized that perseverance, once established as a habit, helps in balancing life effectively.
Looking to the future of business, he discussed the idea of “business movement,” where companies evolve beyond their original models—just as Amazon expanded from a bookstore to finance, insurance, and data centers. He highlighted the importance of adaptability, especially as the world grapples with climate change and the rise of experiential commerce. He stressed that only innovative companies that are willing to adapt will survive.
“Learning should never end,” Dr. Parthasarathy advised, encouraging continuous learning and adaptability. He introduced the concept of shifting from a 70:30 to a 30:70 ratio—where 70% of repetitive tasks should be automated through technologies like AI, allowing professionals to focus 70% of their time on future-oriented strategies.
In closing, Dr. Parthasarathy left the audience with memorable words: “Keep your eyes on the horizon but your feet firmly on the ground.” He urged everyone to remain grounded while aiming high, recounting his personal journey of perseverance and growth, starting alone and gradually building a strong network of like-minded individuals.
The session concluded with a lively Q&A segment, where participants had the opportunity to seek advice from Dr. Parthasarathy on their professional challenges. The feedback from attendees was overwhelmingly positive, reflecting the event’s success and the profound impact of Dr. Parthasarathy’s insights.
Seminar on new Capital Gains and Buyback tax regime
Seminar on new Capital Gains and Buyback tax regime

Pursuant to stakeholder representations, Finance (No.2) 2024 has transformed the tax treatment of capital gains and buy back of shares. The government has tried to reduce the categories of various asset classes and bring uniformity & consistency in holding period and long term/short term capital gains tax rates. Responding to post budget representations, the indexation benefit was also restored at the enactment stage in a limited manner to ensure that long term capital gains tax burden of land or building or both on resident individuals/HUFs is not increased for assets acquired prior to July 23, 2024. The taxation of buyback of shares is restored in the hands of shareholders as a combination of dividend and capital gains instead of buyback distribution tax in the hands of the company.
The transformative changes in capital gains and buyback taxation for both residents and non-residents requires an in-depth evaluation for both tax compliance and future tax planning. In view of the above, Bombay Chamber organised a half-day physical seminar where tax experts from Deloitte Haskins & Sells LLP, viz. Hiren Shah and Akhil Muchhala discussed the aspects with practical case studies on the new Capital Gains tax regime and new Buyback tax regime. The session was attended by good participation and it was very interactive and very informative.
The next three decades belong to India, says Dhiraj Relli at Envision 2024
The next three decades belong to India, says Dhiraj Relli at Envision 2024
In the first half of 2024, Indian companies raised an impressive $8.6 billion through Initial Public Offerings (IPOs), surpassing the combined figures from the previous two years. India now accounts for 25% of global IPO listings, positioning itself as a key player in the global capital markets. With upcoming billion-dollar IPOs from companies like Swiggy, LG Electronics, and Hyundai Motor, investor confidence in India’s economic growth continues to soar.
These developments were highlighted during the panel discussion, Envision 2024: India’s Growth Story With Capital Markets, organised by the Bombay Chamber in partnership with Kirtane & Pandit Consulting, the Knowledge Partner. The event focused on India’s burgeoning IPO market and its implications for future economic expansion.
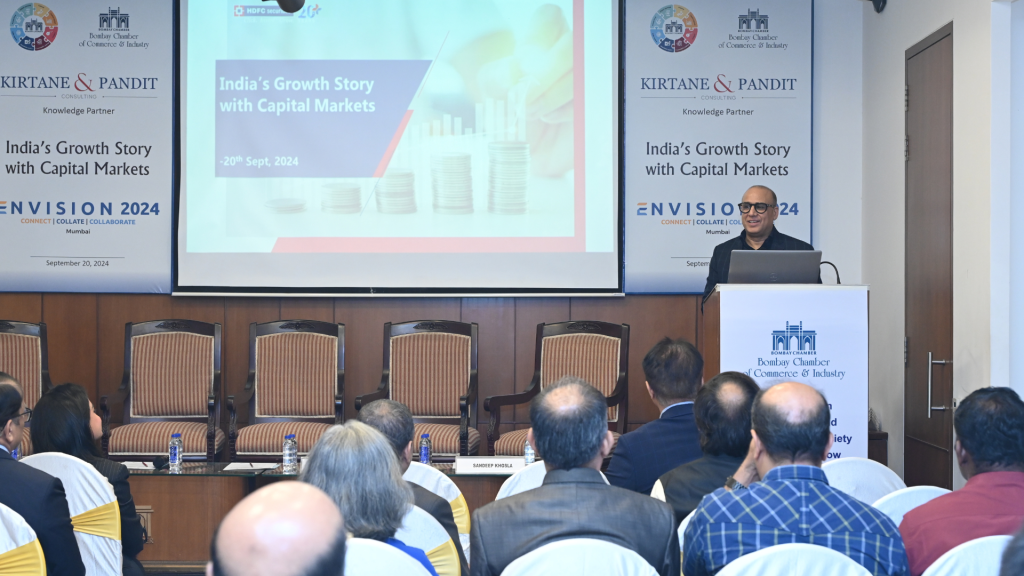

In his keynote address, Dhiraj Relli, Managing Director and CEO of HDFC Securities, emphasised India’s long-term growth potential. “The next three decades belong to India, with the ‘Viksit Bharat’ theme driving our economic progress,” Relli stated. He also highlighted that India’s investor base has tripled in the last five years, now standing at 10 crore investors.
Relli pointed to a shift in investor behavior, noting that retail and High Net Worth Individuals (HNIs) are becoming more adept at navigating the markets. “For the first time in my three decades of experience, I’ve seen retail investors consistently making money in the markets,” he said. This marks a significant departure from past cycles, where retail investors often suffered losses during market downturns.
He further explained that India has seen a 12x increase in market participation over the last decade. “Equity premiums have surged 10x in the last five years, and IPO activity is booming with ₹61,000 crore raised this financial year, excluding SME IPOs, which have also gained momentum.”
Relli also warned of the risks of falling into the middle-income trap, stressing that India must grow rich before it grows old. Comparing India to China, he highlighted the country’s potential for greater penetration in consumer goods. “Our per capita income and affordability will increase, leading to a shift in consumerism. The economic structure is moving from a pyramid to a diamond shape, where more of the population will experience affluence.”
He projected that by 2029, India could become a $7 trillion economy, with the potential to reach $10 trillion by 2032, provided it sustains a growth rate of 11%.
The event also featured a panel discussion on IPO readiness, titled IPO Readiness- The Road to Going Public, moderated by CS Shweta Gokarn, Founder of Shweta Gokarn & Co. and STGY Global Consulting.
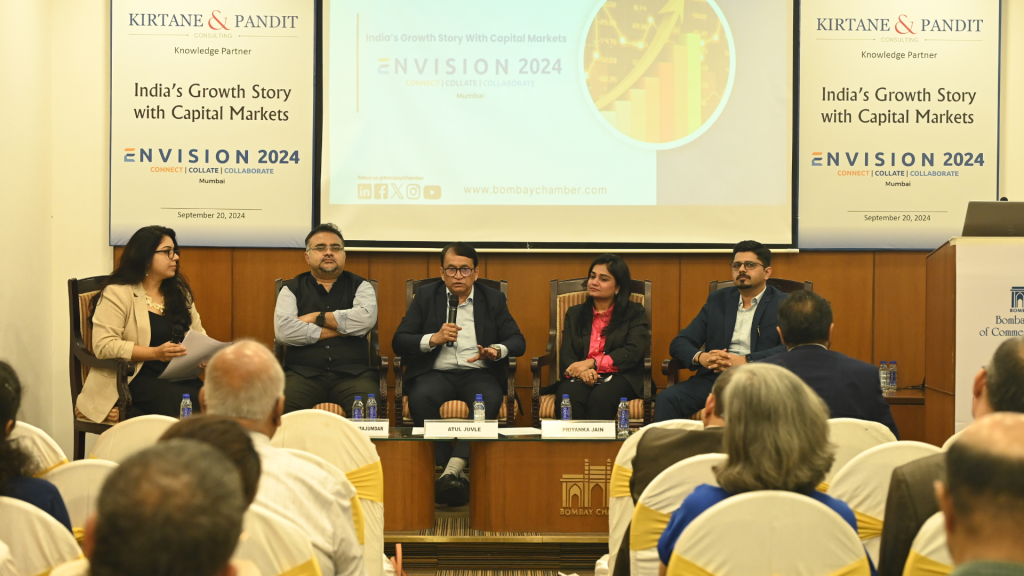

Panelists included Subhadeep Majumdar, Chief Manager at NSE, Atul Juvle, Senior GRC Advisor, Priyanka Jain, Partner at Vaish Associates Advocates, and Akshay Purandare, Partner at Kirtane & Pandit. They shared best practices and insights on navigating the IPO process, emphasising the need for thorough preparation and adherence to disclosure obligations. The session covered essential topics such as the role of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) in facilitating IPOs, economic factors driving India’s growth, and the legal and compliance challenges companies face when going public.
Advanced Certificate Course on International Trade and Custom Regulations
Advanced Certificate Course on International Trade and Custom Regulations

Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry organised an Advanced Certificate Course on International Trade and Custom Regulations on September 19 & 20, 2024 at the Ruby by renowned trade consultant Dr Joshua Ebenezer.
The certificate course was attended by professionals from diverse industries, focusing on enhancing their understanding of global trade, customs regulations, and audit practices.
Day 1: Global Trade Fundamentals and Post-Clearance Audits
The session kicked off at 10:30 AM, with an insightful discussion on the genesis and evolution of global trade organizations such as the World Trade Organisation (WTO) and the World Customs Organisation (WCO). Participants learned about the core functions of these institutions, their impact on global trade, and the obligations of member countries under various trade agreements.
The session also covered post-clearance audits and the advance ruling mechanism, offering participants practical insights into navigating the complexities of customs compliance and decision-making processes within the international trade framework.

Day 2: Customs Valuation, Rules of Origin and Advanced Audits
Due to popular demand, the second day commenced earlier at 9:30 AM. The focus was on customs valuation, rules of origin, export controls, and audits and investigations, with special attention to the newly introduced advanced customs audit processes. Participants engaged in a robust Q&A session, where they discussed complex scenarios and solutions tailored to their industries.
The day concluded at 5:00 pm, with participants praising the content-rich program and the interactive format that kept them fully engaged without distractions from their phones or work.
Feedback and Future Sessions
The participants provided very positive feedback about the program, appreciating both the content and the interactive nature of the sessions. Based on this encouraging response, the Chamber is exploring the possibility of conducting more such sessions shortly to meet the growing demand for expertise in customs and international trade.
The program was a resounding success, providing attendees with invaluable insights into international trade and customs regulations. This initiative marks a milestone in the Bombay Chamber’s efforts to provide high-quality certification courses, and we look forward to welcoming more participants in future sessions.
U.S.-India Alliance for Women’s Economic Empowerment convenes first in-person meeting
U.S.-India Alliance for Women’s Economic Empowerment convenes first in-person meeting
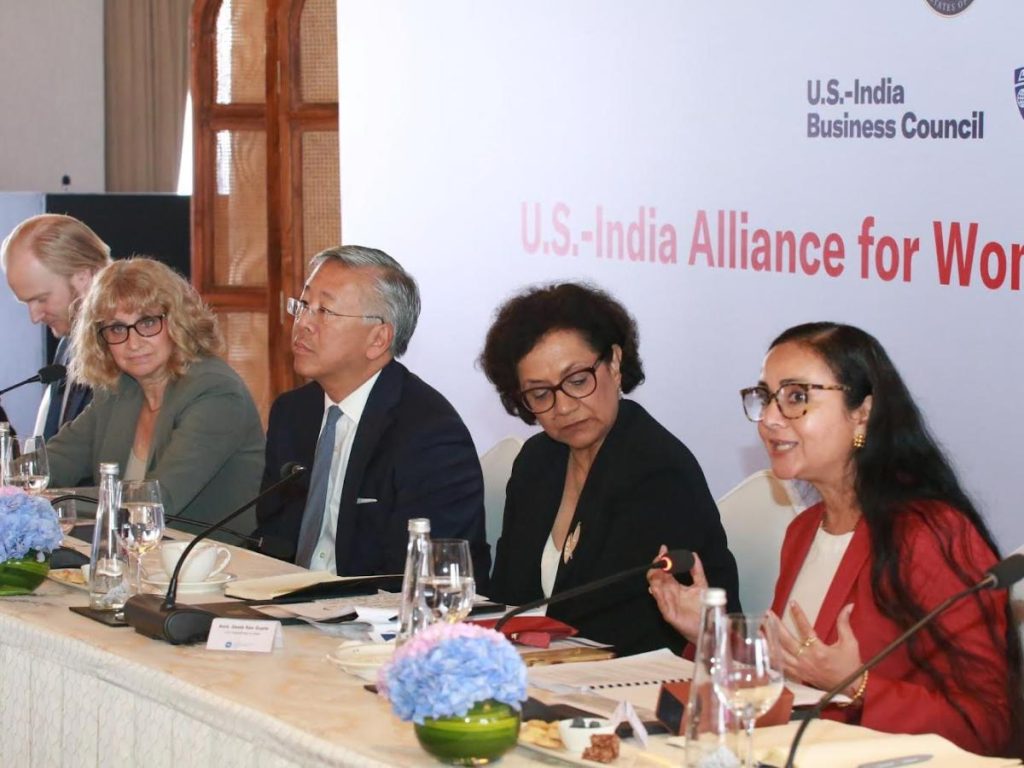

The U.S.-India Alliance for Women’s Economic Empowerment and the U.S.-India Business Council (USIBC) convened the inaugural Alliance members meeting recently on the margins of USIBC’s Ideas Summit. The Alliance, launched in 2021, aims to dismantle silos between public and private entities, fostering collaboration to accelerate women’s economic security.
Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues and Alliance co-chair, Dr. Geeta Rao Gupta, delivered opening remarks. She was joined by fellow U.S. Department of State Alliance co-chairs, Assistant Secretary for South and Central Asian Affairs Donald Lu, and Deputy Assistant Secretary for India Nancy Izzo Jackson, and USAID Deputy Assistant Administrator for Asia Änjali Kaur.
“Women’s safe and meaningful economic participation is one of the most important issues of our time,” said Assistant Secretary Lu. “It is a pillar of secure, educated, healthy, and prosperous societies. Few other issues rival its potential to transform India’s future – and the world’s.”
Ambassador Rao Gupta emphasised the challenges and opportunities in advancing women’s economic participation in India. Despite progress, India ranks 142 out of 146 countries in economic parity and opportunity, according to the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap report. Women’s formal labor force participation remains significantly below the global average, and gender-based violence persists as a major issue.
“As India reassumes its historic place as a global power, its economic success story can only be complete by uplifting Indian women in education and the workforce,” said Ambassador (ret.) Atul Keshap, President of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce’s U.S.-India Business Council. “That’s why empowering women to succeed in the formal economy is a key topic at the 49th India Ideas Summit. Together with the State Department, our Alliance anchor partners, and Alliance members, we advanced actionable initiatives to equip women to contribute across all sectors of Indian industry, including civil aviation, hospitality, manufacturing, and renewable energy.”
The Alliance has three main objectives: advancing women’s corporate workforce participation, including through safety in the workforce; promoting women’s entrepreneurship; and increasing the presence of women and girls in STEM fields.
During the meeting, Alliance members discussed ongoing initiatives and explored new opportunities for collaboration. Ambassador Rao Gupta encouraged participants to use the forum to share ideas and establish new partnerships that could drive transformative change.
“We are all here because our commitment to women’s economic inclusion goes beyond mere compliance,” she noted. “Achieving meaningful inclusion requires funding, expertise, networks, and thoughtful collaboration. This is the essence of what the Alliance seeks to achieve.”
USAID Deputy Assistant Administrator for Asia Änjali Kaur, emphasised how the Alliance is a vital platform to drive collaboration towards shared goals. “USAID is proud to be a co-chair of the U.S.-India Alliance for Women’s Economic Empowerment. Through USAID’s work across corporate, philanthropic, and civil society sectors, we are driving impactful change to help women transition from the informal to the formal economy and thrive.”
As the meeting concluded, Deputy Assistant Secretary Nancy Izzo Jackson urged members to stay focused on the strategic importance of their work. “When women are economically secure, their families thrive, communities prosper, and nations grow stronger.”
RBI Deputy Governor unveils product offerings for transforming ATM infrastructure at GFF 2024
RBI Deputy Governor unveils product offerings for transforming ATM infrastructure at GFF 2024

At the Global Fintech Fest (GFF) 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Deputy Governor Shri T. Rabi Sankar announced the launch of product offerings aimed at transforming the ATM infrastructure in the country. Unveiled in association with National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the initiatives include UPI Interoperable Cash Deposit (UPI-ICD) and banks showcasing Digital Banking Units (DBUs).
The introduction of UPI ICD allows customers to deposit cash at ATMs operated by banks and white label ATM operators (WLAOs) using UPI to their own bank account or any other bank account without the need for a physical card. These ATMs are cash recycler machines which are used for both cash deposits and withdrawals. Leveraging their mobile numbers linked to UPI, virtual payment addresses (VPA) and account IFSCs, customers can now make cash deposits, making the process more seamless, inclusive and accessible.
Consumers will be able to access these features as the banks gradually roll them out. ATM machines with open architecture can host bank apps positioning them as DBUs offering cash deposits, withdrawals and other banking services such as opening bank accounts, applying for credit cards, initiate fixed deposits, applying for safe deposit lockers, etc. Additionally, recently at the GFF 2024, Shri Vivek Deep, Executive Director, RBI announced rebranding of Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) to Bharat Connect. This is an important step to refresh and strengthen BBPS brand. Bharat Connect embodies NPCI Bharat BillPay’s (NBBL’s) values and vision for stakeholders and customers, going beyond a bill payment system to create an ecosystem that connects individuals and businesses, through an integrated platform. The launches took place in the presence of Shri Ajay Kumar Choudhary, Non-Executive Chairman and Independent Director, NPCI.
Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) prepares for Special Campaign 4.0
Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) prepares for Special Campaign 4.0
Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) is preparing for the implementation of Special Campaign 4.0 for institutionalising Swachhata and minimising pendency in the department and across 19 organisations under its administrative control. The Preparatory Phase of the Campaign will start from 16th to 30th September 2024 to identify targets in respect of Pendency’s of PMO, VIP, State Govt., MP, Cabinet References, and Record/Space Management. While the Implementation Phase will start from October 2, 2024 and will last up to October 31, 2023. During the Implementation Phase special focus will be on achieving the targets identified.
With the beginning of the preparatory phase of the Special campaign, approx. 70 field/outstation offices have been identified under its 19 Attached, Subordinate, and Autonomous Organisations spread across the country for conducting Special Campaign 4.0. Guidelines have been shared with all field functionaries to mobilise their efforts to prepare for the Special Campaign 4.0. Training on Record Management was conducted for ASO/SO/US/DS/Dir. level officers of DPIIT for efficient management of Record and Space.
In its earlier administrative efficiency spree, DPIIT successfully completed various activities under Special Campaign 3.0 for institutionalising Swachhata and minimising pendency in the Government. DPIIT and its 19 Attached, Subordinate and Autonomous Organisations spread across the country, participated in the Campaign and achieved overwhelming results in reducing the pendency.

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when lookin